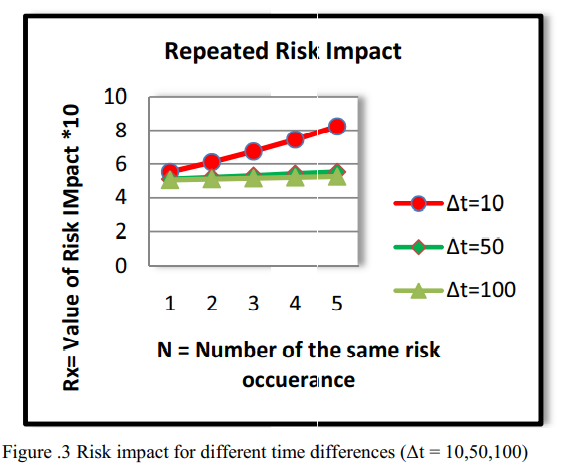
Organizational risk assessment based on attacks repetition
Risk assessment is a very critical and important process to protect the organization assets and reputation against security threats and risks. It provides a clear picture of the current threats that the organization is facing and helps the top management to take the right decision to eliminate or mitigate those risks. Usually if the vulnerability is exploited, the same attack may be happen twice or more in a different time periods because the vulnerability has been exploited and not mitigated. In this paper, we are illustrating our observation of the relation between the risk value and the
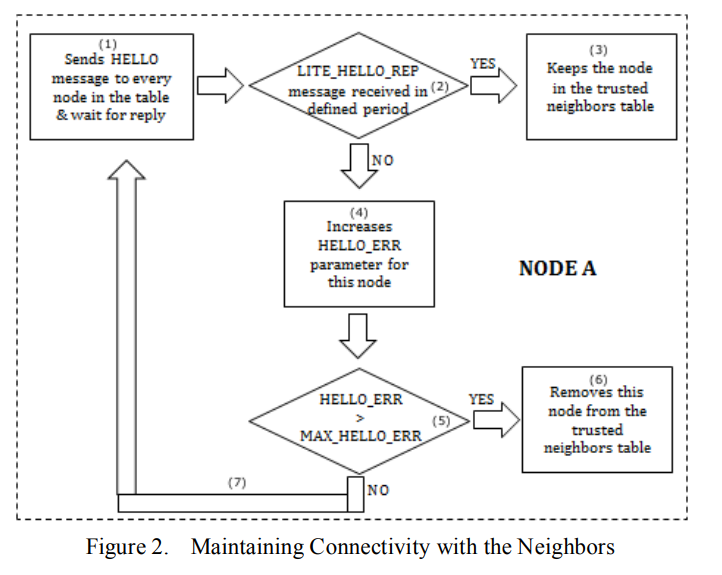
Immunizing the SAODV protocol against routing information disclosure
Secure routing protocols presents one of the most important challenges of Mobile Ad hoc Networks (MANETs). This is due to their special characteristics such as shared wireless medium, stringent resource constraints and highly dynamic network topology. This paper presents a solution to the problem of routing information disclosure and traffic analysis in a new way that doesn't require exchanging a group secret key between one-hop neighbors. In addition, the proposed solution maintains the routing data integrity and node authentication features. Furthermore, the solution provides a new method
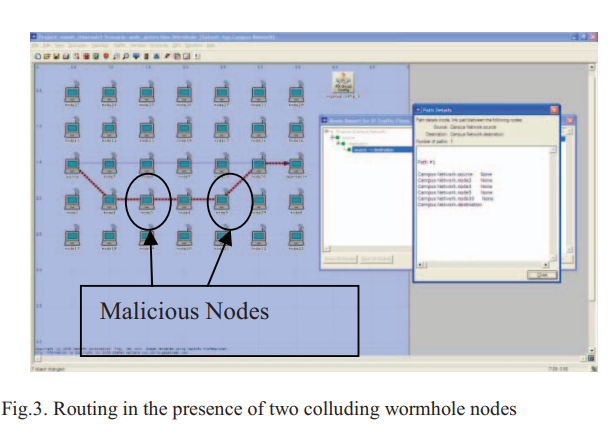
An innovative approach for the wormhole attack detection and prevention in wireless ad hoc networks
