Guidance optimization for tactical homing missiles and air defense systems
The aim of this paper is to develop a functional approach to optimize the engagement effectiveness of the tactical homing missiles and air defense systems by utilizing the differential geometric concepts. In this paper the engagement geometry of the interceptor and the target is developed and expressed in differential geometric terms in order to demonstrate the possibilities of the impact triangles and specify the earliest interception based on the direct intercept geometry. Optimizing the missile heading angle and suitable missile velocity against the target velocity is then examined to
Chiral phase structure of the sixteen meson states in the SU(3) Polyakov linear-sigma model for finite temperature and chemical potential in a strong magnetic field
In characterizing the chiral phase-structure of pseudoscalar ( ), scalar ( ), vector ( ) and axial-vector ( t) meson states and their dependence on temperature, chemical potential, and magnetic field, we utilize the SU(3) Polyakov linear-sigma model (PLSM) in the mean-field approximation. We first determine the chiral (non)strange quark condensates, and , and the corresponding deconfinement order parameters, and , in thermal and dense (finite chemical potential) medium and finite magnetic field. The temperature and the chemical potential characteristics of nonet meson states normalized to the
Hardware Advancements Effects on MANET Development, Application and Research
Mobile devices' development has remarkably improved in light of the fast growing hardware advancements. These advancements include multicore processor chips, ultra large main memories and batteries that last for hours even when running modern applications such as file transfer, voice communication and video streaming ...etc. In this paper, we shed the light on recent and future trends of hardware advancements for mobile devices, and their impact on MANET developments. In addition, the effect of such advancements is investigated on application and different research areas. © Springer-Verlag
Advances in system dynamics and control
Complex systems are pervasive in many areas of science. With the increasing requirement for high levels of system performance, complex systems has become an important area of research due to its role in many industries. Advances in System Dynamics and Control provides emerging research on the applications in the field of control and analysis for complex systems, with a special emphasis on how to solve various control design and observer design problems, nonlinear systems, interconnected systems, and singular systems. Featuring coverage on a broad range of topics, such as adaptive control
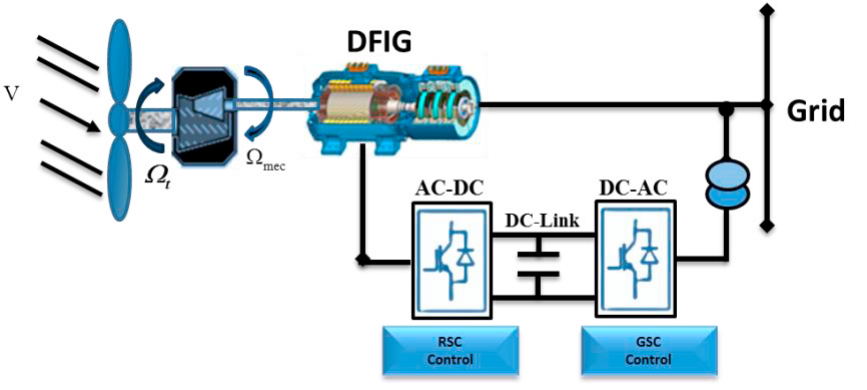
Sensor Faults Detection and Estimation for a Dfig Equipped Wind Turbine
Doubly Fed Induction Generator (DFIG) based on wind turbines demand a high degree of reliability and availability and they are characterized by expensive and safety critical maintenance work. This paper deals with a new strategy for detection and estimation of current sensor faults in the stator and rotor of a DFIG. First, a state space model of a DFIG is developed based on voltages and flux equations, which can be used in order to estimate states and to generate residuals by using a Luenberger observer. Then, the residuals results are exploited for faults detection and estimation. Finally
Towards mature temporal accuracy assessment of processors models and simulators for real-time systems development
