Merits of photocatalytic and antimicrobial applications of gamma-irradiated Co: XNi1- xFe2O4/SiO2/TiO2; X = 0.9 nanocomposite for pyridine removal and pathogenic bacteria/fungi disinfection: Implication for wastewater treatment
In this paper, we report a layer-by-layer approach for the preparation of a concentric recyclable composite (CoxNi1-xFe2O4/SiO2/TiO2; x = 0.9) designed for wastewater treatment. The prepared composite was investigated by X-ray diffraction spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) supported with energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy to analyze crystallinity, average particle size, morphology and elemental composition, respectively. The antimicrobial activities of the prepared composite have been investigated against multi-drug
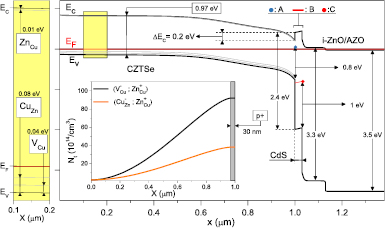
Modelling of Cu2ZnSnSe4-CdS-ZnO thin film solar cell
We present a device model for the Cu2ZnSnSe4-CdS-ZnO solar cell with a total area efficiency of 9.7% reported in 2013 (Brammertz et al 2013 Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 163904). The simulations were performed using SCAPS program. In the device model, we reproduce rigorously the full range of layers and device properties estimated experientially using various characterization techniques. We include in the device model barriers at the back contact and the absorber/buffer interfaces, the photo-doped CdS buffer layer and defect states at the CdS/ZnO interface. A perfect match with the electrical
A study on the feasibility of producing polylactic acid from cotton and coffee waste in Egypt
The amount of solid waste is growing In Egypt. It is estimated to be 20 million tons annually according to the Ministry of environment forecasts. The typical competence of collection in urban areas signifies 40 – 80%, although the middling proficiency of assortment processes and transport in rustic areas signifies 40 % which is considered hazardous for communal health and environment deprived of handling solid waste in integrated framework for solid waste management system. The reprocessing and treatment procedures in Egypt represent about 9.5 % of the entire urban solid waste, which is
Frequency survey simulation for developing novel radio frequency energy harvesting model
Renewable Energy sources are the center of attraction for research and development all over the world nowadays, the demand of a lasting cheap source of energy that is environmental friendly, is the main challenge recently. Energy Harvesting is a new technology that is going to make a revolution in the coming decade. Energy Harvesting is a technique to provide alternative sources of energy that are environmental friendly and low in cost. Radio Frequency Energy Harvesting is one of the methods to provide electrical energy from the ambient Radio Frequency waves that already exists in the
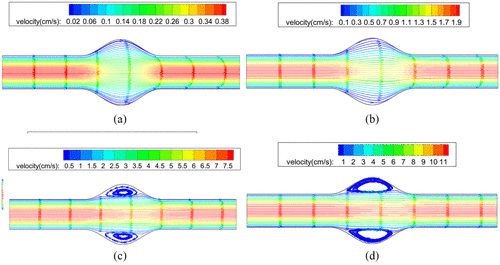
Numerical simulation of Oldroyd-B fluid with application to hemodynamics
Oldroyd-B viscoelastic fluid is numerically simulated using the stabilized Galerkin least squares finite element method. The instabilities due to the connective nature of the Oldroyd-B model is treated using the discrete viscous elastic split stress method. The model is used to study the behavior of the flow of blood through an abdominal aortic segment. The results show that the viscoelastic nature of the blood should be considered specially at low shear rates. © The Author(s) 2019.
Comparison and analysis of water main performance models
Evaluating the condition state of infrastructure assets is one of the most integral pieces of information to the asset manager. Water infrastructure poses specific challenges compared to sewer infrastructure where techniques like CCTV are now being consistently used to assess condition. The number of water main breaks is commonly used as a proxy for water main condition. Statistical water main performance models rely on using past breakage patterns and rates to predict future performance of the water main network. Performance models can be broadly classified into two groups. Rate-of-failure
Characterization of defects in 9.7% efficient Cu2ZnSnSe 4-CdS-ZnO solar cells
We have fabricated Cu2ZnSnSe4-CdS-ZnO solar cells with a total area efficiency of 9.7%. The absorber layer was fabricated by selenization of sputtered Cu10Sn90, Zn, and Cu multilayers. A large ideality factor of the order of 3 is observed in both illuminated and dark IV-curves, which seems to point in the direction of complex recombination mechanisms such as recombination through fluctuating potentials in the conduction and valence bands of the solar cell structure. A potential barrier of about 135 meV in the device seems to be responsible for an exponential increase of the series resistance
Analytic and numeric analysis for deformation of non-prismatic beams resting on elastic foundations
Background: The buckling load as well as the natural frequency under axial load for non-prismatic beam is a changeling problem. Determination of buckling load, natural frequency, and elastic deflection is very important in civil applications. The current paper used both perturbation method (PM), analytic method, and differential quadrature method (DQM), numerical method, to find buckling load and natural frequency with different end supports. The deflection of the beam resting on an elastic foundation under transverse distributed and axial loads is also obtained. Both PM and DQM are used for
Two-dimensional heat conduction in a rigid thermal conductor within the dual-phase-lag model by one-sided Fourier transform
An exact analytical solution in closed form is obtained for a two-dimensional initial-boundary-value problem of heat wave propagation in a thick slab of an anisotropic rigid thermal conductor within the dual-phase-lag model. One-sided Fourier transform technique is used to obtain a formal solution. The method requires an essential change of the dependent variable in order to guarantee a suitable asymptotic time behavior of the unknown function. The solution satisfies prescribed boundary temperatures and zero initial conditions. Numerical results are presented to put in evidence the effect of
Analytical solution for nonlinear interaction of euler beam resting on a tensionless soil
The nonlinear interaction between an elastic Euler beam and a tensionless soil foundation is studied. Exact analytical solutions of the challenging problem are rather complicated. The basic obstacle is imposing compatibility conditions at lift-off points. These points are determined as a part of the solution although being needed to get the solution itself. In the current work, solutions are derived using the approximate Rayleigh-Ritz method. The principal of vanishing variation of potential energy is adopted. The solution is approximated using a set of suitable trial functions. Lift-off
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