Due to their diverse applications, ad hoc networks are appealing for use in many domains. However, their features of open medium, absence of infrastructure, dynamic changing network topology, cooperative algorithms, lack of centralized monitoring and management point, resource constraints and lack of a clear line of defense, they are vulnerable to many attacks. Therefore, there is a major concern about their security. Amongst attacks we are particularly interested in a severe attack called the wormhole attack. In this paper, we propose a scheme for the wormhole attack detection and prevention
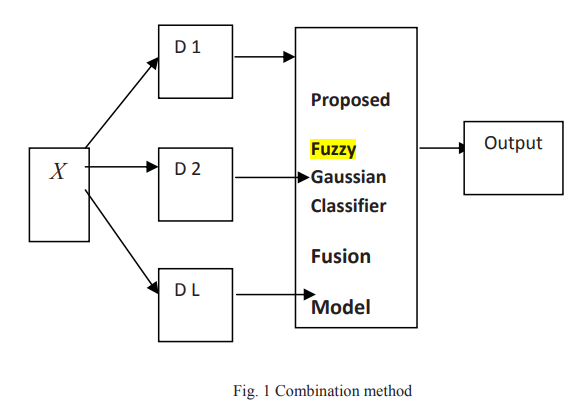
Fuzzy gaussian classifier for combining multiple learners
In the field of pattern recognition multiple classifier systems based on the combination of outputs from different classifiers have been proposed as a method of high performance classification systems. The objective of this work is to develop a fuzzy Gaussian classifier for combining multiple learners, we use a fuzzy Gaussian model to combine the outputs obtained from K-nearest neighbor classifier (KNN), Fuzzy K-nearest neighbor classifier and Multi-layer Perceptron (MLP) and then compare the results with Fuzzy Integral, Decision Templates, Weighted Majority, Majority Naïve Bayes, Maximum
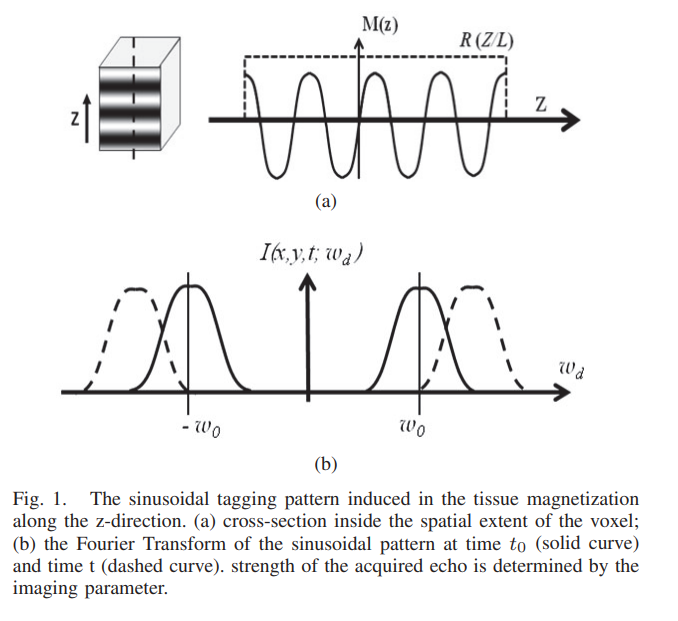
Maximum likelihood estimator for signal intensity in STEAM-based MR imaging techniques
Stimulated echo acquisition mode (STEAM) is a generic imaging technique that lies at the core of many magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques such MRI tagging, displacement encoded MRI, black-blood cardiac imaging. Nevertheless, tissue deformation causes frequency shift of the MR signal and leads to severe signal attenuation. In this work, a maximum likelihood estimator for the signal amplitude is proposed and used to correct the image artifacts. Numerical simulation and real MR data are used to test and validate the proposed method. © 2011 IEEE.
