
Multi-view human action recognition system employing 2DPCA
A novel algorithm for view-invariant human action recognition is presented. This approach is based on Two-Dimensional Principal Component Analysis (2DPCA) applied directly on the Motion Energy Image (MEI) or the Motion History Image (MHI) in both the spatial domain and the transform domain. This method reduces the computational complexity by a factor of at least 66, achieving the highest recognition accuracy per camera, while maintaining minimum storage requirements, compared with the most recent reports in the field. Experimental results performed on the Weizmann action and the INIRIA IXMAS
Multiplicity per rapidity in Carruthers and hadron resonance gas approaches
The multiplicity per rapidity of the well-identified particles π-, π+, k-, k+, p¯ , p, and p- p¯ measured in different high-energy experiments, at energies ranging from 6.3 to 5500 GeV, is successfully compared with the Cosmic Ray Monte Carlo event generator. For these rapidity distributions, we introduce a theoretical approach based on fluctuations and correlations (Carruthers approach) and another one based on statistical thermal assumptions (hadron resonance gas approach). Both approaches are fitted to both sets of results deduced from experiments and simulations. We found that the
In silico identification of potential key regulatory factors in smoking-induced lung cancer
Background: Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide and is the most commonly diagnosed cancer. Like other cancers, it is a complex and highly heterogeneous disease involving multiple signaling pathways. Identifying potential therapeutic targets is critical for the development of effective treatment strategies. Methods: We used a systems biology approach to identify potential key regulatory factors in smoking-induced lung cancer. We first identified genes that were differentially expressed between smokers with normal lungs and those with cancerous lungs, then integrated

Labour productivity in building construction: A field study
This paper describes a field study conducted over a period of 11-months on labour productivity observed during the construction of a new university campus in Cairo, Egypt. The campus is being built on 127 acres and the field study was conducted during the construction of two main buildings; each of 20,000 m 2 built up area. The study utilized work sampling (WS), craftsman questionnaire (CQ), and foreman delay survey (FDS) methods to analyze labour productivity of three indicative and labour-intensive trades, namely formwork, masonry work, and HVAC duct installation. The results were also
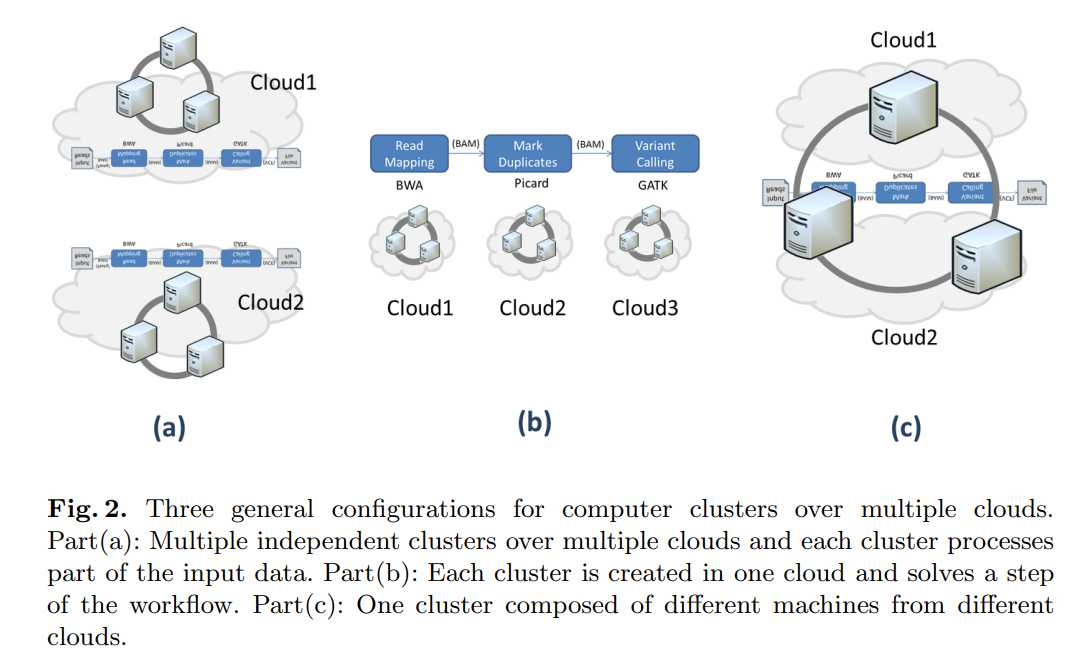
Supporting bioinformatics applications with hybrid multi-cloud services
Cloud computing provides a promising solution to the big data problem associated with next generation sequencing applications. The increasing number of cloud service providers, who compete in terms of performance and price, is a clear indication of a growing market with high demand. However, current cloud computing based applications in bioinformatics do not profit from this progress, because they are still limited to just one cloud service provider. In this paper, we present different use case scenarios using hybrid services and resources from multiple cloud providers for bioinformatics
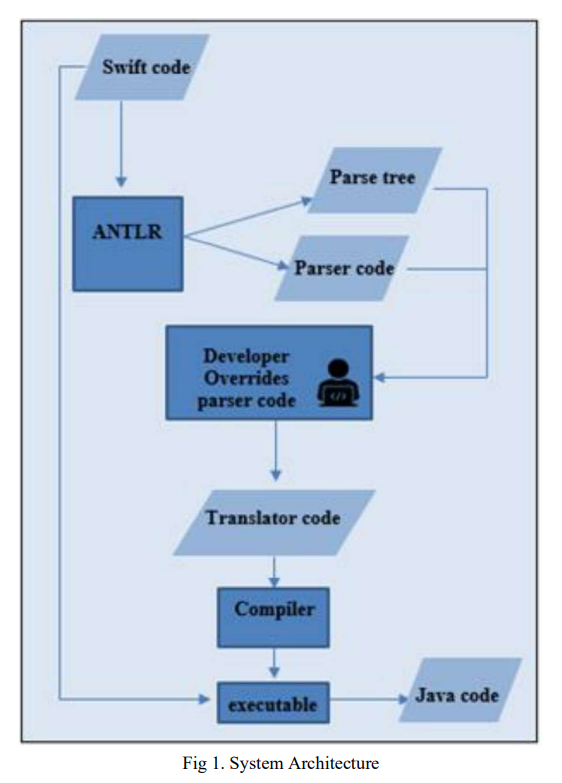
Trans-Compiler based Mobile Applications code converter: Swift to java
