Tactile sensing biohybrid soft E-skin based on bioimpedance using aloe vera pulp tissues
Soft and flexible E-skin advances are a subset of soft robotics field where the soft morphology of human skin is mimicked. The number of prototypes that conformed the use of biological tissues within the structure of soft robots—to develop “Biohybrid Soft Robots”—has increased in the last decade. However, no research was conducted to realize Biohybrid E-skin. In this paper, a novel biohybrid E-skin that provides tactile sensing is developed. The biohybrid E-skin highly mimics the human skin softness and morphology and can sense forces as low as 0.01 newton. The tactile sensing feature is
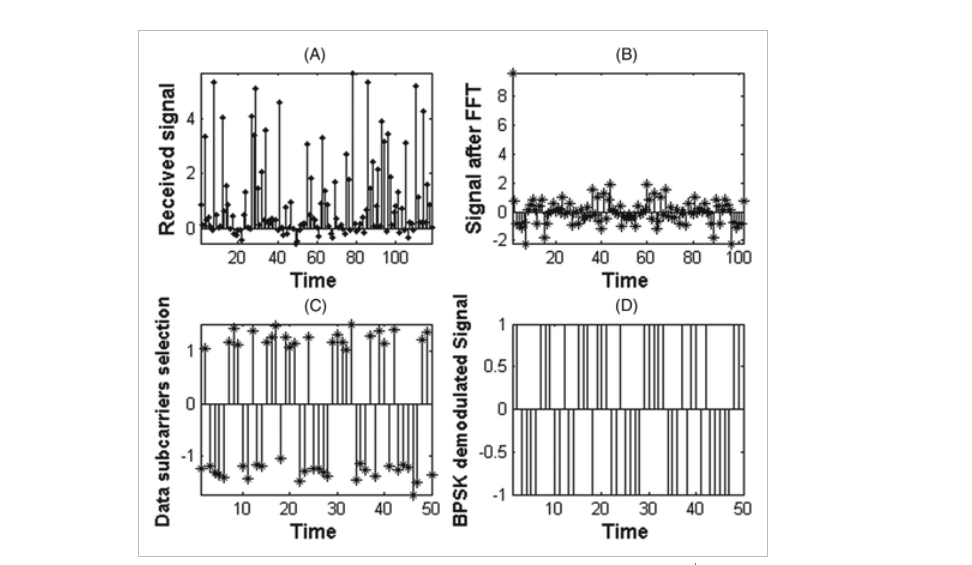
Odd clipping optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing for VLC system
The Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) has emerged as one of the promising techniques because of its robustness to multipath fading with high-speed data transmission. Classical bipolar OFDM cannot be used in intensity modulated with direct detection (IM/DD) optical communication systems, as visible light communication (VLC), so many optical modulation techniques as asymmetrical clipped optical OFDM (ACO-OFDM) and DC-Clipped OFDM (DCO-OFDM) have been investigated. In this paper, we introduce a novel optical modulation scheme that meets the optical communications requirements. The
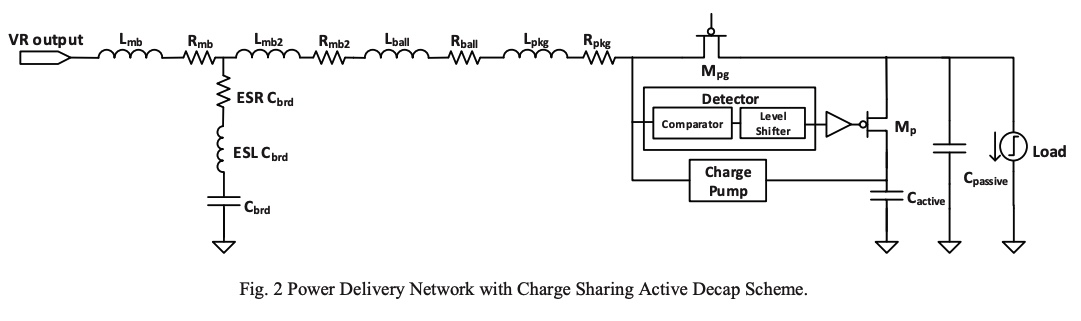
