Proactive power allocation and caching node selection for regular service guarantees
This paper studies the potential of proactive resource allocation to prolong the communication sessions in networks with limited energy budgets and stringent quality-of-service (QoS) requirement, particularly a regular service guarantee. A threshold-based proactive communication policy is proposed to minimize the consumed transmission energy and maximize the network lifetime based on the different link states and the buffer state at the destination node. A closed-form expression is presented for the proactive gain in terms of the channel gain threshold, the amount of the proactively-
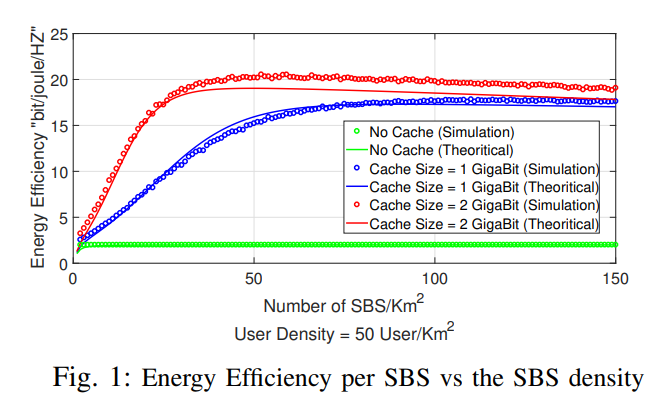
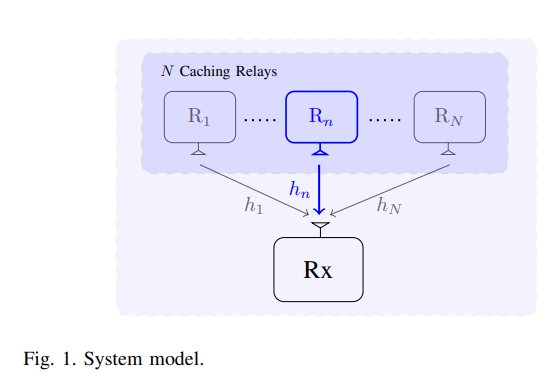
On Caching and Base Station Densification Tradeoff for Maximized Energy Efficiency
In this paper, we study a two-tier cellular network with cache-enabled small base stations (SBSs). In our model, a SBS has the ability to coordinate with neighboring SBSs and fetch data from their caches. We focus on the effect of SBSs' density on the network's energy efficiency. To this end, stochastic geometry theory is used to model the SBSs and users distributions, which enables us to find closed-form expressions for the network's energy efficiency as a function of the SBSs density and the cache size at each SBS. The optimal SBSs density that maximizes the energy efficiency is
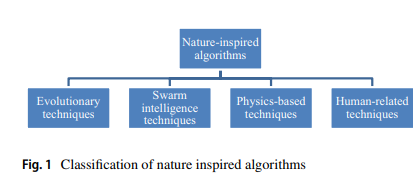
Gaining-sharing knowledge based algorithm for solving optimization problems: a novel nature-inspired algorithm
This paper proposes a novel nature-inspired algorithm called Gaining Sharing Knowledge based Algorithm (GSK) for solving optimization problems over continuous space. The GSK algorithm mimics the process of gaining and sharing knowledge during the human life span. It is based on two vital stages, junior gaining and sharing phase and senior gaining and sharing phase. The present work mathematically models these two phases to achieve the process of optimization. In order to verify and analyze the performance of GSK, numerical experiments on a set of 30 test problems from the CEC2017 benchmark for

Gaining-Sharing Knowledge Based Algorithm with Adaptive Parameters for Engineering Optimization
