Study of alternative back contacts for thin film Cu2ZnSnSe4-based solar cells
Cu2ZnSnSe4 thin film solar cells are usually fabricated on a soda lime glass substrate with a molybdenum (Mo) back contact. It is suspected that degradation in electrical performance occurs due to the formation of a barrier between the absorber and Mo back contact. To overcome such degradation, Titanium Nitride (TiN), Titanium Tungsten (TiW), Chromium (Cr), Titanium (Ti) and Aluminum (Al) deposited on Mo-coated glass substrates are investigated as alternative back contact materials. Physical and electrical characterization as well as photoluminescence measurements are performed. Compositional

Multi-reader RFID tag identification using bit tracking (MRTI-BT)
In this paper we study the problem of tag identification in multi-reader RFID systems. In particular, we propose a novel solution to the reader-to-reader collisions and tag collisions in multi-reader systems, using the concept of bit tracking [1]. Towards this objective, we propose the multi-reader RFID tag identification using bit tracking (MRTI-BT) algorithm which allows concurrent tag identification, by neighboring RFID readers, as opposed to time-consuming scheduling. First, MRTI-BT identifies tags exclusive to different RFIDs, concurrently. Second, the concept of bit tracking and the
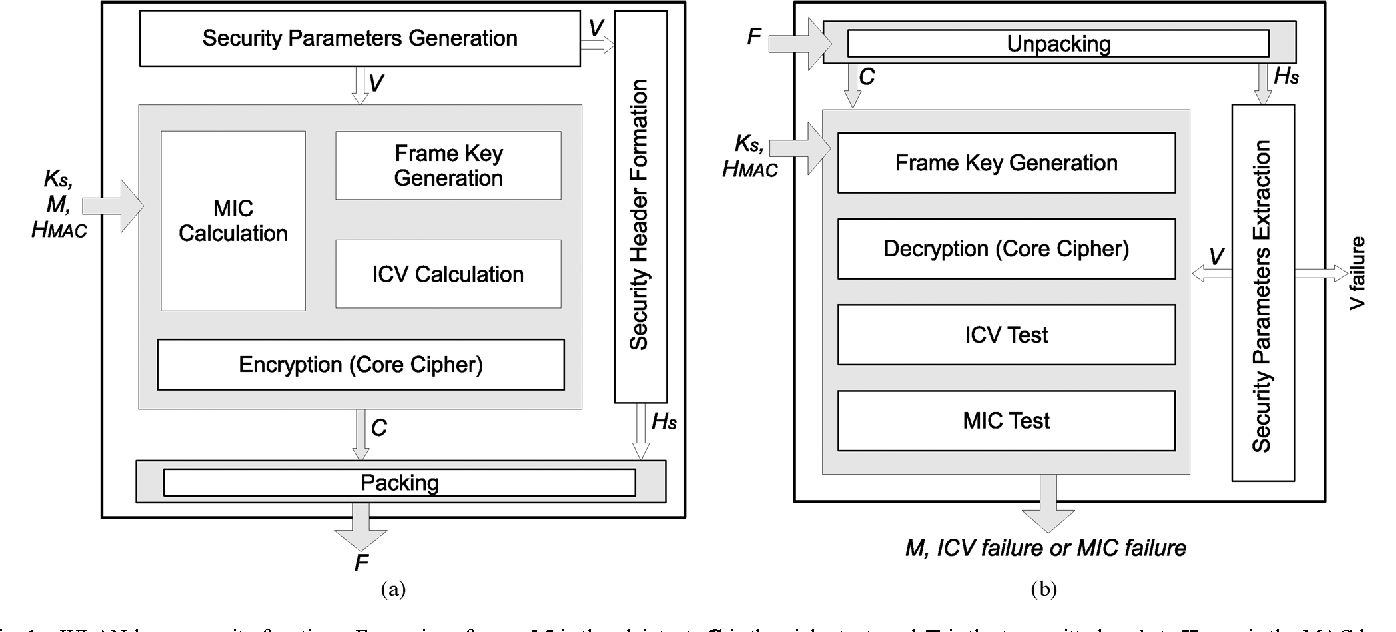
Keys through ARQ: Theory and practice
This paper develops a novel framework for sharing secret keys using the Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) protocol. We first characterize the underlying information theoretic limits, under different assumptions on the channel spatial and temporal correlation function. Our analysis reveals a novel role of dumb antennas in overcoming the negative impact of spatial correlation on the achievable secrecy rates. We further develop an adaptive rate allocation policy, which achieves higher secrecy rates in temporally correlated channels, and explicit constructions for ARQ secrecy coding that enjoy low
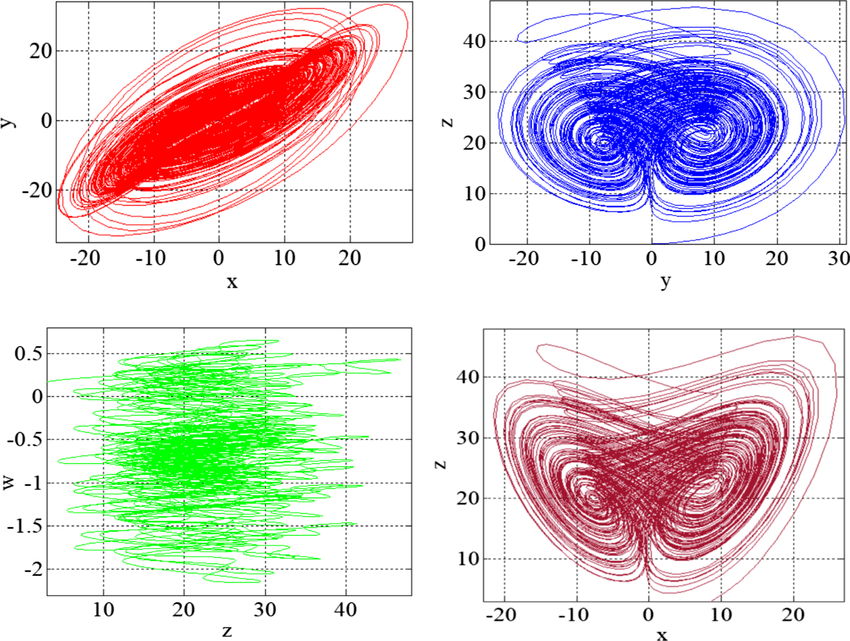
New hybrid synchronisation schemes based on coexistence of various types of synchronisation between master-slave hyperchaotic systems
In this paper, we present new approaches to study the co-existence of some types of synchronisation between hyperchaotic dynamical systems. The paper first analyses, based on stability theory of linear continuous-Time systems, the co-existence of the projective synchronisation (PS), the function projective synchronisation (FPS), the full state hybrid function projective synchronisation (FSHFPS) and the generalised synchronisation (GS) between general master and slave hyperchaotic systems. Successively, using Lyapunov stability theory, the coexistence of three different synchronisation types is
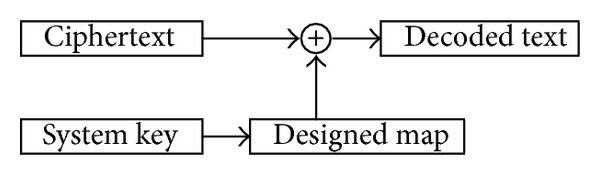
Trajectory control and image encryption using affine transformation of lorenz system
This paper presents a generalization of chaotic systems using two-dimensional affine transformations with six introduced parameters to achieve scaling, reflection, rotation, translation and/or shearing. Hence, the location of the strange attractor in space can be controlled without changing its chaotic dynamics. In addition, the embedded parameters enhance the randomness and sensitivity of the system and control its response. This approach overpasses performing the transformations as post-processing stages by applying them on the resulting time series. Trajectory control through dynamic
