Comparative Studies of Using Nano Zerovalent Iron, Activated Carbon, and Green Synthesized Nano Zerovalent Iron for Textile Wastewater Color Removal Using Artificial Intelligence, Regression Analysis, Adsorption Isotherm, and Kinetic Studies
Daily, a big extent of colored, partially treated textile effluents drained into the sanitation systems causing serious environmental concerns. Therefore, the decolorization treatment process of wastewater is crucial to improve effluent quality. In the present study, 3 different sorbent materials, nano zerovalent iron (nZVI), activated carbon (AC), and green-synthesized nano zerovalent iron (GT-nZVI), have been prepared for raw textile wastewater decolourization. The prepared nanomaterials were characterized via X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy
Multiobjective optimisation algorithm for sewer network rehabilitation
Understanding of deterioration mechanisms in sewers helps asset managers in developing prediction models for estimating whether or not sewer collapse is likely. Effective utilisation of deterioration prediction models along with the development and use of life cycle maintenance cost analysis contribute to reducing operation and maintenance costs in sewer systems. This article presents a model for life-cycle maintenance planning of deteriorating sewer network as a multi-objective optimisation problem that treats the sewer network condition and service life as well as life-cycle maintenance cost
Multiobjective genetic algorithm to allocate budgetary resources for condition assessment of water and sewer networks
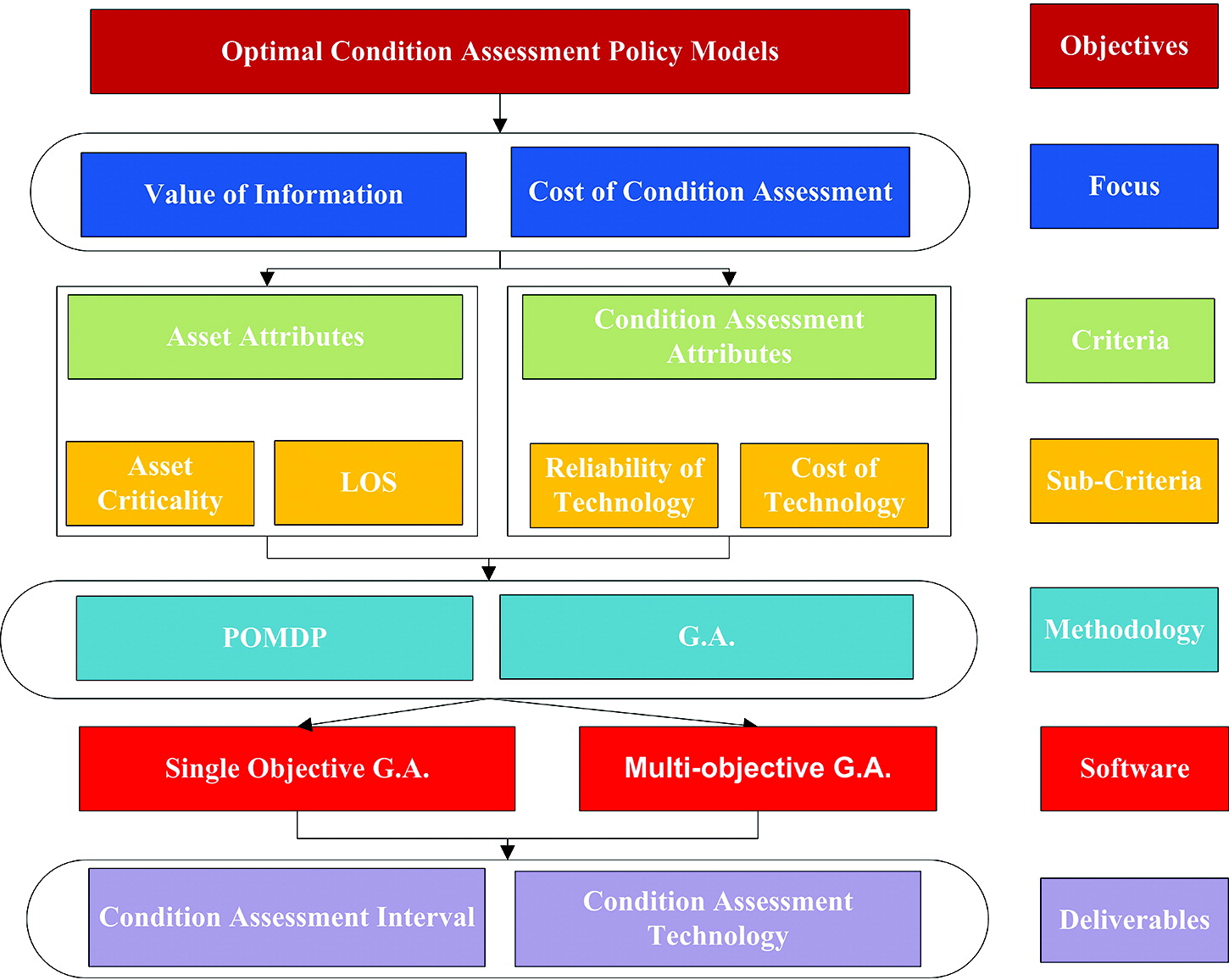
This paper presents a framework for optimizing condition assessment policies by balancing the revealed value of information with the cost of obtaining such information. The computational platform is based on augmenting the asset condition state with an expected level of accuracy. Inaccuracies due to condition assessment reliability are evaluated using the partially observable Markov decision process. The single objective genetic algorithm is used to select the most cost-effective assets to assess considering information inaccuracy under a fixed budget. The model is extended using
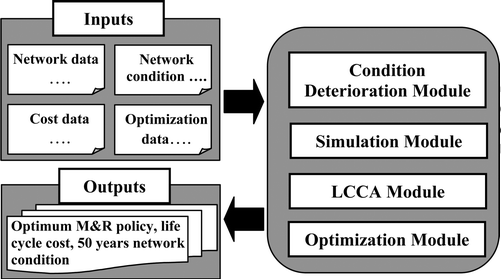
Towards optimum condition assessment policies for water and sewer networks