As optimization algorithms have a great power to solve nonlinear, complex, and hard optimization problems, nature-inspired algorithms have been applied extensively in distinct fields in order to solve real life optimization cases. In this paper, modifications for the recently proposed Gaining-Sharing-Knowledge based algorithm (GSK) are presented for enhancing its performance. Gaining-Sharing-Knowledge algorithm is considered as a perfect example of modern nature-inspired algorithm that considered the human life behavior as a source of inspiration in order to solve optimization problems. GSK
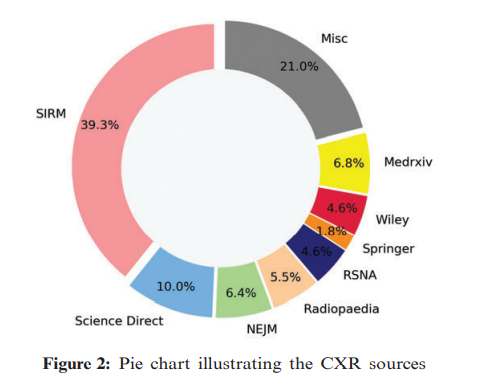
Deep stacked ensemble learning model for COVID-19 classification
COVID-19 is a growing problem worldwide with a high mortality rate. As a result, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared it a pandemic. In order to limit the spread of the disease, a fast and accurate diagnosis is required. A reverse transcript polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test is often used to detect the disease. However, since this test is time-consuming, a chest computed tomography (CT) or plain chest X-ray (CXR) is sometimes indicated. The value of automated diagnosis is that it saves time and money by minimizing human effort. Three significant contributions are made by our
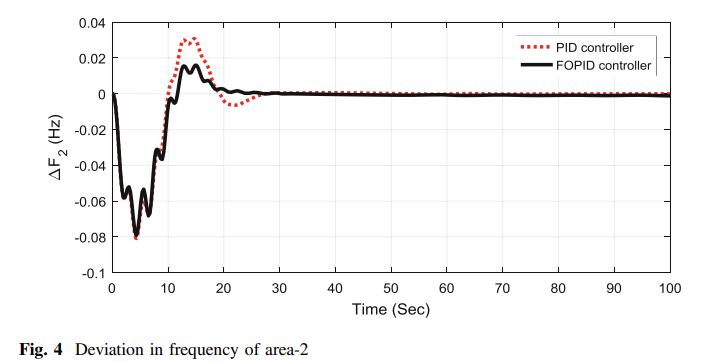
TLBO algorithm optimized fractional-order PID controller for AGC of interconnected power system
The present study focuses on the problem of automatic generation control (AGC) by employing the design of fractional-order proportional–integral– derivative controller (FOPID). A hydrothermal power system with governor dead band (GDB) and generation rate constraint (GRC) is considered for investigation. FOPID controller optimal values are obtained by using teacher learning-based optimization (TLBO) technique, and the employed objective function is integral time-multiplied absolute error (ITAE). The supremacy of the proposed controller is also shown by comparing with PID controller. Further
Software Defined Network Based Management Framework for Wireless Sensor Networks
Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) has growth rapidly over the past years. As it is now applied in many fields as in health care systems, home automation, security surveillance, disaster management and more. Due to the high demand on WSN, it is important to find a solution for one of the major challenges in WSN which is the energy consumption of its battery operated sensor device. So in this paper we propose to use Software Defined technology into WSN to enhance network management and to prolong network lifetime. As the main feature of Software Defined Network (SDN) is the centralization of control
