Prediction of the Hitec Molten Salt Convective Heat Transfer Performance Using Artificial Neural Networks
Hitec molten salt is a ternary eutectic mixture salt that is used as an energy storage medium in concentrated solar power plants to improve the system performance and reduce the operational cost. Thus, the heat transfer performance represented in Nusselt number has been investigated numerically under different inlet temperature and velocity conditions with constant uniform side heat flux. Also, friction factor and mass flow rate are studied numerically. CFD input/output data with 40 studied cases are used as a training dataset of a 2-layer Neural Network for thermo-hydro fields’ accelerated
E-learning system model for university education using uml
High quality education should be the top priority for any nation seeking prosperity. This paper aims to present a conceptual model for e-learning system for developing countries. This is achieved adopting an object-oriented approach and Unified Modeling Language (UML). The functional and dynamic views of the system are presented and explained within this framework. The functional system includes Use Case diagrams and activity diagrams which are developed based on predefined functional requirements of the system. Furthermore, in the dynamic view of the system, interaction diagrams are developed
Effect of thickness and temperature on flexible organic P3HT:PCBM solar cell performance
A blend of poly 3-hexylthiophene (P3HT) and [6, 6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PCBM) is used as a photoactive layer for simulating a bulk heterojunction organic solar using general-purpose photovoltaic device model (GPVDM) software. The optical and electrical performance of the cell had been analyzed by changing the thickness of each layer and substrate material over a range of operating temperatures from -10 °C to - 40 °C. The flexible device exhibits higher PCE compared to a rigid device. The performance of the device was studied using transient simulation at different operating
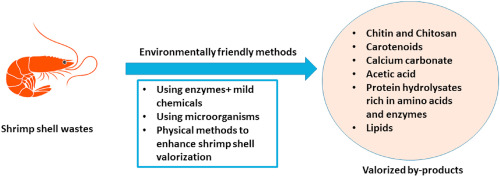
Enhancing barrier properties of chitosan extracted from shrimp shells as a sustainable material for active packaging using natural wastes
Due to the environmental concerns, much responsiveness has been paid to natural polymers and recycle wastes. Disposal of wastes like marine wastes and domestic wastes end up in landfills and open areas which cause environmental crisis. The development of biodegradable active packaging materials is one of the alternatives to reduce the using of synthetic petroleum-based plastics. Biodegradable films are made from biopolymers that were shown to have affinities in improving the shelf life of food product. © 2021 Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
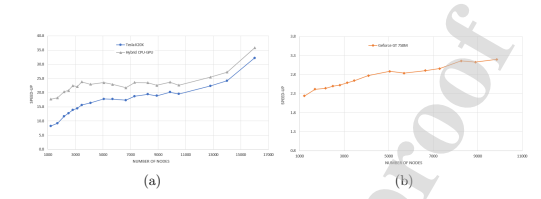
Stabilized variational formulation of an oldroyd-B fluid flow equations on a Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) architecture
The governing equations of the flow of an oldroyd-B fluid are discretized using the finite element method. To overcome the convective nature of the momentum equation, the Galerkin/Least-Squares Finite Element Method (GLS/FEM) is used while the Discrete Elastic–Viscous Stress-Splitting (DEVSS) method is used to overcome the instability due to the absence of diffusion in the constitutive equations. The discretized equations are implemented on a hybrid system between the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) architecture using Compute-Unified-Device-Architecture (CUDA) and a multi-core CPU. The
Efficient Finite Element Modeling of Complex HVAC Applications
A new Finite element model for HVAC applications is introduced. The model incorporates flow turbulence, buoyancy effects and unsteadiness. Also, the model accommodates complicated boundaries due to complex geometries and perforated tiles. Experimental validation is provided and extensive results for flow and temperature contours are presented. Temporal and spatial resolution prove that the model can capture important HVAC features as thermal comfort, buoyancy induced flow, complex boundaries. © 2020 IEEE.
