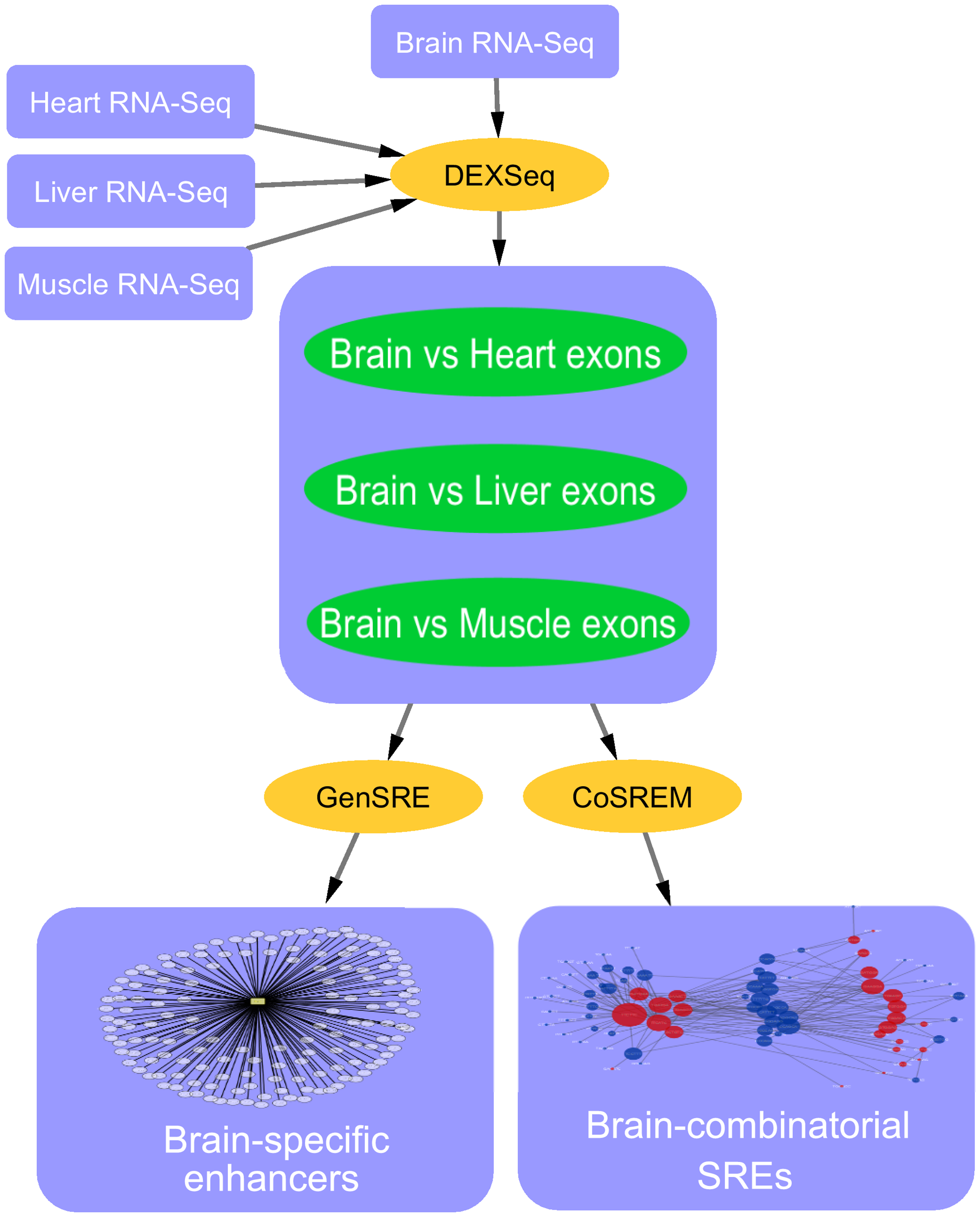
Computational identification of tissue-specific splicing regulatory elements in human genes from RNA-Seq Data
Alternative splicing is a vital process for regulating gene expression and promoting proteomic diversity. It plays a key role in tissue-specific expressed genes. This specificity is mainly regulated by splicing factors that bind to specific sequences called splicing regulatory elements (SREs). Here, we report a genome-wide analysis to study alternative splicing on multiple tissues, including brain, heart, liver, and muscle. We propose a pipeline to identify differential exons across tissues and hence tissue-specific SREs. In our pipeline, we utilize the DEXSeq package along with our previously
Convolutional neural networks for deep feature learning in retinal vessel segmentation
Analysis of retinal vessels in fundus images provides a valuable tool for characterizing many retinal and systemic diseases. Accurate automatic segmentation of these vessels is usually required as an essential analysis step. In this work, we propose a new formulation of deep Convolutional Neural Networks that allows simple and accurate segmentation of the retinal vessels. A major modification in this work is to reduce the intra-class variance by formulating the problem as a Three-class problem that differentiates: large vessels, small vessels, and background areas. In addition, different sizes
Classification of Thyroid Carcinoma in Whole Slide Images Using Cascaded CNN
The objective of this research is to build a 'Whole Slide Images' classification system using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). This system is capable of classifying Thyroid tumors into three types: Follicular adenoma, follicular carcinoma, and papillary carcinoma. Furthermore, the cascaded CNN technique is additionally employed to classify the classified follicular carcinoma into four subclasses: follicular carcinoma, papillary follicular variant, well-differentiated follicular carcinoma, and Poorly-differentiated follicular carcinoma. Results of the proposed CNN architecture showed
