Analytical Markov model for slotted ALOHA with opportunistic RF energy harvesting
In this paper, we investigate the performance of an ALOHA random access wireless network consisting of nodes with and without RF energy harvesting capability. We develop and analyze a Markov model for the system when nodes with RF energy harvesting capability are infinitely backlogged. Our results indicate that the network throughput is improved when the conventional nodes are underloaded. On the contrary, when all types of nodes have finite backlogs, we numerically demonstrate that the network throughput and delay are improved when the overall system is overloaded. We show that there exists a
Improvement of structural efficiency in metals by the control of topological arrangements in ultrafine and coarse grains
Improvement of structural efficiency in various materials is critically important for sustainable society development and the efficient use of natural resources. Recently, a lot of attention in science and engineering has been attracted to heterogeneous-structure materials because of high structural efficiency. However, strategies for the efficient design of heterogenous structures are still in their infancy therefore demanding extensive exploration. In this work, two-dimensional finite-element models for pure nickel with bimodal distributions of grain sizes having ‘harmonic’ and ‘random’

Nanocomposite matrix conjugated with carbon nanomaterials for photocatalytic wastewater treatment
The problem of hazardous wastewater remediation is a complicated issue and a global challenge. Herein, a layered Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4/SiO2/TiO2 composite matrix was prepared and incorporated with three carbon nanomaterials having different dimensionalities, carbon dots (C-dots, 0D), single-walled carbon nanotubes (1D), and reduced graphene oxide (2D), in an effort to create effective photocatalytic nanocomposites for chloramine-T removal from water. Microstructural analyses confirmed the formation of nanocomposites and revealed their chemistry and structure. Elemental mapping revealed a uniform
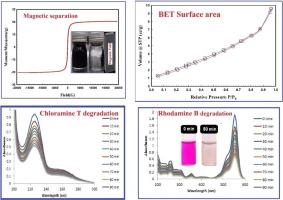
Nanostructured Mg substituted Mn-Zn ferrites: A magnetic recyclable catalyst for outstanding photocatalytic and antimicrobial potentials
With recently increasing the environmental problems and expected energy crisis, it is necessary to synthesis a low-cost, efficient, and UV-light responsive photocatalyst for contaminants’ degradation. The nanostructured spinel ferrite Mn0.5Zn0.5-xMgxFe2O4 NPs (x = 0.0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.375 and 0.50) were synthesized via the sol-gel method. The crystallite size was lied in nano regime ranging from 21.8 to 36.5 nm. The surface chemical composition of the Mn0.5Zn0.5-xMgxFe2O4 NPs was investigated via XPS analysis. Mossbauer spectra showed that the peaks were shifted to higher values of the maximum

Multistep deposition of Cu2Si(S,Se)3 and Cu2ZnSiSe4high band gap absorber materials for thin film solar cells
Cu2ZnSi(S,Se)4 and Cu2Si(S,Se)3 are potential materials to obtain cost effective high band gap absorbers for tandem thin film solar cell devices. A method to synthesize Cu2SiS3, Cu2SiSe3and Cu2ZnSiSe4thin film absorbers is proposed. This method is based on a multistep process, using sequential deposition and annealing processes. X-ray diffraction analysis performed on the final thin films have confirmed the presence of the Cu2Si(S,Se)3 and Cu2ZnSiSe4phases. Scanning electron microscopy images revealed the formation of polycrystalline layers with grains size up to 1 μm. The band gap of the
Stochastic modeling of 2D photonic crystals
Due to the fabrication processes, inaccurate manufacturing of the photonic crystals (PCs) might occur which affect their performance. In this paper, we examine the effects of tolerance variations of the radii of the rods and the permittivity of the material of the two-dimensional PCs on their performance. The presented stochastic analysis relies on plane wave expansion method and Mote Carlo simulations. We focus on two structures, namely Si-Rods PCs and Air-Holes PCs. Numerical results show—for both structures—that uncertainties in the dimensions of the PCs have higher impact on its photonic
Improved memristor-based relaxation oscillator
This paper presents an improved memristor-based relaxation oscillator which offers higher frequency and wider tunning range than the existing reactance-less oscillators. It also has the capability of operating on two positive supplies or alternatively a positive and negative supply. Furthermore, it has the advantage that it can be fully integrated on-chip providing an area-efficient solution. On the other hand, The oscillation concept is discussed then a complete mathematical analysis of the proposed oscillator is introduced. Furthermore, the power consumption of the new relaxation circuit is
Influence of Periodic Surface Nanopatterning Profiles on Series Resistance in Thin-Film Crystalline Silicon Heterojunction Solar Cells
In the frame of the development of thin crystalline silicon solar cell technologies, surface nanopatterning of silicon is gaining importance. Its impact on the material quality is, however, not yet fully controlled.We investigate here the influence of surface nanotexturing on the series resistance of a contacting scheme relevant for thin-film crystalline silicon heterojunction solar cells. Twodimensional periodic nanotextures are fabricated using a combination of nanoimprint lithography and either dry or wet etching, while random pyramid texturing is used for benchmarking. We compare these
Implementing earned value management using bridge information modeling
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has widely become an effective tool in engineering and construction fields. It could be used in: generating shop drawings; detecting clashes; estimating quantities; and controlling documents. Applying BIM technology on bridges is named Bridge Information Modeling (BrIM). Bridge Information Modeling (BrIM) is an intelligent representation of bridges since it contains all information needed about bridges through their whole lifecycle. This paper presents the use of Building Information Modeling in cost and time management of infrastructure bridges. BIM-based
Integration of a 2-D periodic nanopattern into thin-film polycrystalline silicon solar cells by nanoimprint lithography
The integration of 2-D periodic nanopattern defined by nanoimprint lithography and dry etching into aluminum-induced crystallization-based polycrystalline silicon thin-film solar cells is investigated experimentally. Compared with the unpatterned cell, an increase of 6% in the light absorption has been achieved thanks to the nanopattern, which, in turn, increased the short-circuit current from 20.6 to 23.8 mA/cm2. The efficiency, on the other hand, has limitedly increased from 6.4% to 6.7%. We show using the transfer length method that the surface topography modification caused by the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 3
- Next page ››