Modeling and simulation are becoming extensively used in embedded and Real-Time Systems (RTSs) development throughout the development life-cycle, from the system-level design space exploration to the fine grained time analysis and evaluation of the system and even its components performance. At the core of these systems lies the processor which has been also the center of attention for most of the modeling and simulation efforts related to RTS simulation. Although the temporal accuracy of such models and simulators is of critical importance for Real-Time (RT) applications, it is not yet mature
Evidence of forward–backward correlation of pions in ultra-relativistic ring- and jet-like events in 16O- Ag/ Br interactions at Elab= 60 A GeV
An investigation on the presence of the forward–backward correlations in the pions multiplicity, emitted in 16O- Ag/ Br interactions at energy Elab= 60 A GeV are carried out. The study of the forward–backward correlation between various observables which is separated by two different pseudorapidity intervals can be treated as an important probe to defining the primordial conditions for the formation of the Quark Gluon Plasma (QGP). We have observed the dependency of correlation fluctuations and correlation strength on pseudorapidity (η) and the increasing width of the pseudorapidity bin size
A step forward enhancing green buildings in developing countries
Sustainability is essential for maintaining certain levels of life quality for next generations. Accordingly, Egypt started to establish its own rating system to achieve sustainable development. There are several green building rating systems that are recently used such as: The LEED (Leadership in energy and environmental Design) rating system, Green Pyramid Rating System “GPRS”, and TARSHEED rating system. GPRS and LEED are almost the same since GPRS is based on LEED. Due to the significant cultural and environmental changes between Egypt and the United States, LEED rating system cannot be
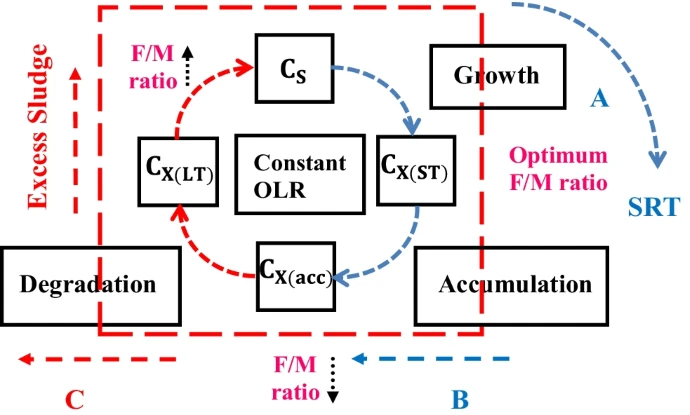
Modified fractional-order model for biomass degradation in an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket reactor at Zenein Wastewater Treatment Plant
This paper presents a modified fractional-order model (FOM) for microorganism stimulation in an up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactor treating low-strength wastewater. This study aimed to examine the famine period of methanogens due to biomass accumulation in the UASB reactor over long time periods at a constant organic loading rate (OLR). This modified model can investigate the substrate biodegradation in a UASB reactor while considering substrate diffusion into biological granules during the feast and famine periods of methanogens. The Grünwald-Letnikov numerical technique was used
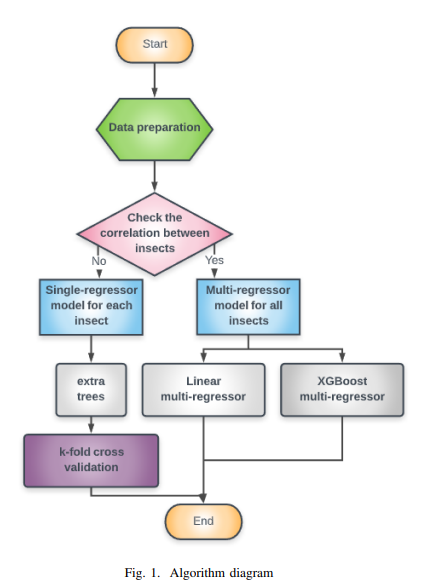
Guava Trees Disease Monitoring Using the Integration of Machine Learning and Predictive Analytics
The increase in population, food demand, and the pollution levels of the environment are considered major problems of this era. For these reasons, the traditional ways of farming are no longer suitable for early and accurate detection of biotic stress. Recently, precision agriculture has been extensively used as a potential solution for the aforementioned problems using high resolution optical sensors and data analysis methods that are able to cope with the resolution, size and complexity of the signals from these sensors. In this paper, several methods of machine learning have been utilized
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 14
- Next page ››
