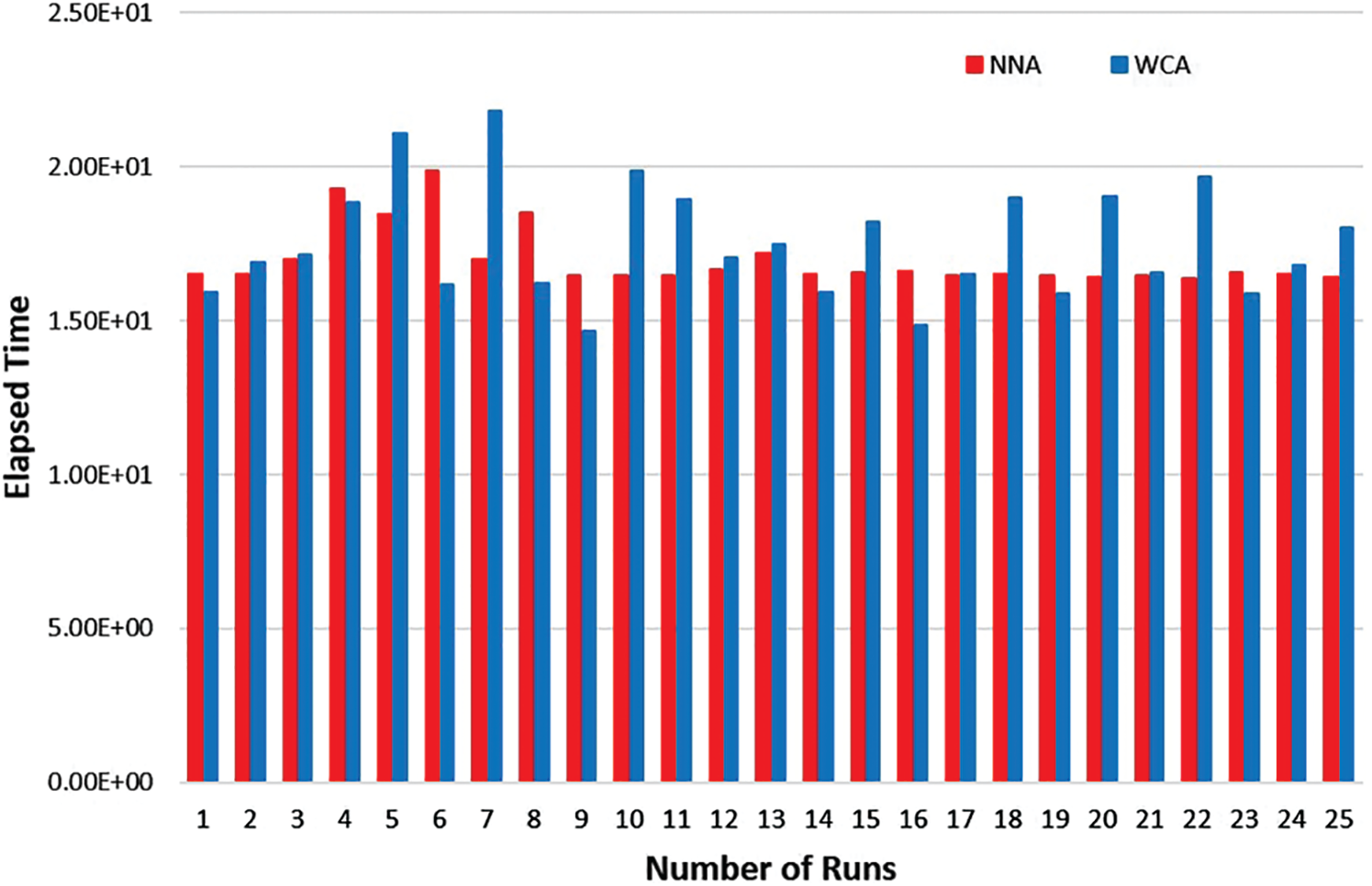
An artificial intelligence approach for solving stochastic transportation problems
Recent years witness a great deal of interest in artificial intelligence (AI) tools in the area of optimization. AI has developed a large number of tools to solve the most difficult search-and-optimization problems in computer science and operations research. Indeed, metaheuristic-based algorithms are a sub-field of AI. This study presents the use of the metaheuristic algorithm, that is, water cycle algorithm (WCA), in the transportation problem. A stochastic transportation problem is considered in which the parameters supply and demand are considered as random variables that follow the
Graph transformer for communities detection in social networks
Graphs are used in various disciplines such as telecommunication, biological networks, as well as social networks. In large-scale networks, it is challenging to detect the communities by learning the distinct properties of the graph. As deep learning has made contributions in a variety of domains, we try to use deep learning techniques to mine the knowledge from large-scale graph networks. In this paper, we aim to provide a strategy for detecting communities using deep autoencoders and obtain generic neural attention to graphs. The advantages of neural attention are widely seen in the field of
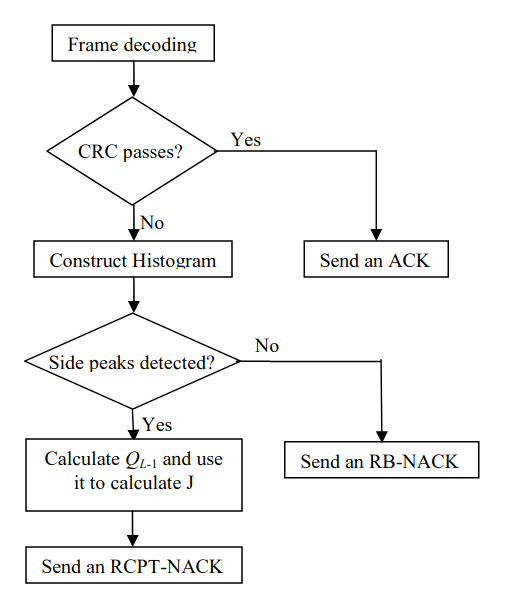
Novel reliability-based hybrid ARQ technique
In this paper we propose a novel technique for hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) systems where turbo codes are used as the forward error correction (FEC) techniques. This technique uses the histogram of the soft values generated by the turbo decoder to control the size and the contents of