Numerous commercial tools like Xamarin, React Native and PhoneGap utilize the concept of cross-platform mobile applications development that builds applications once and runs it everywhere opposed to native mobile app development that writes in a specific programming language for every platform. These commercial tools are not very efficient for native developers as mobile applications must be written in specific language and they need the usage of specific frameworks. In this paper, a suggested approach in TCAIOSC tool to convert mobile applications from Android to iOS is used to develop the
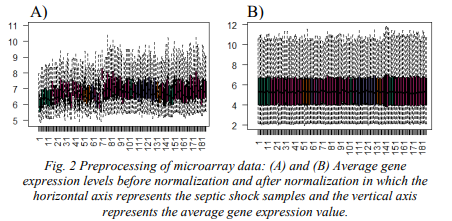
Studying Genes Related to the Survival Rate of Pediatric Septic Shock
Pediatric septic shock is generally considered as a devastating clinical syndrome that can lead to tissue damage and organ failure due to the over exaggerated immune response to an infection. Therefore, in this paper, we attempted to early identify the clinical course of such disease with the aid of peripheral blood T-cells of 181 pediatric patients who admitted to Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Accordingly, 34 differential expressed genes have been identified as biological genetic biomarkers. Minimum redundancy and maximum relevance feature selection strategy has been proposed for the discovery
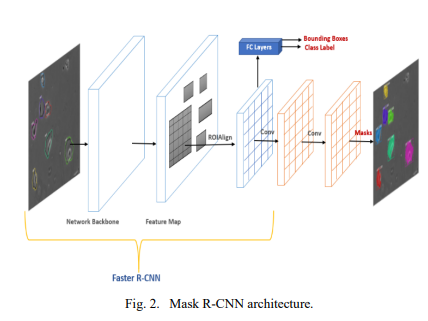
Instance Segmentation of 2D Label-Free Microscopic Images using Deep Learning
The precise detection and segmentation of cells in microscopic image sequences is an essential task in biomedical research, such as drug discovery and studying the development of tissues, organs, or entire organisms. However, the detection and segmentation of cells in phase contrast images with a halo and shade-off effects is still challenging. Lately, Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask R-CNN) has been introduced for object detection and instance segmentation of natural images. This study investigates the efficacy of the Mask R-CNN to instantly detect and segment label-free
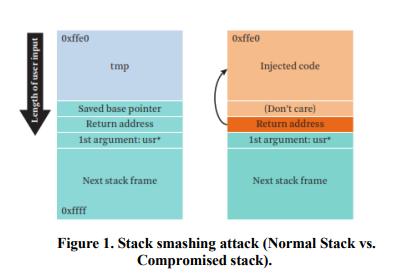
Survey of Code Reuse Attacks and Comparison of Mitigation Techniques
Code-Reuse Attacks (CRAs) are solid mechanisms to bypass advanced software and hardware defenses. Due to vulnerabilities found in software which allows attackers to corrupt the memory space of the vulnerable software to modify maliciously the contents of the memory; hence controlling the software to be able to run arbitrary code. The CRAs defenses either prevents the attacker from reading program code, controlling program memory space directly or indirectly through the usage of pointers. This paper provides a thorough evaluation of the current mitigation techniques against CRAs with regards to
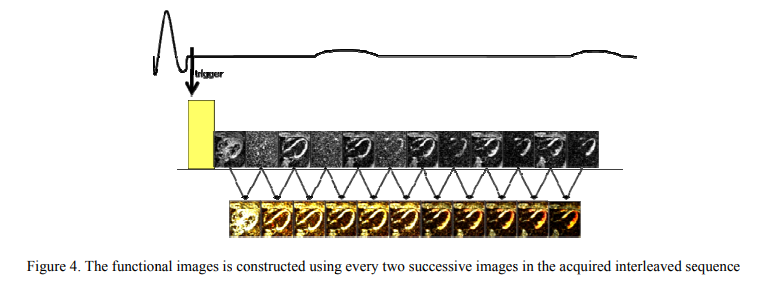
Strain correction in interleaved strain-encoded (SENC) cardiac MR
The strain encoding (SENC) technique directly encodes regional strain of the heart into the acquired MR images and produces two images with two different tunings so that longitudinal strain, on the short-axis view, or circumferential strain on the long-axis view, are measured. Interleaving acquisition is used to shorten the acquisition time of the two tuned images by 50%, but it suffers from errors in the strain calculations due to inter-tunings motion of the heart. In this work, we propose a method to correct for the inter-tunings motion by estimating the motion-induced shift in the spatial
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 3
- Next page ››