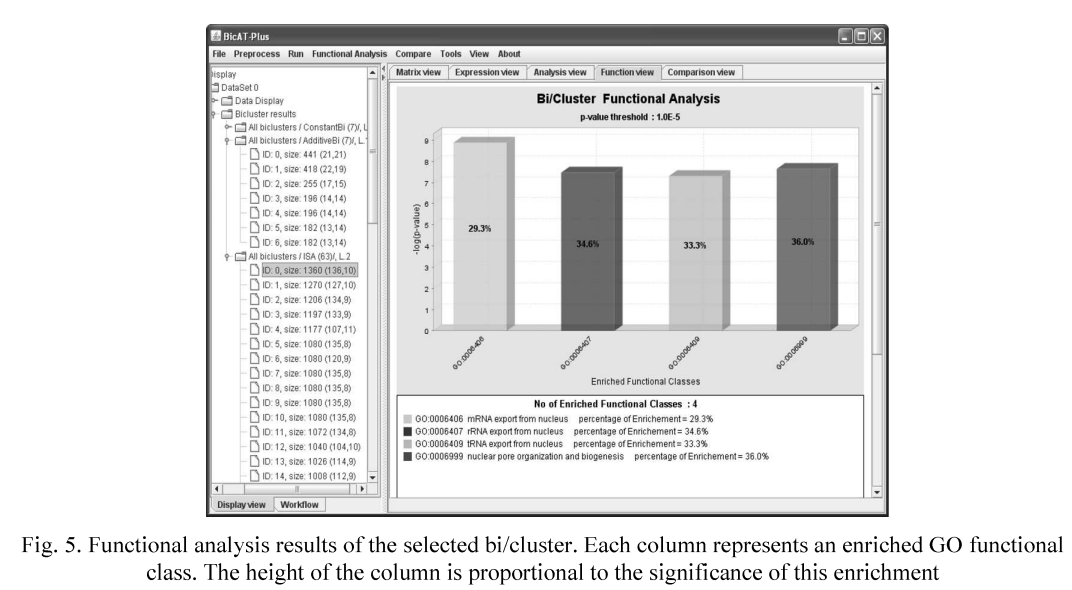
BicATPlus: An automatic comparative tool for Bi/Clustering of gene expression data obtained using microarrays
In the last few years the gene expression microarray technology has become a central tool in the field of functional genomics in which the expression levels of thousands of genes in a biological sample are determined in a single experiment. Several clustering and biclustering methods have been introduced to analyze the gene expression data by identifying the similar patterns and grouping genes into subsets that share biological significance. However, it is not clear how the different methods compare with each other with respect to the biological relevance of the biclusters and clusters as well
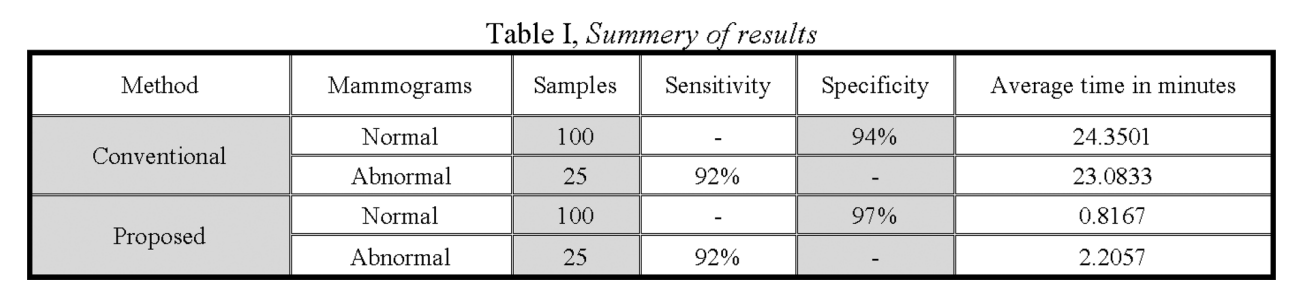
Fast fractal modeling of mammograms for microcalcifications detection
Clusters of microcalcifications in mammograms are an important early sign of breast cancer in women. Comparing with microcalcifications, the breast background tissues have high local self-similarity, which is the basic property of fractal objects. A fast fractal modeling method of mammograms for detecting the presence of microcalcifications is proposed in this paper. The conventional fractal modeling method consumes too much computation time. In the proposed method, the image is divided into shade (homogeneous) and non-shade blocks based on the dynamic range and only the non-shade blocks are
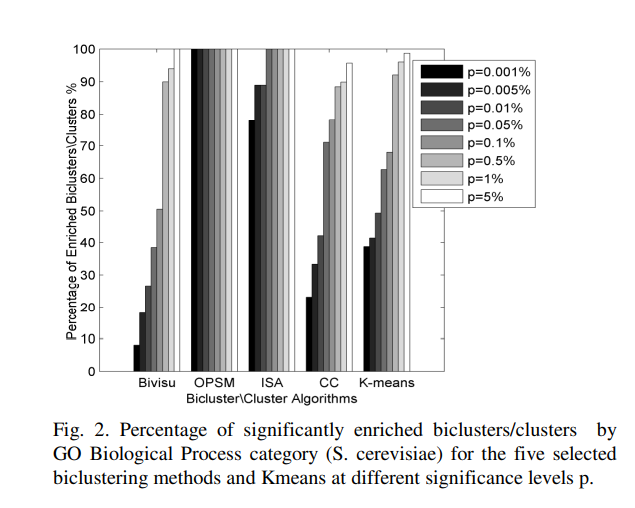
An automatic gene ontology software tool for bicluster and cluster comparisons