the retransmissions needed when the packet can not be decoded correctly. These soft values represent the reliabilities of the information bits; hence the proposed technique is a reliability-based (RB) HARQ technique. The proposed technique is compared to the conventional RB-HARQ and the conventional rate
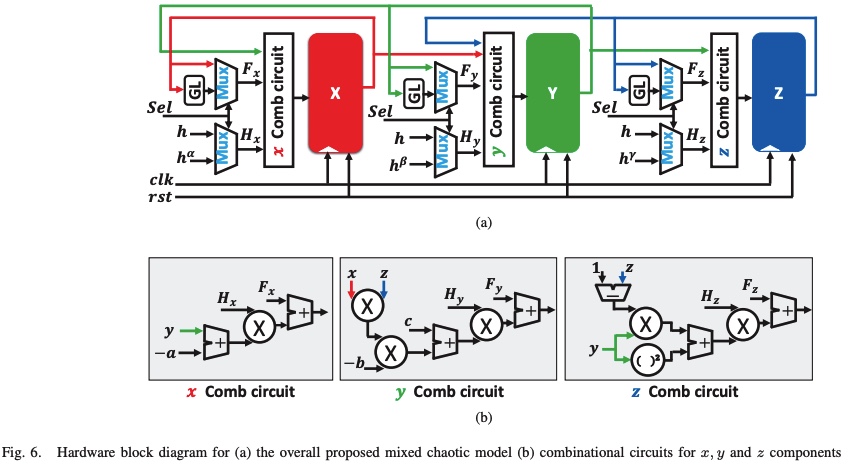
A Digital Hardware Implementation for A new Mixed-Order Nonlinear 3-D Chaotic System
This paper introduces a generic modeling for a 3-D nonlinear chaotic based on fractional-order mathematical rules. Also, a novel modeling for the system using a mixture between integer and fractional-order calculus is proposed. Dynamics of the new realization are illustrated using phase portrait diagrams with complex behavior. Also, a great change in the parameter ranges is investigated using bifurcation diagrams. MATLAB and Xilinx ISE 14.5 are used in system simulations. Furthermore, the digital hardware implementation is done using Xilinx FPGA Virtex-5 kit. The synthesis report shows that

Bridge information modeling in sustainable bridge management
Bridge Management Systems (BMS) play a crucial role in maintenance and rehabilitation decisions related to bridges. This paper presents using Bridge Information Modeling (BrIM) framework that adopts BMS features including; databases, inspection module, and condition assessment module. The proposed BrIM framework creates a database of bridges' components and generates inspection spreadsheets. It also visualizes bridge components considering the information stored in the database and inspection spreadsheets, using Structured Query Language (SQL) statements. The paper presents the integration of
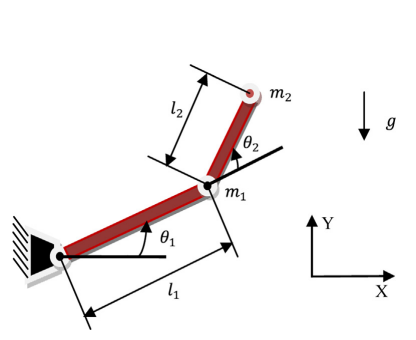
Design of fractional order fuzzy sliding mode controller for nonlinear complex systems
