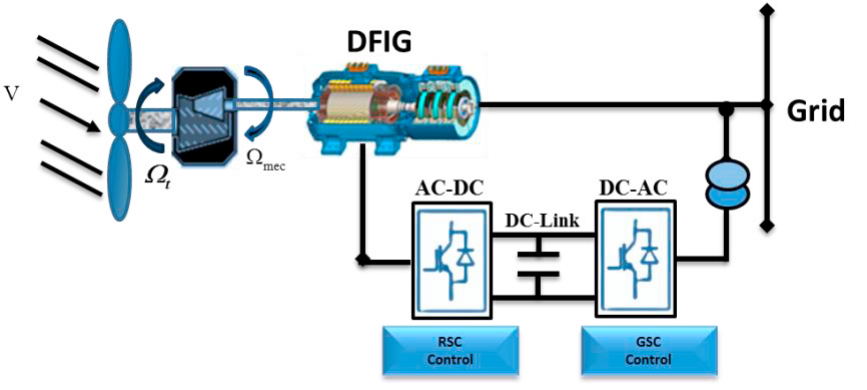
Sensor Faults Detection and Estimation for a Dfig Equipped Wind Turbine
Doubly Fed Induction Generator (DFIG) based on wind turbines demand a high degree of reliability and availability and they are characterized by expensive and safety critical maintenance work. This paper deals with a new strategy for detection and estimation of current sensor faults in the stator and rotor of a DFIG. First, a state space model of a DFIG is developed based on voltages and flux equations, which can be used in order to estimate states and to generate residuals by using a Luenberger observer. Then, the residuals results are exploited for faults detection and estimation. Finally
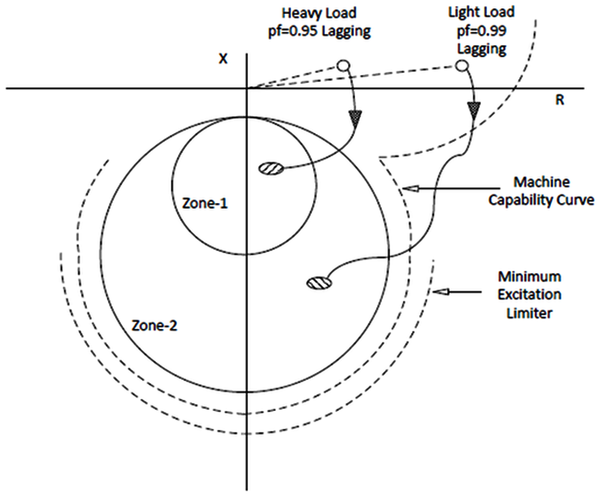
Advances in system dynamics and control
Complex systems are pervasive in many areas of science. With the increasing requirement for high levels of system performance, complex systems has become an important area of research due to its role in many industries. Advances in System Dynamics and Control provides emerging research on the applications in the field of control and analysis for complex systems, with a special emphasis on how to solve various control design and observer design problems, nonlinear systems, interconnected systems, and singular systems. Featuring coverage on a broad range of topics, such as adaptive control
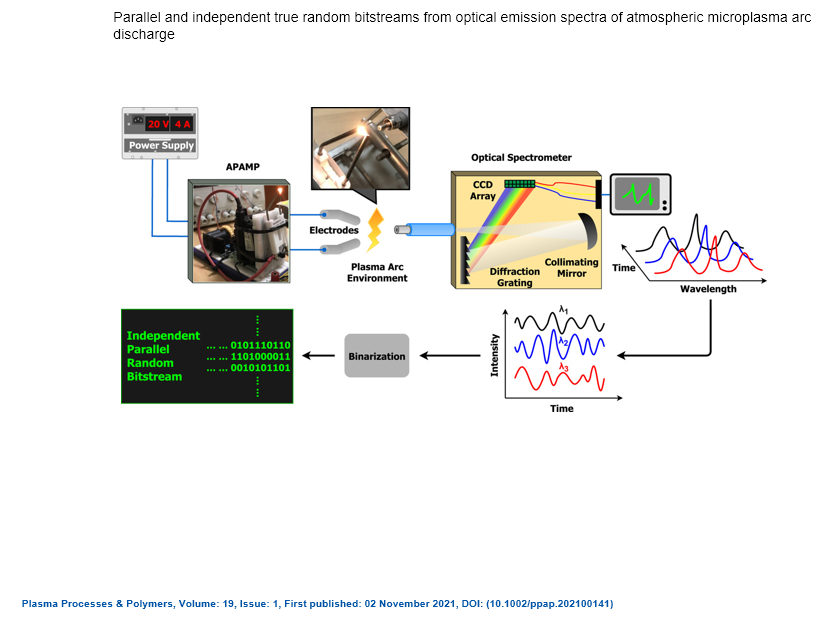
Parallel and independent true random bitstreams from optical emission spectra of atmospheric microplasma arc discharge
In this study, we propose the possibility of generating several parallel and independent random bitstreams from the time-varying optical emission spectra of an atmospheric pressure air microplasma system. This is achieved by splitting the plasma arc emission into discrete wavelengths using an optical spectrometer and then monitoring the fluctuating intensities of each wavelength as an independent time series. As a proof of concept, we considered eight wavelengths centered at 377.8, 389.1, 425.8, 591.4, 630.5, 673.0, 714.2, and 776.4 nm corresponding to atomic emissions lines from species
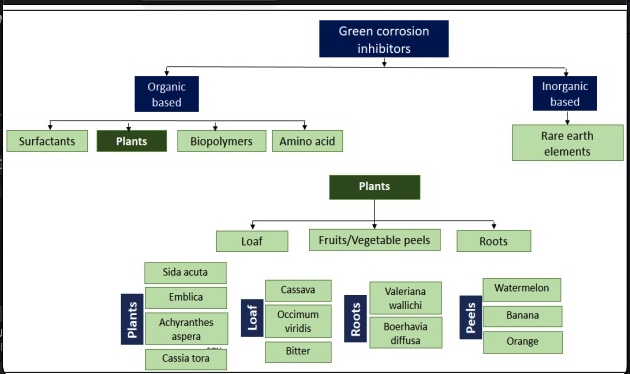
A critical review on green corrosion inhibitors based on plant extracts: Advances and potential presence in the market
