Optimum Scheduling of the Disinfection Process for COVID-19 in Public Places with a Case Study from Egypt, a Novel Discrete Binary Gaining-Sharing Knowledge-Based Metaheuristic Algorithm
The aim of this paper is to introduce an improved strategy for controlling COVID-19 and other pandemic episodes as an environmental disinfection culture for public places. The scheduling aims at achieving the best utilization of the available working day-time hours, which is calculated as the total consumed disinfection times minus the total loosed transportation times. The proposed problem in network optimization identifies a disinfection group who is likely to select a route to reach a subset of predetermined public places to be regularly disinfected with the most utilization of the
Regression Modeling for the Ventilation Effect on COVID-19 Spreading in Metro Wagons
The effect of different ventilation parameters on the infection potential of COVID-19 in a metro wagon is numerically studied. Two key indicators are used to quantify this potential. Based on the numerical results a regression analysis is performed to come up with the most suitable regression model for these key parameters. The proposed regression models are helpful in quantifying the infection risk at different ventilation scenarios. © 2021 IEEE.
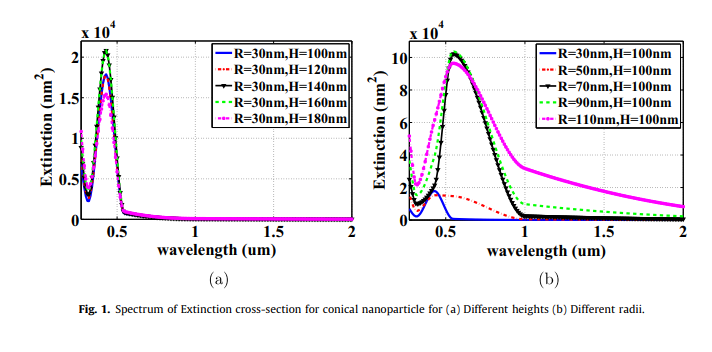
J-V characteristics of plasmonic photovoltaics with embedded conical and cylindrical metallic nanoparticles
Plasmonic photovoltaics (PVs) are promising structures that improve thin-film photovoltaics performance, where optical absorption is improved via embedding metallic nanoparticles in the PV's active layer to trap the incident optical wave into the photovoltaic cell. The presented work investigates the design of PV with both structures of conical and cylindrical metallic nanoparticles through studying their extinction cross-sections and electric field distributions. Also, the impact of these nanoparticles in silicon PVs on the optical absorption enhancement is investigated. The figure of merit
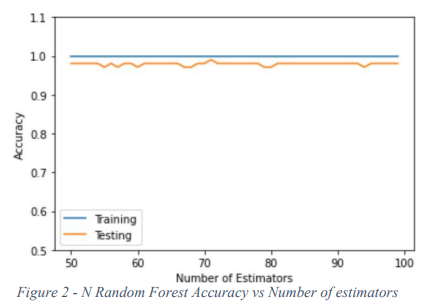
Diabetes Prediction Using Machine Learning: A Comparative Study
Diabetes is a common, metabolic disease, that results in a high level of blood sugar. Patients diagnosed with diabetes suffer from a body that cannot effectively use the insulin or cannot produce a sufficient amount of insulin. Providing a method of detection via symptoms that can be noticed by the patient can prompt the patient to seek medical assistance more promptly and in turn to be correctly diagnosed and treated. This paper proposed a solution for the problem using machine learning techniques. We applied eight algorithms on a data set of 521 subjects. The results are compared to each
CFD analysis of transient blood flow in a cerebral aneurysm: A comparison between a healthy and diseased model
The unsteady flow field variations between healthy and diseased three-dimensional rigid posterior cerebral artery are numerically investigated. The Computational hemodynamic simulations have been known to provide valuable clinical information to researchers and surgeons that proved to be crucial for the assessment of medical risks, pre-surgical conditioning and treatment planning. The wall shear stress (WSS) and wall pressure are the most important hemodynamic variables, and both are used to give accurate description about the health status of the artery. The results showed that at the
Numerical investigation of hematocrit variation effect on blood flow in an arterial segment with variable stenosis degree
Numerical simulations of blood flow in arteries are important in the understanding and diagnosis of many cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis and arterial stenosis. More realistic mathematical models representing blood rheology offer a better understanding of these diseases. In this study, blood is considered an Oldroyd-B fluid with a shear-thinning property and a shear rate-dependent relaxation time that is adopted by fitting experimental data. The Quemada model is used to represent the shear-thinning property with hematocrit variation. The stabilized finite element method is used
Further experimental evidence of the fractional-order energy equation in supercapacitors
Due to the dispersive porous nature of its material, carbon–carbon supercapacitors have a current–voltage relationship which is modeled by a fractional-order differential equation of the form i(t)=Cα[Formula presented] where α≤1 is a dispersion coefficient and Cα is a pseudo-capacitance not measurable in Farads. Hence, the energy stored in a capacitor, known to equal CV2/2 where C is the capacitance in Farad and V is the voltage applied, does not apply to a supercapacitor. In a recent work (Allagui et al., 2016), a fractional-order energy equation that enables the quantification of the energy
Fuzzy firefly clustering for tumour and cancer analysis
Swarm intelligence represents a meta-heuristic approach to solve a wide variety of problems. Searching for similar patterns of genes is becoming very essential to predict the expression of genes under various conditions. Firefly clustering inspired by the behaviour of fireflies helps in grouping genes that behave alike. Contrasting hard clustering methodology, fuzzy clustering assigns membership values for every gene and predicts the possibility of belonging to every cluster. To distinguish highly expressed and suppressed genes, the research in this paper proposes an efficient fuzzy-firefly
Fractional-order mathematical model for Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia
This paper is dedicated to develop a fractional order model of the rate of change of cancerous blood cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia using fractional-order differential equations as well as tackling the factors that affect this rate and compare between them. The simulated cases (using MATLAB) prove that the proposed model is doable in terms of the variables positions in the equations and its effect on the overall population. Also, the effect of the Pactional order is investigated through three parameters sets and it has shown strong influence on the dynamic response. © 2017 IEEE.
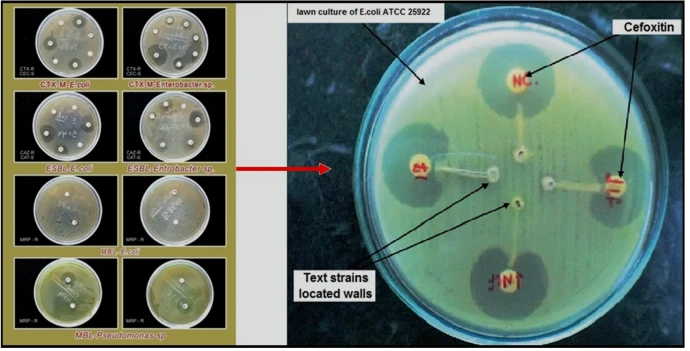
Molecular identification of extended spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs)-producing strains in clinical specimens from Tiruchirappalli, India
Worldwide, the phenomenal antimicrobial resistance with its consequences of fatal diseases has been alerted; it is because the morbidity and mortality at a shocking rate. Therefore, there is an urgent quest of innovative antimicrobials agents; it is that communicable disease is a worldwide trouble as of the growth and wideness of drug-resistant pathogens. As for the aim of the research, it is widely investigative to the prevalence of Gram-negative pathogens of E. coli and K. pneumoniae in different age groups, gender along with the identification of ESBL-producing pathogens and antimicrobial
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 13
- Next page ››