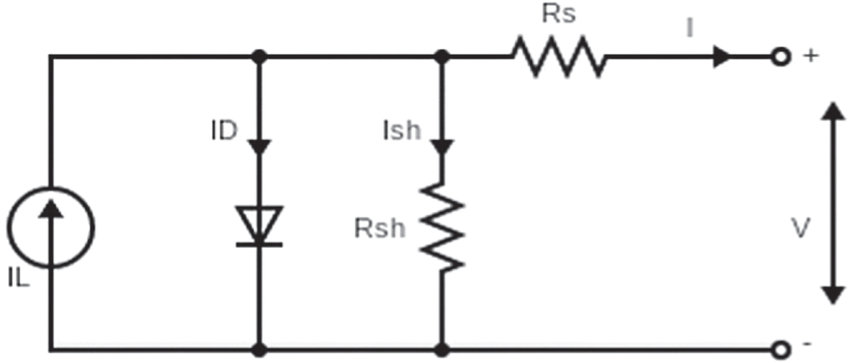
Comparative Study of Nusselt Number Correlations for Hitec Molten Salt
Molten salt has been realized as a potential candidate as a clean non-pollutant heat transfer fluid for concentrated solar power plants because of its high heat capacity and broad ranges of operational temperatures. In this study, the Nusselt number of the commercially known Hitec molten salt is numerically assessed, using k-ϵ model turbulence model with non-equilibrium wall functions, for the ranges of 104-105 Reynolds number and 104-105 W/m2 uniform surface heat flux. Moreover, the present work is compared against previously published work with success. The proposed numerical model provides
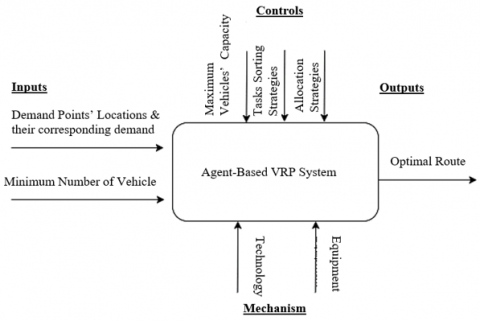
Modelling of agent-based vehicle routing problem using unified modelling language
The Vehicle Routing Problem (VRP) is among the most studied optimization problems in the field of supply chain management. Typically, VRP requires dispatching a fleet of vehicles from a central depot to deliver demand to pre-determined spatially dispersed customers, with the objective of minimizing the total routing cost, and the constraint of not exceeding vehicles' capacities. Agent Based Modelling (ABM) assists industries in the use of technology to support their decision-making process. This paper proposes a model of an Agent Based Vehicle Routing Problem System. The system under study is

Modelling of Crime Record Management System Using Unified Modeling Language
Crime records management is a system that helps police keep records of citizens’ complaints files, investigation evidence and processes. In addition, it helps police keep records of the criminals who have been arrested or who are to be arrested. This paper aims to model the Crime Record Management System (CRMS) using various Unified Modeling Language (UML) diagrams, to demonstrate an explicit visualization of the system. Also, showing the communication among different actors, and the sequence of activities and interactions. The perspective of modeling the CRMS is by covering four stages, which
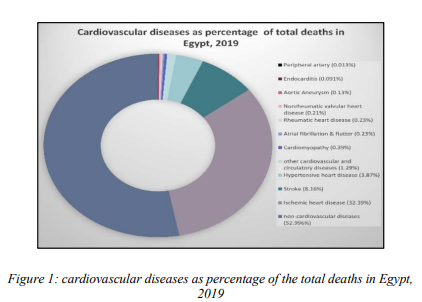
CFD analysis of transient blood flow in a cerebral aneurysm: A comparison between a healthy and diseased model
The unsteady flow field variations between healthy and diseased three-dimensional rigid posterior cerebral artery are numerically investigated. The Computational hemodynamic simulations have been known to provide valuable clinical information to researchers and surgeons that proved to be crucial for the assessment of medical risks, pre-surgical conditioning and treatment planning. The wall shear stress (WSS) and wall pressure are the most important hemodynamic variables, and both are used to give accurate description about the health status of the artery. The results showed that at the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