Corrosion occurs in all sectors including oil pipelines, drinking water and sewerage in the majority of cases linked to corrosion of steel. Good corrosion management includes optimising corrosion control actions and minimising lifecycle corrosion costs whilst meeting environmental goals. The toxicity of commonly used synthetic inhibitors are the subject of recent legislations (REACH and PARCOM) have led to search on more eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors. Extensive research is conducted to assess the corrosion inhibition rate of diverse green inhibitors. However, it was not adequately
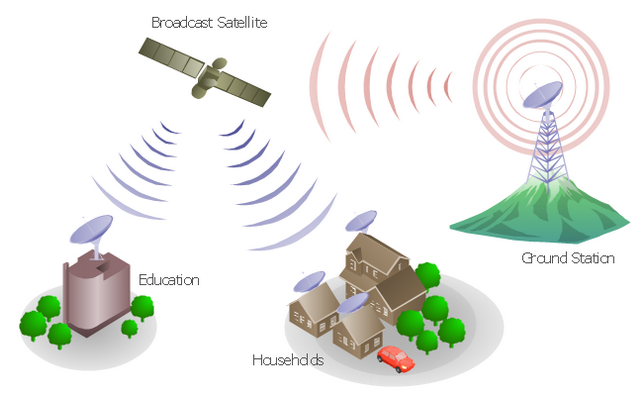
ITS navigation and live timetables for the blind based on RFID robotic localization algorithms and ZigBee broadcasting
This paper tries to alleviate some challenges facing blind and visually impaired people in public transportation systems by providing them with in-station navigation information and real-time schedule information. Novel system architecture for the Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) navigation for blind and visually impaired people based on recent Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) localization technologies, commonly used in robotics, is proposed. Furthermore, a live timetable using a new ZigBee network broadcasting protocol with detailed frame structure is used for provision of real
Real-time scale-adaptive compressive tracking using two classification stages
In this paper, we describe a method for Scale-Adaptive visual tracking using compressive sensing. Instead of using scale-invariant-features to estimate the object size every few frames, we use the compressed features at different scale then perform a second stage of classification to detect the best-fit scale. We describe the proposed mechanism of how we implement the Bayesian Classifier used in the algorithm and how to tune the classifier to address the scaling problem and the method of selecting the positive training samples and negative training samples of different scales. The obtained
Innovative human-robot interaction for a robot tutor in biology game
Robots nowadays, are introduced to many domains and fields. One of these fields is education. We introduce integrating robots and games in education. We have designed a humanoid robot tutoring biology. Our robot is interacting with a student to play a game to enhance and examine the student's knowledge. In our game, we developed cognitive capabilities for the robot. We analyzed the features that both the robot and the game have to possess, and we developed a system for organ detection and recognition with the highest possible accuracy and lowest processing time. Our game introduces a multi