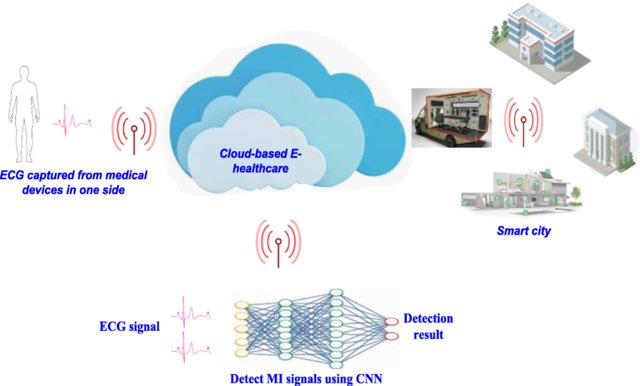
Detection of myocardial infarction based on novel deep transfer learning methods for urban healthcare in smart cities
One of the common cardiac disorders is a cardiac attack called Myocardial infarction (MI), which occurs due to the blockage of one or more coronary arteries. Timely treatment of MI is important and slight delay results in severe consequences. Electrocardiogram (ECG) is the main diagnostic tool to monitor and reveal the MI signals. The complex nature of MI signals along with noise poses challenges to doctors for accurate and quick diagnosis. Manually studying large amounts of ECG data can be tedious and time-consuming. Therefore, there is a need for methods to automatically analyze the ECG data
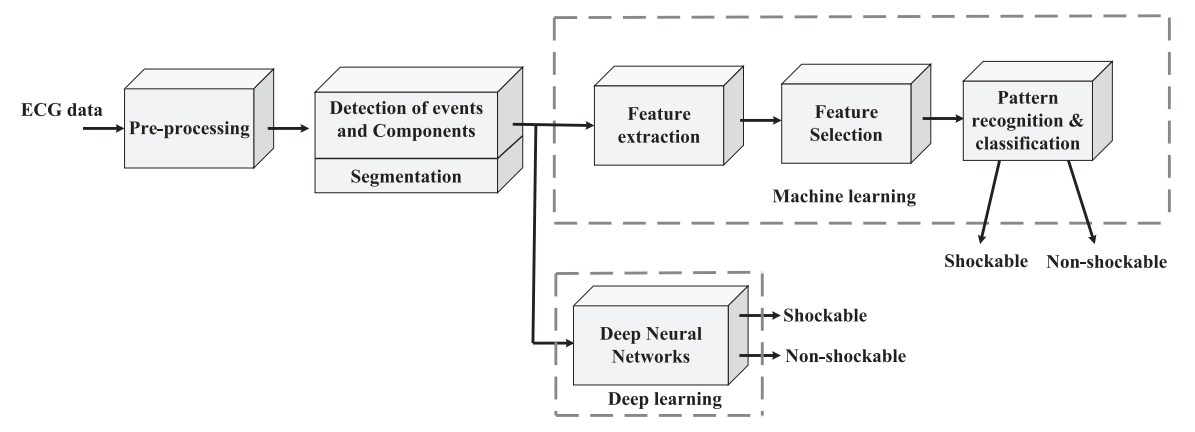
Automated detection of shockable ECG signals: A review
Sudden cardiac death from lethal arrhythmia is a preventable cause of death. Ventricular fibrillation and tachycardia are shockable electrocardiographic (ECG)rhythms that can respond to emergency electrical shock therapy and revert to normal sinus rhythm if diagnosed early upon cardiac arrest with the restoration of adequate cardiac pump function. However, manual inspection of ECG signals is a difficult task in the acute setting. Thus, computer-aided arrhythmia classification (CAAC) systems have been developed to detect shockable ECG rhythm. Traditional machine learning and deep learning

Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics): Preface
[No abstract available]

Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics): Preface
[No abstract available]
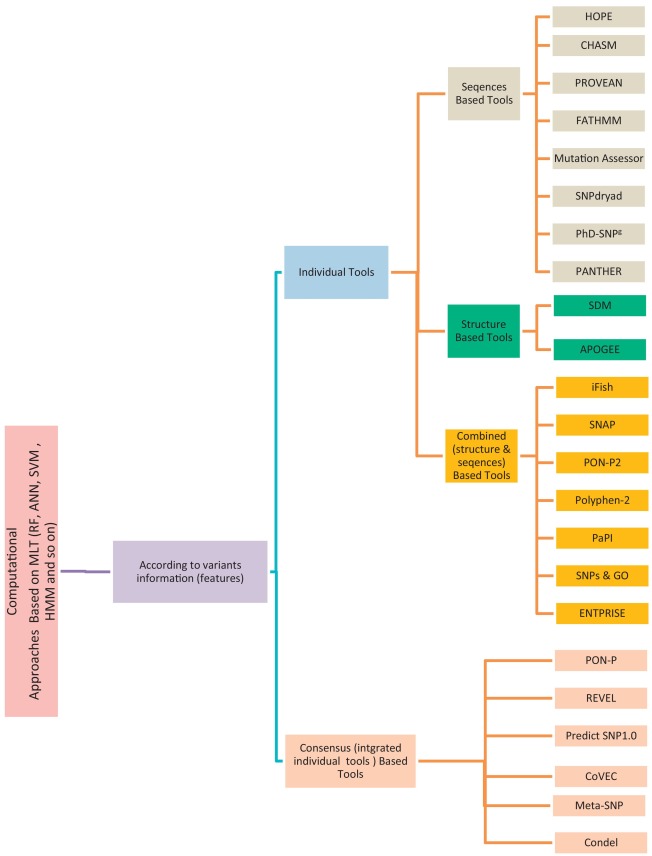
A review study: Computational techniques for expecting the impact of non-synonymous single nucleotide variants in human diseases
