Nanomaterial-based drug delivery systems as promising carriers for patients with COVID-19
Once the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the COVID-19 outbreak to be pandemic, massive efforts have been launched by researchers around the globe to combat this emerging infectious disease. Here we review the most recent data on the novel SARS-CoV-2 pathogen. We analyzed its etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, prevention, and current medications. After that, we summarized the promising drug delivery application of nanomaterial-based systems. Their preparation routes, unique advantages over the traditional drug delivery routes and their toxicity though risk analysis were also covered
An eco-concerned development of a fast, precise and economical spectrophotometric assay for the antiviral drug simeprevir based on ion-pair formation
Simeprevir sodium (SMV) is one of the antiviral drugs used for the treatment of virus C. The current strategy develops and validates a new eco-concerned tool for its quantification in the pure and pharmaceutical formulations. Sulfonephthalein acid dyes were used for this purpose, applying visible analyses based on ion-pair formation. A linear relation between the absorbed signal and the drug concentration is obtained up to 67.0 μg mL-1 with r2 of 0.9989-0.9999. The measurement is carried out at 410, 415, 410, and 403 nm for bromocresol green, bromoxelenol blue, bromothymol blue, and
Study of Energy Harvesters for Wearable Devices
Energy harvesting was and still an important point of research. Batteries have been utilized for a long time, but they are now not compatible with the downsizing of technology. Also, their need to be recharged and changed periodically is not very desirable, therefore over the years energy harvesting from the environment and the human body have been investigated. Three energy harvesting methods which are the Piezoelectric energy harvesters, the Enzymatic Biofuel cells, and Triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) are being discussed in the paper. Although Biofuel cells have been investigated for a
FPGA Realizations of Chaotic Epidemic and Disease Models including Covid-19
The spread of epidemics and diseases is known to exhibit chaotic dynamics; a fact confirmed by many developed mathematical models. However, to the best of our knowledge, no attempt to realize any of these chaotic models in analog or digital electronic form has been reported in the literature. In this work, we report on the efficient FPGA implementations of three different virus spreading models and one disease progress model. In particular, the Ebola, Influenza, and COVID-19 virus spreading models in addition to a Cancer disease progress model are first numerically analyzed for parameter
Implementation of a Pulsed-Wave Spectral Doppler Module on a Programmable Ultrasound System
Pulsed wave Doppler ultrasound is commonly used in the diagnosis of cardiovascular and blood flow abnormalities. Doppler techniques have gained clinical significance due to its safety, real-time performance and affordability. This work presents the development of a pulsed wave spectral Doppler module, which was integrated into a reconfigurable ultrasound system. The targeted system adopts a hardware-software partitioning scheme where an FPGA handles the front-end and a PC performs the back-end. Two factors were considered during the design. First, the data transfer rate between hardware and
Fractional-order bio-impedance modeling for interdisciplinary applications: A review
Bio-impedance circuit modeling is a popular and effective non-invasive technique used in medicine and biology to fit the measured spectral impedance data of living or non-living tissues. The variations in impedance magnitude and/or phase at different frequencies reflect implicit biophysical and biochemical changes. Bio-impedance is also used for sensing environmental changes and its use in the agriculture industry is rapidly increasing. In this paper, we review and compare among the fractional-order circuit models that best fit bio-impedance data and the different methods for identifying the
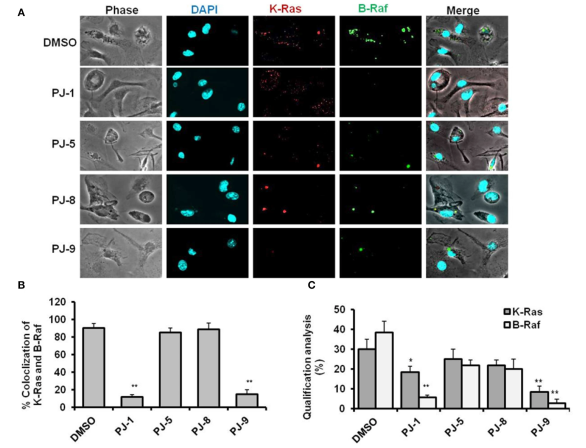
Selective Regulation of B-Raf Dependent K-Ras/Mitogen-Activated Protein by Natural Occurring Multi-kinase Inhibitors in Cancer Cells
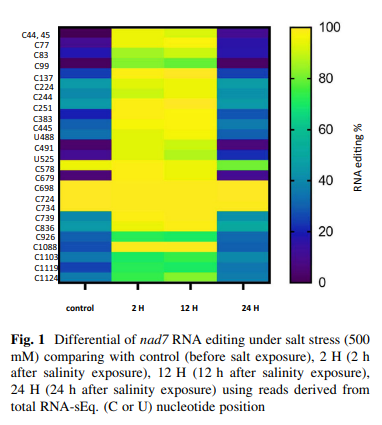
Salinity stress reveals three types of RNA editing sites in mitochondrial Nad7 gene of wild barley both in silico and in qRT-PCR experiments
Cellular respiration is an important process performed by mitochondria. Nad complex is the major complex involved in this process and one of the main subunits in this complex is the nad7 (nad dehydrogenase subunit 7). In Hordeum vulgare subsp. spontaneum, four nad7 cDNAs are described at 500 mM salinity, 0 h, or control (GenBank accession no. MW433884), after 2 h (GenBank accession no. MW433885), after 12 h (GenBank accession no. MW433886) and after 24 h (GenBank accession no. MW433887). Twenty six RNA editing sites were revealed in positions: C44, C45, C77, C83, C99, C137, C224, C244, C251
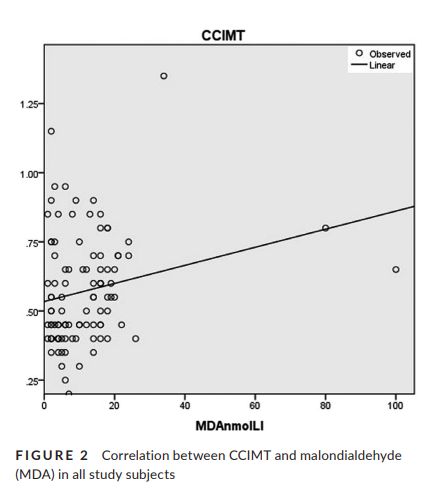
Support for increased cardiovascular risk in non-segmental vitiligo among Egyptians: A hospital-based, case–control study
Background: Data have been accumulating in the past few years that identify vitiligo as a disorder with systemic implications. Results and methods: In this hospital-based, cross-sectional, case–control study, 50 patients with non-segmental vitiligo and 50 age- and sex-matched controls underwent analysis of serum lipid profile, oxidative stress biomarkers and carotid duplex. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were significantly higher in patients than controls (p-value <.001, <.001, respectively); on the other hand, total antioxidant capacity (TAC) was significantly lower in
Association between long noncoding RNA taurine-upregulated gene 1 and microRNA-377 in vitiligo
Background: Taurine-upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) is one of the long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) that plays a role in melanogenesis. MicroRNA-377 (miRNA-377) is a conserved noncoding RNA that regulates angiogenesis and promotes oxidative stress. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) are components of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily. PPAR-γ activators stimulate melanogenesis. Interleukin (IL)-17 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of several immunological diseases. This work aimed at detecting the expression levels of lncRNA TUG1, miRNA-377, PPAR-γ, and IL-17 among vitiligo
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 18
- Next page ››
