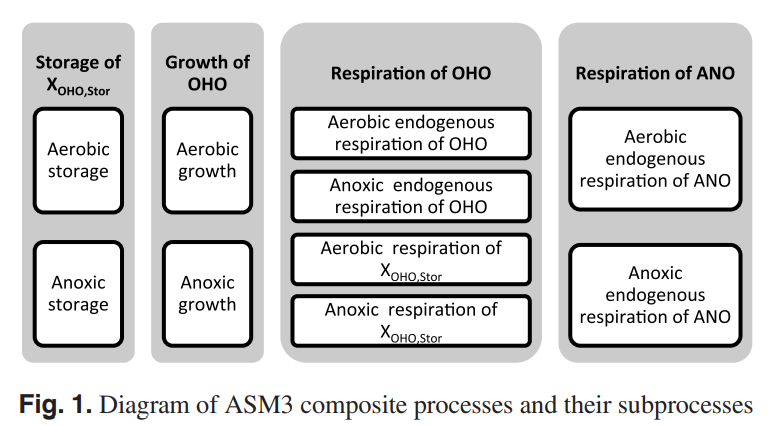
Comparison and database development of four recent ASM3 model extensions
In the last decade, many Activated Sludge Model No. 3 (ASM3) extensions were proposed to adopt new concepts such as simultaneous storage and growth of heterotrophic organisms and two-step nitrification-denitrification processes. From these ASM3 model extensions, four are included in this study: ASM3 with two-step nitrification-denitrification, ASM3 for simultaneous autotrophic and heterotrophic storage-growth, ASM3 extension for two-step nitrification-denitrification, and ASM3 for simultaneous storage-growth and nitrification-denitrification. The four models are analyzed and compared to the
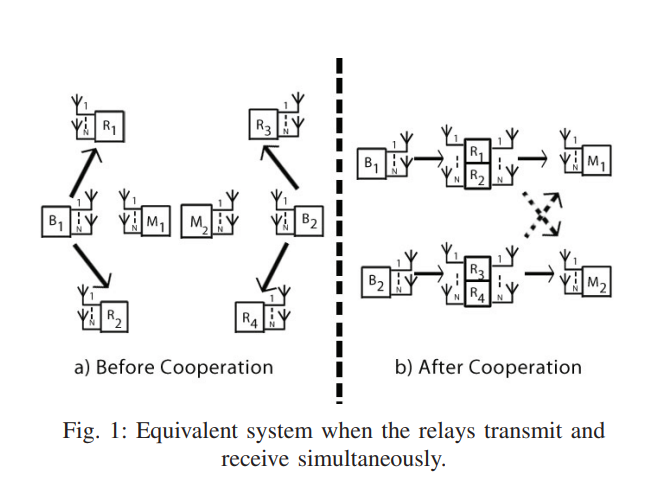
Alternate relaying and the degrees of freedom of one-way cellular relay networks
In this paper, a cellular relaying network consisting of two source-destination pairs, and four decode-and-forward relays operating in half-duplex mode is considered. Each source is assisted by two relays and all nodes are equipped with N antennas. In order to compensate for the loss of capacity by a factor of half due to the half-duplex mode, an alternate transmission protocol among the two relays is proposed. An outer bound on the degrees of freedom (DoF) of this system is developed. A constructive proof of achievability based on two different schemes is provided. Aligning the inter-relay
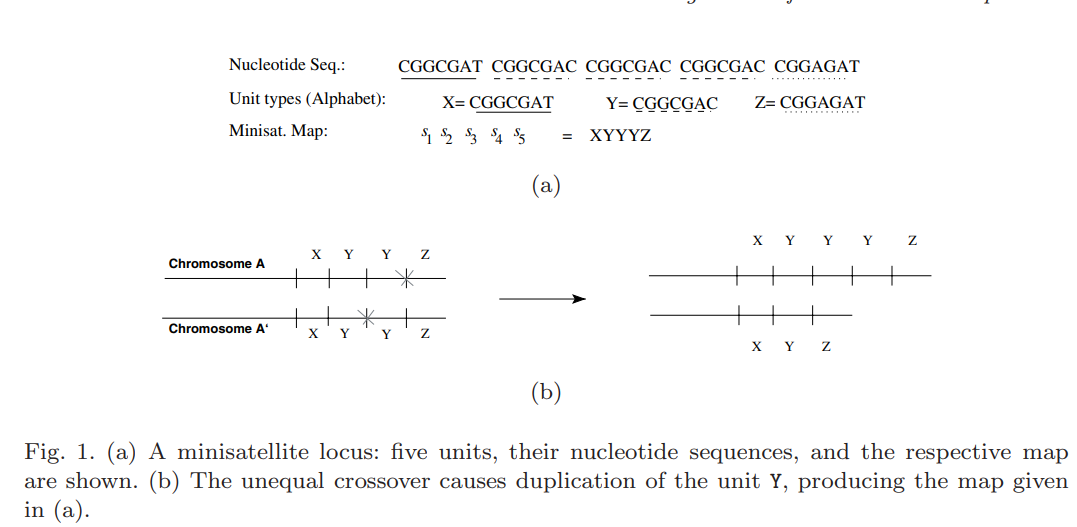
Alignment of minisatellite maps based on run-length encoding scheme