A fully integrated charge sharing active decap scheme for power supply noise suppression
Power supply noise has become a major challenge for proper operation of circuits with continuous scaling of CMOS technology along with supply voltage scaling. Conventional passive decoupling capacitors exhibit significant die area penalty resulting in a limited regulation effect. This paper presents a fully integrated charge-sharing-based active decap scheme for power supply noise suppression. The proposed idea is based on allocating a portion of the available passive decap to be used as an active decap that is charged up to a higher voltage and shares its boosted charge with the noisy rail
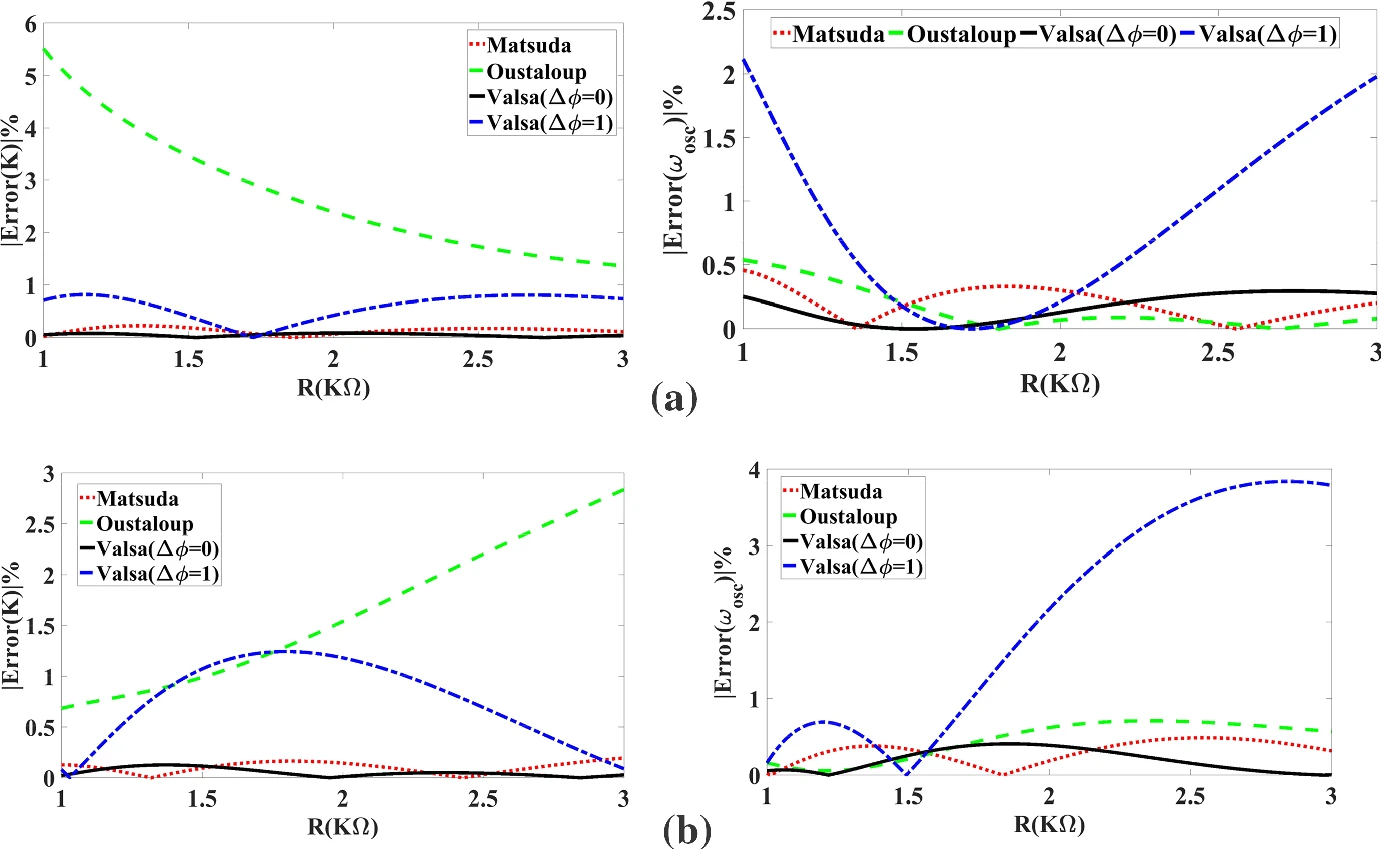
All Possible Topologies of the Fractional-Order Wien Oscillator Family Using Different Approximation Techniques
This paper introduces all the possible topologies of the Wien bridge oscillator family. This family has 72 topologies, 24 of them contain only RC or RL pairs, and the rest contain mixed pairs. The complete mathematical analysis of all twelve possible capacitive-based topologies is proposed in the fractional-order domain. The investigated circuits can be categorized into two groups, each with a similar characteristic equation. Three integer-order approximation techniques for the Laplacian operator sα are employed to solve and simulate the Wien bridge system. The studied approximations are those