Controlling a nonlinear, time-varying, uncertain, coupled multiinput-multioutput (MIMO) complex system is always a challenging task for control engineers. A linear PID controller is not able to control effectively these complex systems and a robust adaptive controller is needed for perfect control. In this chapter, a fractional order fuzzy sliding mode proportional derivative (FOFSMCPD) controller is presented to control a two-link planar rigid robotic manipulator system. Literature reveals that sliding mode controllers (SMC) have the serious issue of fast oscillations, called chattering, in
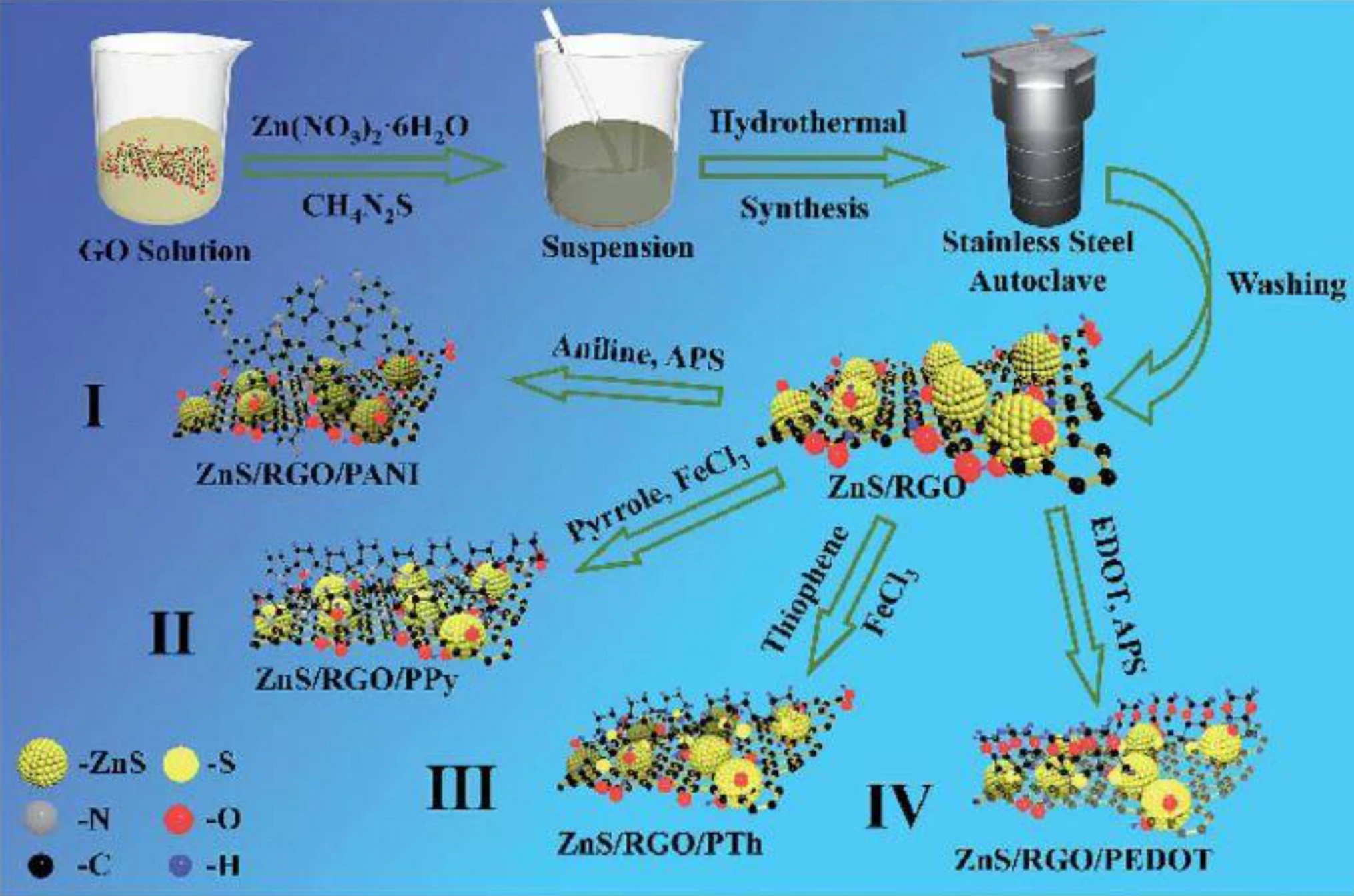
Advanced materials and technologies for supercapacitors used in energy conversion and storage: a review
Supercapacitors are increasingly used for energy conversion and storage systems in sustainable nanotechnologies. Graphite is a conventional electrode utilized in Li-ion-based batteries, yet its specific capacitance of 372 mA h g−1 is not adequate for supercapacitor applications. Interest in supercapacitors is due to their high-energy capacity, storage for a shorter period and longer lifetime. This review compares the following materials used to fabricate supercapacitors: spinel ferrites, e.g., MFe2O4, MMoO4 and MCo2O4 where M denotes a transition metal ion; perovskite oxides; transition metals
Atmospheric pressure air microplasma current time series for true random bit generation
Generating true random bits of high quality at high data rates is usually viewed as a challenging task. To do so, physical sources of entropy with wide bandwidth are required which are able to provide truly random bits and not pseudorandom bits, as it is the case with deterministic algorithms and chaotic