Subsequent duplication events are responsible for the evolution of the minisatellite maps. Alignment of two minisatellite maps should therefore take these duplication events into account, in addition to the well-known edit operations. All algorithms for computing an optimal alignment of two maps, including the one presented here, first deduce the costs of optimal duplication scenarios for all substrings of the given maps. Then, they incorporate the pre-computed costs in the alignment recurrence. However, all previous algorithms addressing this problem are dependent on the number of distinct
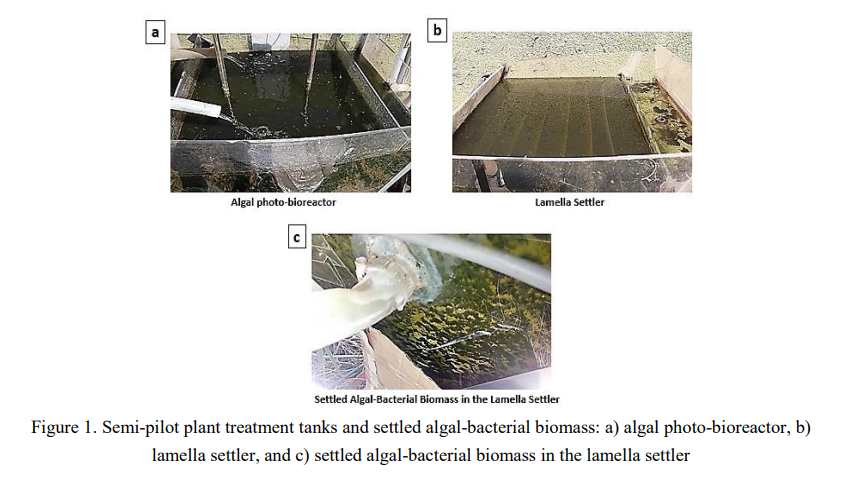

(562bb) Semi-pilot plant for tertiary treatment of domestic wastewater using algal photo-bioreactor, with artificial intelligence
This study attempted to investigate the removal of biological oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total suspended solids (TSS), ammonia-nitrogen (NH4-N), and total phosphorus (TP) from secondary treated domestic wastewater using algal photo-bioreactor. A semi-pilot plant was constructed and operated for 112 days under continuous flow conditions at Zenin wastewater treatment plant, Giza, Egypt (WWTP) which consists of an algal photo-bioreactor with an effective volume of 188 litters and a lamella settler. The removal of the studied parameters was studied at different hydraulic
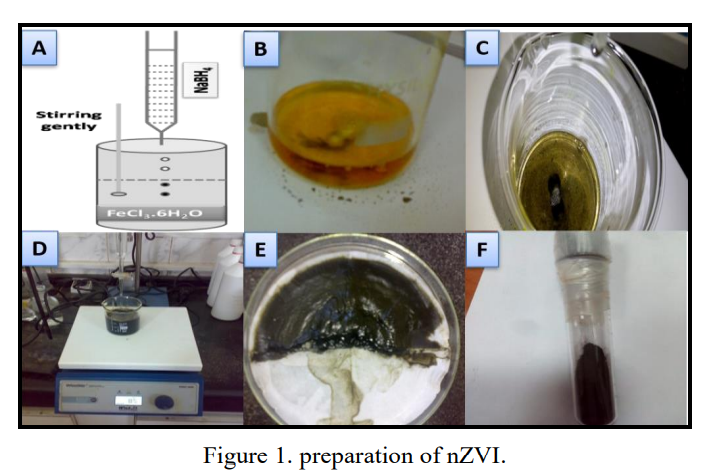
(670d) Study the degradation and adsorption processes of organic matters from domestic wastewater using chemically prepared and green synthesized nano zero-valent iron
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) using chemically prepared and green synthesized nano zero-valent iron (nZVI) has proved to be effective in removing organic contaminants. The green synthesized nano iron (GT-nZVI) was prepared by using extracted black tea reducing agent. The prepared nZVI particles were characterized using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDAX) analysis. The main purpose of this study is to compare between chemically prepared nZVI and GT-nZVI in the biological oxygen demand (BOD) removal efficiency from