With ageing water and sewer infrastructure in North America, assessing the condition of these assets has received increased attention in the past few years. Condition assessment is an integral component in any asset management program. Determining the condition of buried infrastructure tends to be more cumbersome, costly and error-prone compared to other surface infrastructure like roads and buildings. For sewers, CCTV is considered the industry standard for condition assessment technologies. For pressurized water pipelines, technologies tend to be more costly and uncertain (e.g
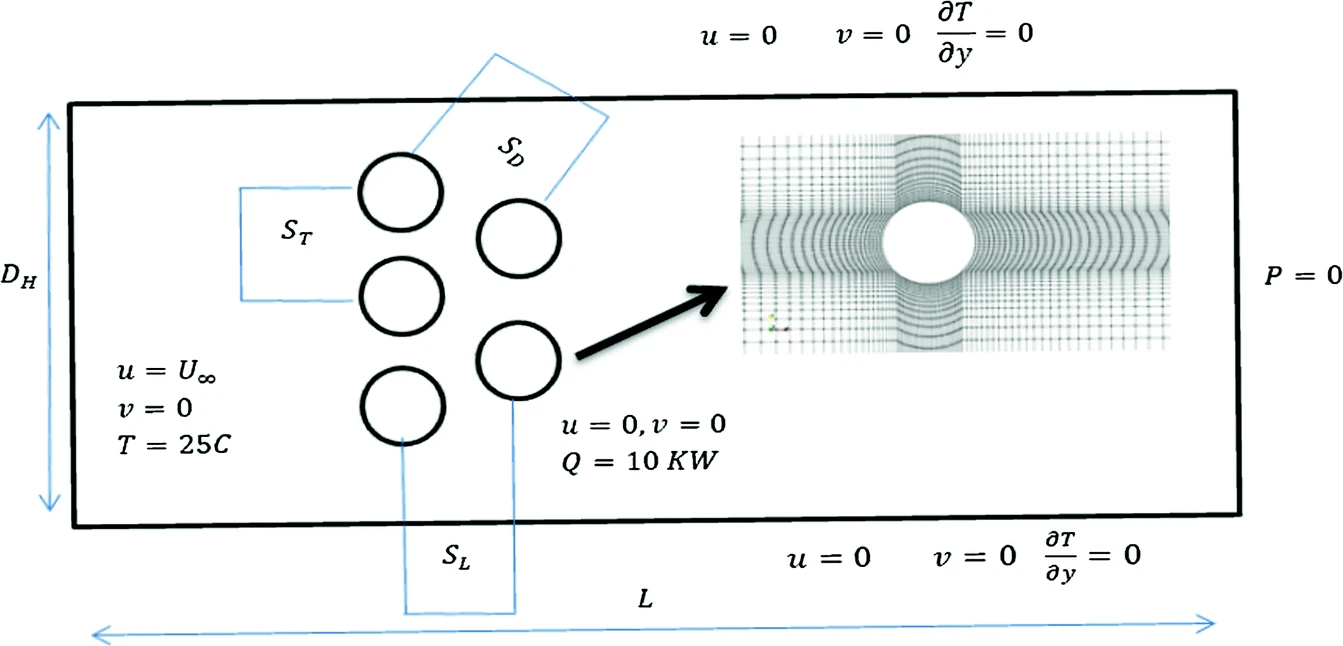
Tuning of PID Controller Using Particle Swarm Optimization for Cross Flow Heat Exchanger Based on CFD System Identification
This paper illustrates the design of proportional–integral–derivative controller (PID) controller of 10 KW air heaters for achieving the set point temperature as fast as possible with minimum response overshoot. Computational fluid dynamic (CFD) numerical simulations are utilized to predict the natural response of 10 KW input power for the air heater. CFD results are validated with experimental empirical correlations that insure the reliability of open loop results. The open loop response of CFD transient simulations is used to model the air heater transfer function and design the classical
Tandem Organic Solar Cell Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology
Organic solar cells have many advantages such as their ease of manufacturing, flexibility, and low cost compared to perovskite and silicon solar cells. However, increasing their power conversion efficiency (PCE) is still challenging. In this paper, response surface methodology of design of experiments (DOE) is used to optimize the PCE of a tandem organic solar cell. The cell is based on boron sub-phthalocyanine to reduce the series resistance between the layers. The optimization process is performed by formulating an empirical polynomial regression model relating the PCE to the active layers'
The effect of the geometric and thermal parameters on the thermal stresses during the passive cooling of printed circuit boards
The effect of components' thermal properties in addition to their geometric configuration on the developed thermal stress in a model printed circuit board (PCB) is investigated. This effect is quantified through three parameters, the average normalized temperature gradient, maximum normalized temperature gradient and the uniformity factor. It is found that the effect of the geometric configuration, especially that of the heat-generating component, is more significant than the thermal properties of the components. © 2019 IEEE.