Non-Synonymous Single-Nucleotide Variants (nsSNVs) and mutations can create a diversity effect on proteins as changing genotype and phenotype, which interrupts its stability. The alterations in the protein stability may cause diseases like cancer. Discovering of nsSNVs and mutations can be a useful tool for diagnosing the disease at a beginning stage. Many studies introduced the various predicting singular and consensus tools that based on different Machine Learning Techniques (MLTs) using diverse datasets. Therefore, we introduce the current comprehensive review of the most popular and recent
Towards scalable and cost-aware bioinformatics workflow execution in the cloud - Recent advances to the tavaxy workflow system
Cloud-based scientific workflow systems can play an important role in the development of cost effective bioinformatics analysis applications. So far, most efforts for supporting cloud computing in such workflow systems have focused on simply porting them to the cloud environment. The next due steps are to optimize these systems to exploit the advantages of the cloud computing model, basically in terms of managing resource elasticity and the associated business model. In this paper, we introduce new advancements in designing scalable and cost-effective workflows in the cloud using the Tavaxy
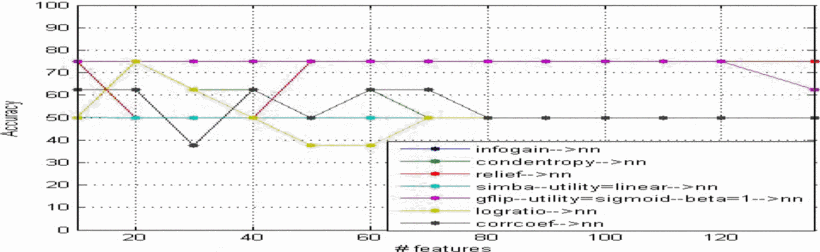
Feature selection in computer aided diagnostic system for microcalcification detection in digital mammograms
In this paper an approach is proposed to develop a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system that can be very helpful for radiologist in diagnosing microcalcifications' patterns in digitized mammograms earlier and faster than typical screening programs and showed the efficiency of feature selection on the CAD system. The proposed method has been implemented in four stages: (a) the region of interest (ROI) selection of 32x32 pixels size which identifies clusters of microcalcifications, (b) the feature extraction stage is based on the wavelet decomposition of locally processed image (region of
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 9
- Next page ››