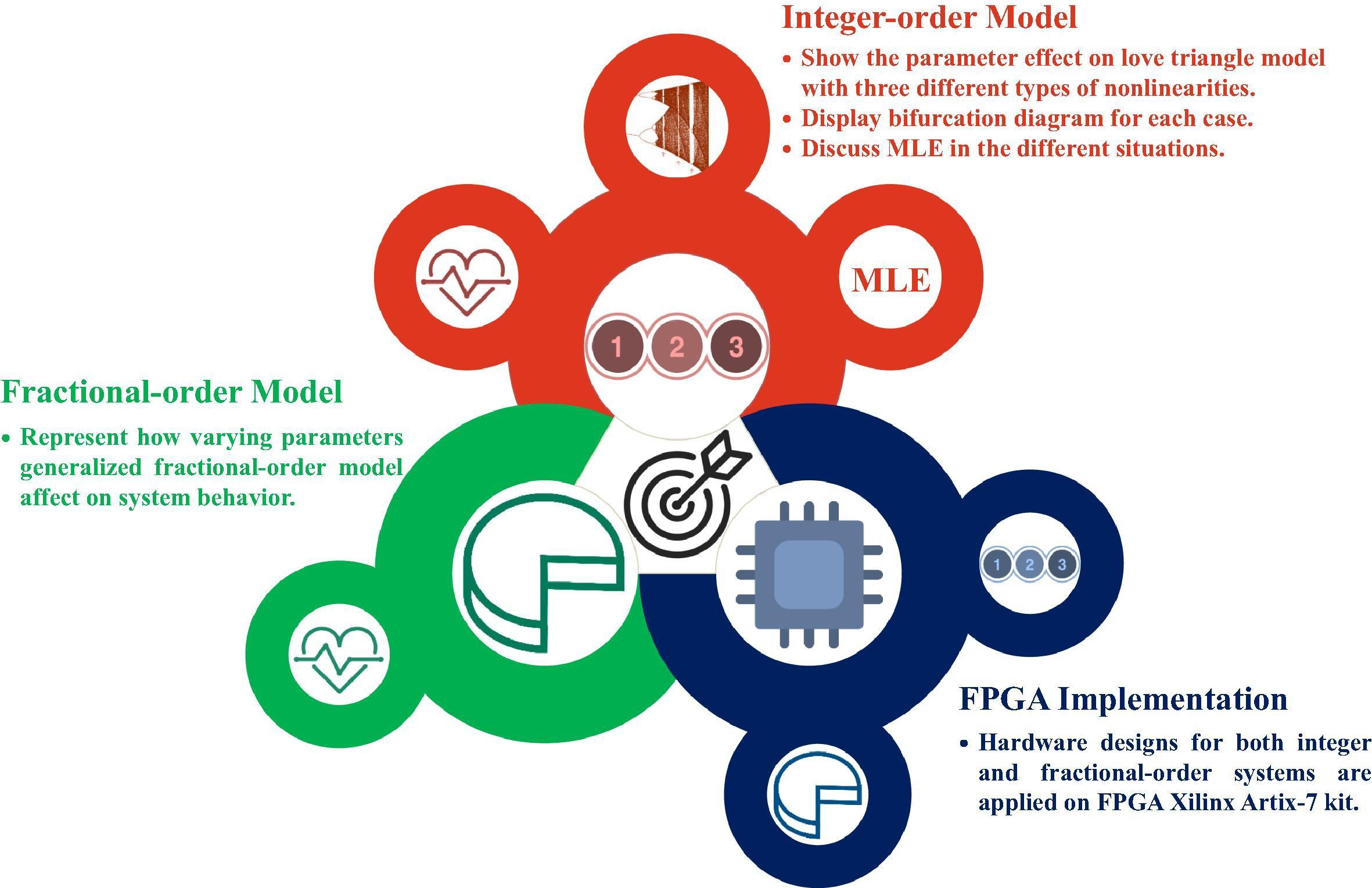
A study of the nonlinear dynamics of human behavior and its digital hardware implementation
This paper introduces an intensive discussion for the dynamical model of the love triangle in both integer and fractional-order domains. Three different types of nonlinearities soft, hard, and mixed between soft and hard, are used in this study. MATLAB numerical simulations for the different three categories are presented. Also, a discussion for how the kind of personalities affects the behavior of chaotic attractors is introduced. This paper suggests some explanations for the complex love relationships depending on the impact of memory (IoM) principle. Lyapunov exponents, Kaplan-Yorke
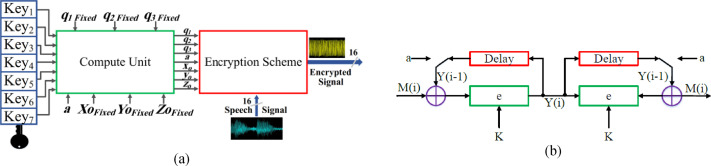
FPGA implementation of sound encryption system based on fractional-order chaotic systems
This paper introduces design and FPGA implementation of sound encryption system based on a fractional-order chaotic system. Also, it presents the FPGA implementation of Tang, Yalcin, and Özoǧuz fractional order chaotic systems. The Grunwald-Letnikov (GL) definition is used to generalize the investigated systems into the fractional-order domain. Also, the variation of parameters for each system is investigated against the window size of the GL definition. Xilinx ISE 14.5 is used to simulate the proposed design. Also, some hardware reduction techniques are applied to decrease hardware