We propose an Automatic Gene Ontology (AGO) software as a flexible, open-source Matlab software tool that allows the user to easily compare the results of the bicluster and cluster methods. This software provides several methods to differentiate and compare the results of candidate algorithms. The results reveal that bicluster/cluster algorithms could be considered as integrated modules to recover the interesting patterns in the microarray datasets. The further application of AGO could to solve the dimensionality reduction of the gene regulatory networks. Availability: AGO and help file is
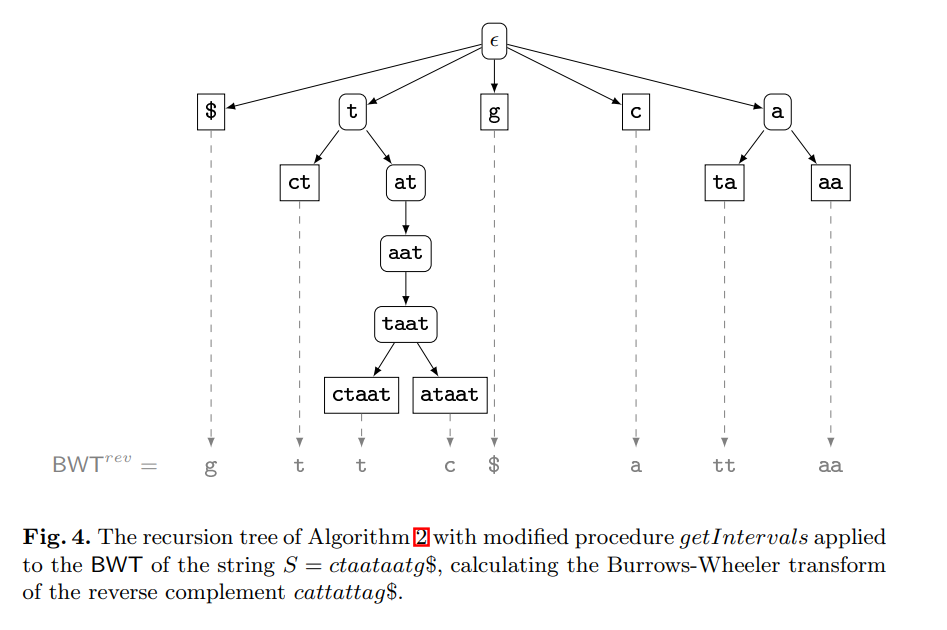
Computing the burrows-wheeler transform of a string and its reverse
The contribution of this paper is twofold. First, we provide new theoretical insights into the relationship between a string and its reverse: If the Burrows-Wheeler transform (BWT) of a string has been computed by sorting its suffixes, then the BWT and the longest common prefix array of the reverse string can be derived from it without suffix sorting. Furthermore, we show that the longest common prefix arrays of a string and its reverse are permutations of each other. Second, we provide a parallel algorithm that, given the BWT of a string, computes the BWT of its reverse much faster than all

Bivariate Double Density Discrete Wavelet for Enhanced Image Denoising
Image denoising is of paramount importance in image processing. In this paper, we propose a new design technique for the design of Double density Discrete Wavelet Transform (DD DWT) AND DD CWT filter bank structure. These filter banks satisfy the perfect reconstruction as well as alias free properties of the DWT. Next, we utilized this filter bank structure in image denoising. Our denoising scheme is based on utilizing the interscale correlation/interscale dependence between wavelet coefficients of a DD DWT of the noisy image. This is known as the Bivariate Shrinkage scheme. More precisely, we
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 36
- Next page ››