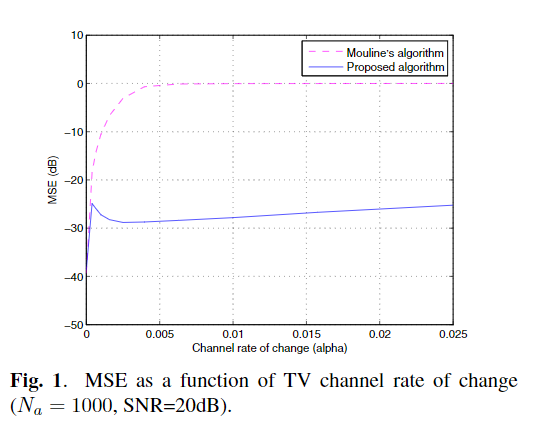
A subspace method for the blind identification of multiple time-varying FIR channels
A new method is proposed for the blind subspace-based identification of the coefficients of time-varying (TV) single-input multiple-output (SIMO) FIR channels. The TV channel coefficients are represented via a finite basis expansion model, i.e. linear combination of known basis functions. In contrast to earlier related works, the basis functions need not be limited to complex exponentials, and therefore do not necessitate the a priori estimation of frequency parameters. This considerably simplifies the implementation of the proposed method and provides added flexibility in applications. The
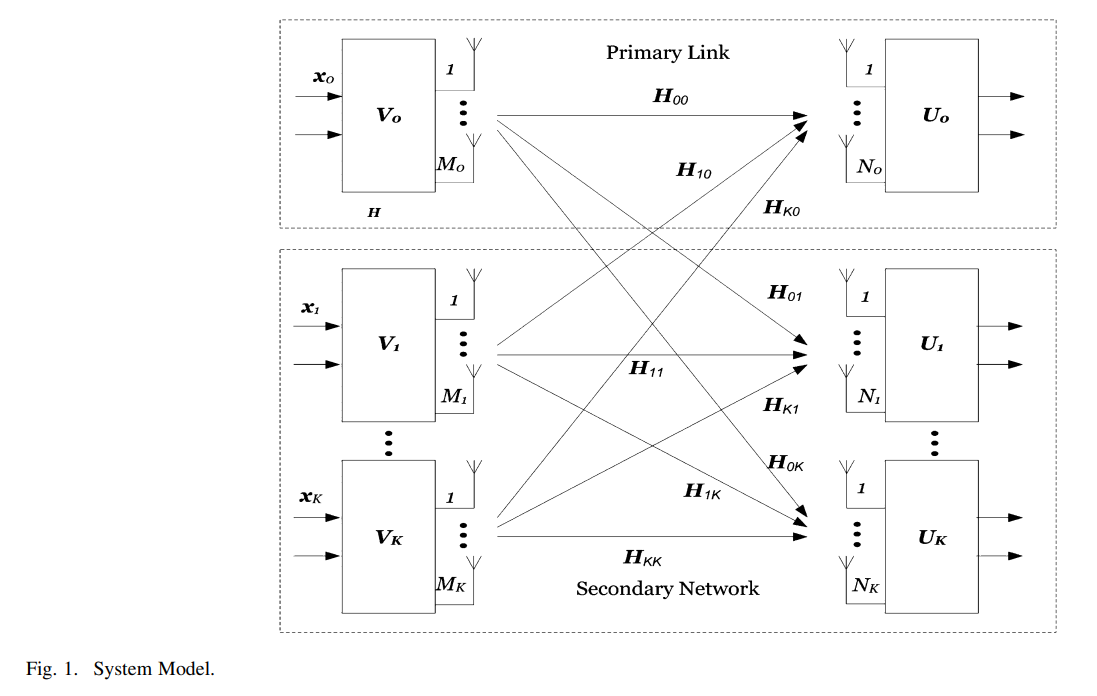
Constrained interference alignment and the spatial degrees of freedom of mimo cognitive networks
An interference alignment (IA) scheme is presented that allows multiple opportunistic transmitters (secondary users) to use the same frequency band of a pre-existing primary link without generating any interference. The primary and secondary transmit-receive pairs are equipped with multiple antennas. Under power constraints on the primary transmitter, the rate of the primary user is maximized by water-filling on the singular values of its channel matrix leaving some eigen modes unused, and hence, the secondary users can align their transmitted signals to produce a number of interference-free
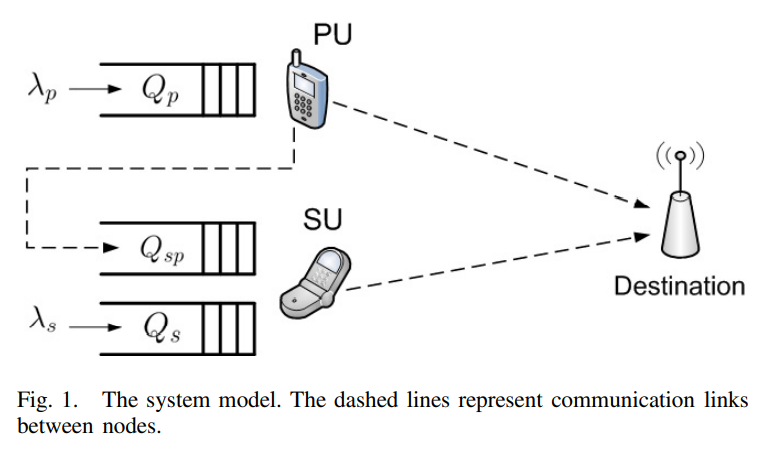
Optimizing Cooperative Cognitive Radio Networks Performance with Primary QoS Provisioning
We consider the problem of optimizing the performance of a cooperative cognitive radio user subject to constraints on the quality-of-service (QoS) of the primary user (PU). In particular, we design the probabilistic admission control parameter of the PU packets in the secondary user (SU) relaying queue and the randomized service parameter at the SU under non-work-conserving (non-WC) and WC cooperation policies. In the non-WC policy, two constrained optimization problems are formulated; the first problem is maximizing the SU throughput while the second problem is minimizing the SU average delay
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 21
- Next page ››
