Towards optimum condition assessment policies for water and sewer networks
With ageing water and sewer infrastructure in North America, assessing the condition of these assets has received increased attention in the past few years. Condition assessment is an integral component in any asset management program. Determining the condition of buried infrastructure tends to be more cumbersome, costly and error-prone compared to other surface infrastructure like roads and buildings. For sewers, CCTV is considered the industry standard for condition assessment technologies. For pressurized water pipelines, technologies tend to be more costly and uncertain (e.g
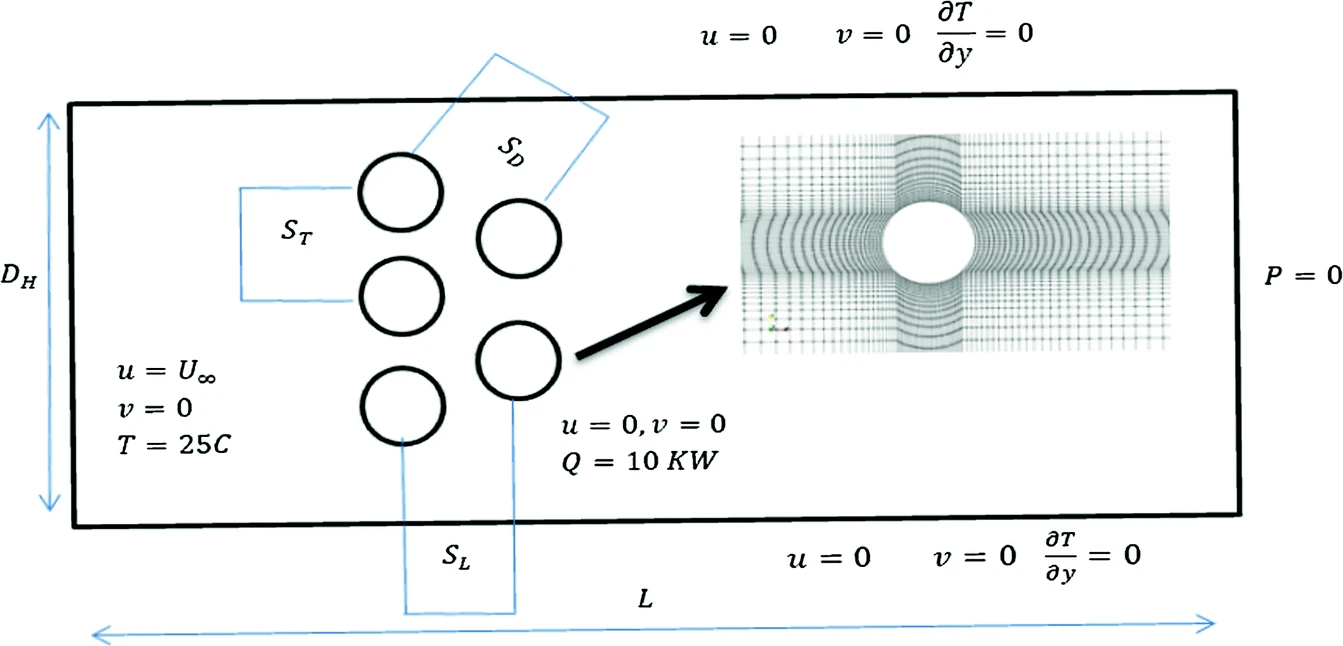
Tuning of PID Controller Using Particle Swarm Optimization for Cross Flow Heat Exchanger Based on CFD System Identification
This paper illustrates the design of proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID) controller of 10 KW air heaters for achieving the set point temperature as fast as possible with minimum response overshoot. Computational fluid dynamic (CFD) numerical simulations are utilized to predict the natural response of 10 KW input power for the air heater. CFD results are validated with experimental empirical correlations that insure the reliability of open loop results. The open loop response of CFD transient simulations is used to model the air heater transfer function and design the classical
Coagulation/flocculation process for textile mill effluent treatment: experimental and numerical perspectives
This study investigates the feasibility of applying coagulation/flocculation process for real textile wastewater treatment. Batch experiments were performed to detect the optimum performance of four different coagulants; Ferric Sulphate (Fe2(SO4)3), Aluminium Chloride (AlCl3), Aluminium Sulphate (Al2(SO4)3) and Ferric Chloride (FeCl3) at diverse ranges of pH (1–11) on the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), colour, total nitrogen (TN) and turbidity from real textile wastewater. At pH 9, FeCl3 demonstrated the most effective removal for all studied
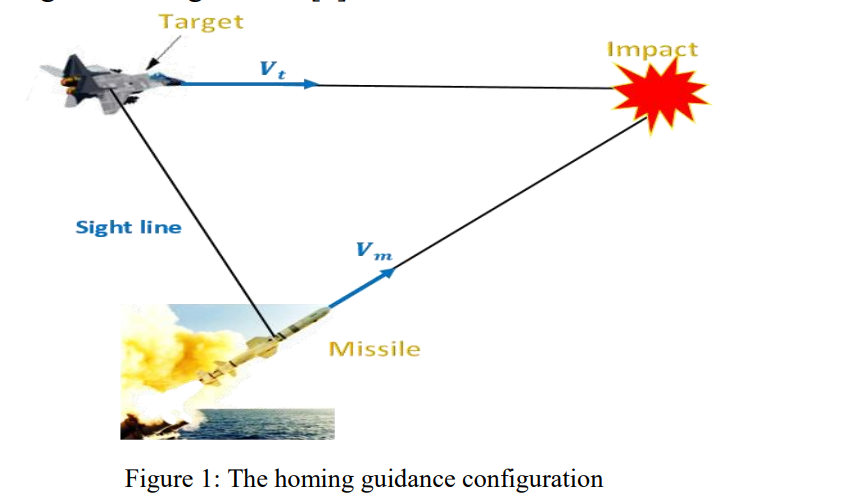
Intercept algorithm for maneuvering targets based on differential geometry and lyapunov theory
Nowadays, the homing guidance is utilized in the existed and under development air defense systems (ADS) to effectively intercept the targets. The targets became smarter and capable to fly and maneuver professionally and the tendency to design missile with a small warhead became greater, then there is a pressure to produce a more precise and accurate missile guidance system based on intelligent algorithms to ensure effective interception of highly maneuverable targets. The aim of this paper is to present an intelligent guidance algorithm that effectively and precisely intercept the
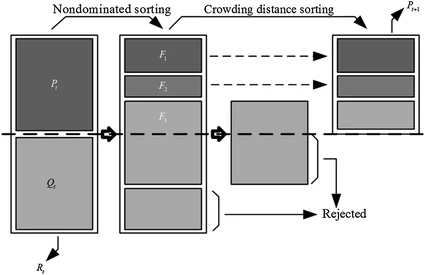
Chaotic system modelling using a neural network with optimized structure
In this work, the Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are used to model a chaotic system. A method based on the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) is used to determine the best parameters of a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) artificial neural network. Using NSGA-II, the optimal connection weights between the input layer and the hidden layer are obtained. Using NSGA-II, the connection weights between the hidden layer and the output layer are also obtained. This ensures the necessary learning to the neural network. The optimized functions by NSGA-II are the number of neurons in the