systems. In this work we demonstrate a reliable high-speed true random bit generator (TRBG) device based on the unpredictable electrical current time series of atmospheric pressure air microplasma (APAMP). After binarization of the sampled current time series, no further post-processing was
Asymmetric degrees of freedom of the full-duplex MIMO 3-way channel
In this paper, we characterize the asymmetric total degrees of freedom (DoF) of a multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) 3-way channel. Each node has a separate-antenna full-duplex MIMO transceiver with a different number of antennas, where each antenna can be configured for either signal transmission or reception. Each node has two unicast messages to be delivered to the two other nodes. We first derive upper bounds on the total DoF of the system. Cut-set bounds in conjunction with genie-aided bounds are derived to characterize the achievable total DoF. Afterwards, we analytically derive the
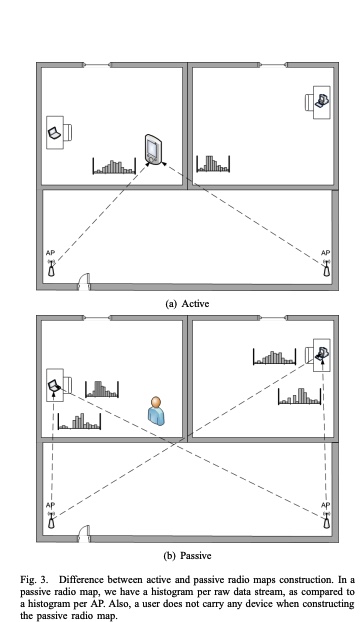
A deterministic large-scale device-free passive localization system for wireless environments
The widespread usage of wireless local area networks and mobile devices has fostered the interest in localization systems for wireless environments. The majority of research in the context of wirelessbased localization systems has focused on device-based active localization, in which a device is attached to tracked entities. Recently, device-free passive localization (DfP) has been proposed where the tracked entity is neither required to carry devices nor participate actively in the localization process. DfP systems are based on the fact that RF signals are affected by the presence of people
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 15
- Next page ››