A Simple BJT Inverse Memristor Emulator and Its Application in Chaotic Oscillators
A generalized inverse memristor emulator is proposed based on two BJT transistors as a diode connected with a first order parallel RC filter. The mathematical model of the circuit is presented where the pinched hysteresis loops (PHLs) with different periodic stimuli are analyzed. The numerical, P-Spice simulations and experimental results are presented indicating that the introduced emulator is a simple voltage-controlled generalized inverse memristor. The results show that the PHLs area is increased with increasing the applied frequency. In addition, the proposed emulator is employed in a
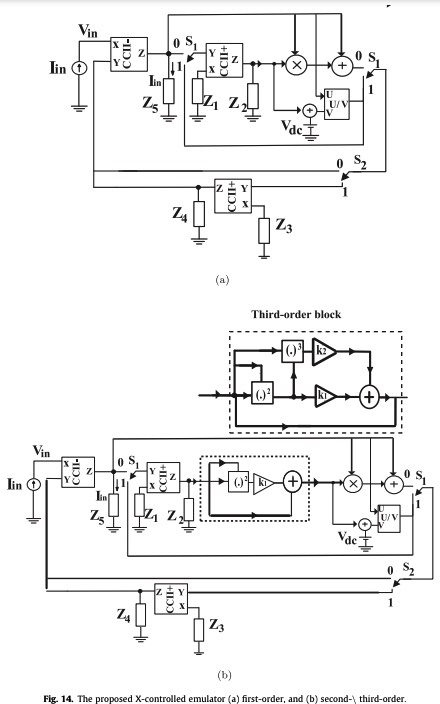
A general emulator for fractional-order memristive elements with multiple pinched points and application
In this paper, X-controlled universal fractional-order memelements (FOMEs) emulator is proposed. The emulation circuit is realized using second-generation current conveyor (CCII) and analog voltage multiplier (AVM)/divider block with two switches to control the type of memelements and emulator mode. The effect of the fractional-order capacitor (FOC) on the pinched hysteresis loop (HL) area and the range of frequency is discussed at different fractional-order α. Additionally, the higher-order meminductor, memristor, memcapacitor, and inverse memristor are discussed presenting multiple pinched
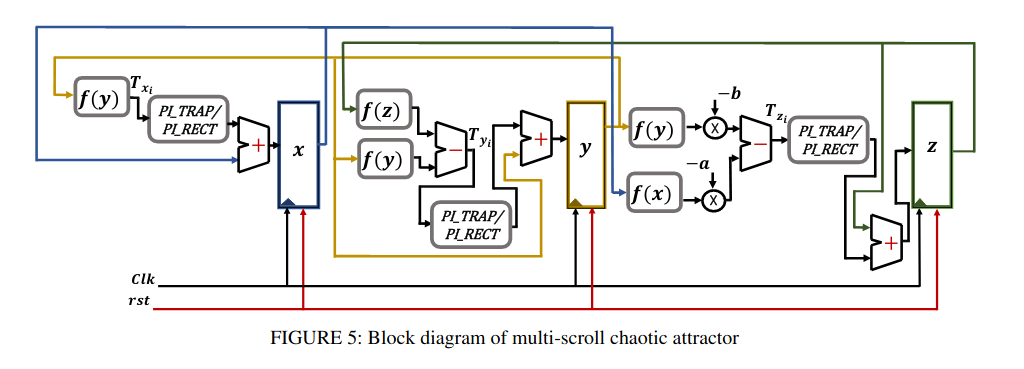