Chaotic system modelling using a neural network with optimized structure
In this work, the Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) are used to model a chaotic system. A method based on the Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) is used to determine the best parameters of a Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) artificial neural network. Using NSGA-II, the optimal connection weights between the input layer and the hidden layer are obtained. Using NSGA-II, the connection weights between the hidden layer and the output layer are also obtained. This ensures the necessary learning to the neural network. The optimized functions by NSGA-II are the number of neurons in the
AROMA: Automatic generation of radio maps for localization systems
Current methods for building radio maps for wireless localization systems require a tedious, manual and error-prone calibration of the area of interest. Each time the layout of the environment is changed or different hardware is used, the whole process of location fingerprinting and constructing the radio map has to be repeated. The process gets more complicated in the case of localizing multiple entities in a device-free scenario, since the radio map needs to take all possible combinations of the location of the entities into account. In this demo, we present a novel system (AROMA) that is
Transmission power adaptation for cognitive radios
In cognitive radio (CR) networks, determining the optimal transmission power for the secondary users (SU) is crucial to achieving the goal of maximizing the secondary throughput while protecting the primary users (PU) from service disruption and interference. In this paper, we propose an adaptive transmission power scheme for cognitive terminals opportunistically accessing a primary channel. The PU operates over the channel in an unslotted manner switching activity at random times. The secondary transmitter (STx) adapts its transmission power according to its belief regarding the PU's state of
FPGA-Based Memristor Emulator Circuit for Binary Convolutional Neural Networks
Binary convolutional neural networks (BCNN) have been proposed in the literature for resource-constrained IoTs nodes and mobile computing devices. Such computing platforms have strict constraints on the power budget, system performance, processing and memory capabilities. Nonetheless, the platforms are still required to efficiently perform classification and matching tasks needed in various applications. The memristor device has shown promising results when utilized for in-memory computing architectures, due to its ability to perform storage and computation using the same physical element
Fractional Order Sliding Mode PID Controller/Observer for Continuous Nonlinear Switched Systems with PSO Parameter Tuning
In this article a fractional order sliding mode PID controller and observer for the stabilization of continuous nonlinear switched systems is proposed. The design of the controller and observer is done following the separation principle, this means that the observer and controller are designed in a separate fashion, so a hybrid controller is implemented by designing the sliding mode controller part using an integral sliding mode surface along with a PIλDμ controller part which is the fractional order PID controller that is implemented to stabilizes the system. For the observer part, an
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