Interfacial modification of perovskite solar cell using zno electron injection layer with pdms as antireflective coating
Recently, perovskite solar cells (PSCs) exhibits tremendous power conversion efficiency and has shown enhanced figures of merit being secured regarding cell stability. In this paper, perovskite solar cell with Zno electron injection layer is presented. The humidity degradation of the perovskite active layer and the efficiency of the cell is observed under several conditions. Using ZnO as a planner electron injection layer (EIL) instead of TiO2, the efficiency of the device significantly improved, showing low-resistance shunting pathways. Also, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) has been used as a
Temperature-aware adaptive task-mapping targeting uniform thermal distribution in MPSoC platforms
As on-chip integration increases, the thermal distribution becomes spatially non-uniform and varies based on the power dissipation. In this paper, we introduce a temperature-aware task-mapping algorithm to prevent hotspots and achieve a highly uniform thermal distribution using adaptive multi-threshold values. The algorithm monitors the temperature of the cores, swaps tasks when the temperature of the core is relatively higher than the average temperature of the chip. Cores are switched off if they exceed an absolute maximum temperature. Using this algorithm, reliability is enhanced by
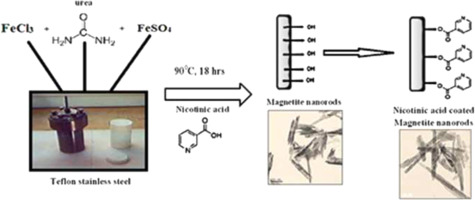
Synthesis of non-aggregated nicotinic acid coated magnetite nanorods via hydrothermal technique
Non-aggregated magnetite nanorods with average diameters of 20-30 nm and lengths of up to 350 nm were synthesized via in situ, template free hydrothermal technique. These nanorods capped with different concentrations (1, 1.5, 2 and 2.5 g) of nicotinic acid (vitamin B3); possessed good magnetic properties and easy dispersion in aqueous solutions. Our new synthesis technique maintained the uniform shape of the nanorods even with increasing the coating material concentration. The effect of nicotinic acid on the shape, particle size, chemical structure and magnetic properties of the prepared
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 10
- Next page ››