Design of Positive, Negative, and Alternating Sign Generalized Logistic Maps
The discrete logistic map is one of the most famous discrete chaotic maps which has widely spread applications. This paper investigates a set of four generalized logistic maps where the conventional map is a special case. The proposed maps have extra degrees of freedom which provide different chaotic characteristics and increase the design flexibility required for many applications such as quantitative financial modeling. Based on the maximum chaotic range of the output, the proposed maps can be classified as positive logistic map, mostly positive logistic map, negative logistic map, and

Multistability Analysis and Function Projective Synchronization in Relay Coupled Oscillators
Regions of stability phases discovered in a general class of Genesio-Tesi chaotic oscillators are proposed. In a relatively large region of two-parameter space, the system has coexisting point attractors and limit cycles. The variation of two parameters is used to characterize the multistability by plotting the isospike diagrams for two nonsymmetric initial conditions. The parameters window in which the jerk system exhibits the unusual and striking feature of multiple attractors (e.g., coexistence of six disconnected periodic chaotic attractors and three-point attraction) is investigated. The
Fractional canny edge detection for biomedical applications
This paper presents a comparative study of edge detection algorithms based on integer and fractional order differentiation. A performance comparison of the two algorithms has been proposed. Then, a soft computing technique has been applied to both algorithms for better edge detection. From the simulations, it shows that better performance is obtained compared to the classical approach. The noise performances of those algorithms are analyzed upon the addition of random Gaussian noise, as well as the addition of salt and pepper noise. The performance has been compared to peak signal to noise
Improved Production Key Performance Indicators (KPI’s) Using Intelligent-Manufacturing Execution Systems (I-MES)
The aim of this research is to reduce the gap between manufacture expertise and management expertise by using modern technology like Manufacturing Execution System (MES) via Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machin Learning (ML). A design of MES has been proposed and implemented on El-Araby Plastic Injection Molding (PIM) factory. This work is based on the International Society of Automation Standard (ISA-S95). A fully automated data management system has been designed and implemented to control data follow between shop floor e.g. (machines and operators) and management floor e.g. (production
Indoor localization and movement prediction algorithms with light-fidelity
Indoor localization has recently attended an increase in interest due to the potential for a wide range of services. In this paper, indoor high-precision positioning and motion prediction algorithms are proposed by using light fidelity (LI-FI) system with angular diversity receiver (ADR). The positioning algorithm uses to estimate the location of an object in the room. Furthermore, the prediction algorithm applies to predict the motion of that object. The simulation results show that the average root mean squares error of the positioning algorithm is about 0.6 cm, and the standard deviation
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 59
- Next page ››