Numerical Simulations and FPGA Implementations of Fractional-Order Systems Based on Product Integration Rules
Product integration (PI) rules are well known numerical techniques that are used to solve differential equations of integer and, recently, fractional orders. Due to the high memory dependency of the PI rules used in solving fractional-order systems (FOS), their hardware implementation is very difficult and resources-demanding. In this paper, modified versions of the PI rules are introduced to facilitate their digital implementations. The studied rules are PI rectangular, PI trapezoidal, and predict-evaluate-correct-evaluate (PECE) rules. The three modified versions of the PI rules are
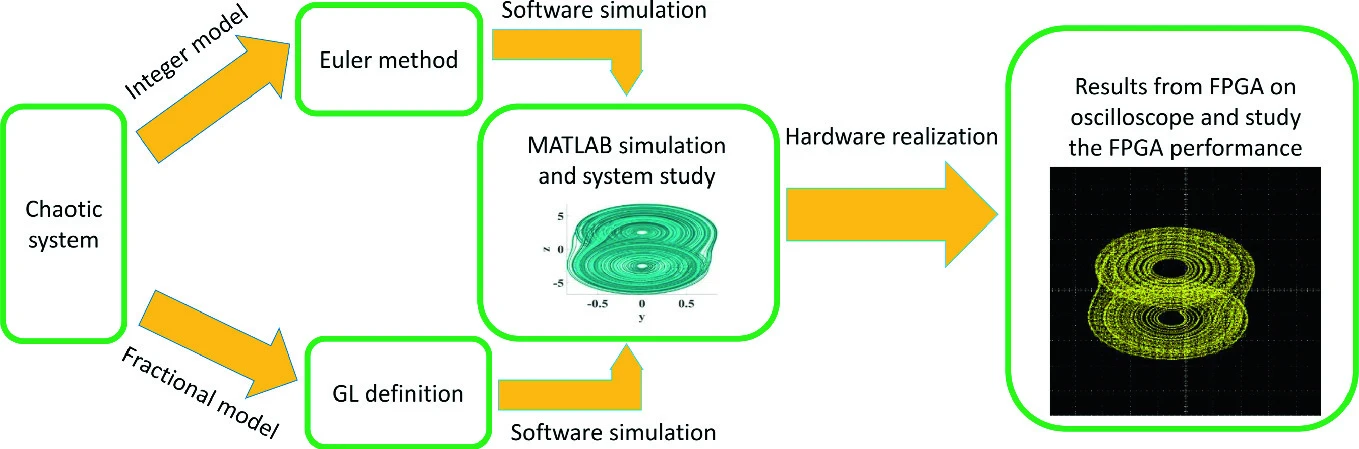
FPGA implementation of integer/fractional chaotic systems
Chaotic systems have remarkable importance in capturing some complex features of the physical process. Recently, fractional calculus becomes a vigorous tool in characterizing the dynamics of complex systems. The fractional-order chaotic systems increase the chaotic behavior in new dimensions and add extra degrees of freedom, which increase system controllability. In this chapter, FPGA implementation of different integer and fractional-order chaotic systems is presented. The investigated integer-order systems include Chua double scroll chaotic system and the modified Chua N-scroll chaotic
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 15
- Next page ››