In-silico development and assessment of a Kalman filter motor decoder for prosthetic hand control
Up to 50% of amputees abandon their prostheses, partly due to rapid degradation of the control systems, which require frequent recalibration. The goal of this study was to develop a Kalman filter-based approach to decoding motoneuron activity to identify movement kinematics and thereby provide stable, long-term, accurate, real-time decoding. The Kalman filter-based decoder was examined via biologically varied datasets generated from a high-fidelity computational model of the spinal motoneuron pool. The estimated movement kinematics controlled a simulated MuJoCo prosthetic hand. This clear-box
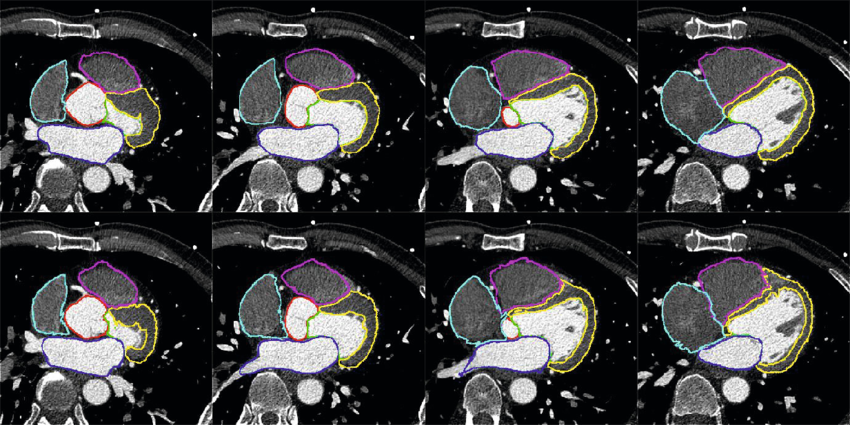
Myocardial segmentation using constrained multi-seeded region growing
Multi-slice short-axis acquisitions of the left ventricle are fundamental for estimating the volume and mass of the left ventricle in cardiac MRI scans. Manual segmentation of the myocardium in all time frames per each cross-section is a cumbersome task. Therefore, automatic myocardium segmentation methods are essential for cardiac functional analysis. Region growing has been proposed to segment the myocardium. Although the technique is simple and fast, non uniform intensity and low-contrast interfaces of the myocardium are major challenges of the technique that limit its use in myocardial
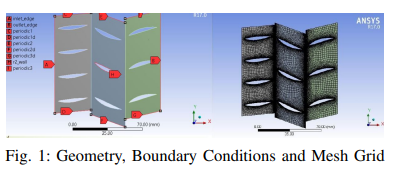
Optimized Preliminary Design of a Multistage Low-Speed Axial FLow Compressor
This paper proposes a technique based on a MAT-LAB code capable of getting an optimized preliminary design of an efficient low-speed compressor qualified for laboratory experiments with relatively low cost. The code was made to design five repeated compressor stages on two steps conducted iteratively, namely 'mean line and radial design' to determine the optimum compressor geometry and then the 'off-design' to test the stability of the design in other working conditions. The optimization tool minimizes a flexible cost function which can be changed if needed to get different designs. A certain
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