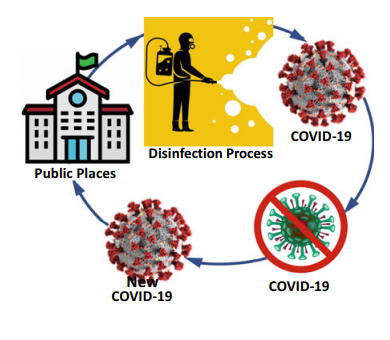
Optimum Scheduling of the Disinfection Process for COVID-19 in Public Places with a Case Study from Egypt, a Novel Discrete Binary Gaining-Sharing Knowledge-Based Metaheuristic Algorithm
The aim of this paper is to introduce an improved strategy for controlling COVID-19 and other pandemic episodes as an environmental disinfection culture for public places. The scheduling aims at achieving the best utilization of the available working day-time hours, which is calculated as the total consumed disinfection times minus the total loosed transportation times. The proposed problem in network optimization identifies a disinfection group who is likely to select a route to reach a subset of predetermined public places to be regularly disinfected with the most utilization of the
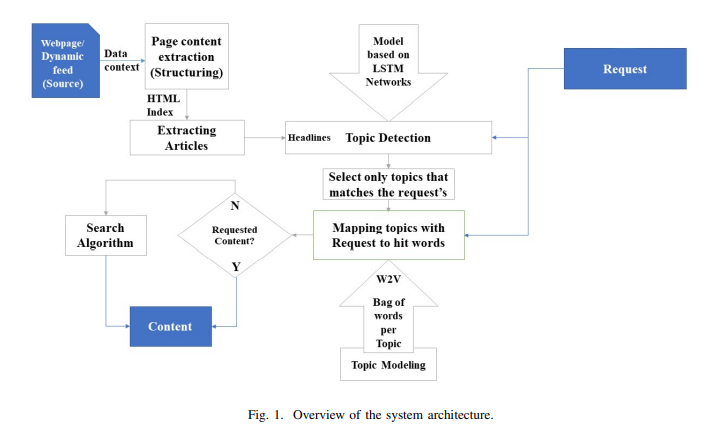
Towards Intelligent Web Context-Based Content On-Demand Extraction Using Deep Learning
Information extraction and reasoning from massive high-dimensional data at dynamic contexts, is very demanding and yet is very hard to obtain in real-time basis. However, such process capability and efficiency might be affected and limited by the available computational resources and the consequent power consumption. Conventional search mechanisms are often incapable of real-time fetching a predefined content from data source, without concerning the increased number of connected devices that contribute to the same source. In this work, we propose and present a concept for an efficient approach
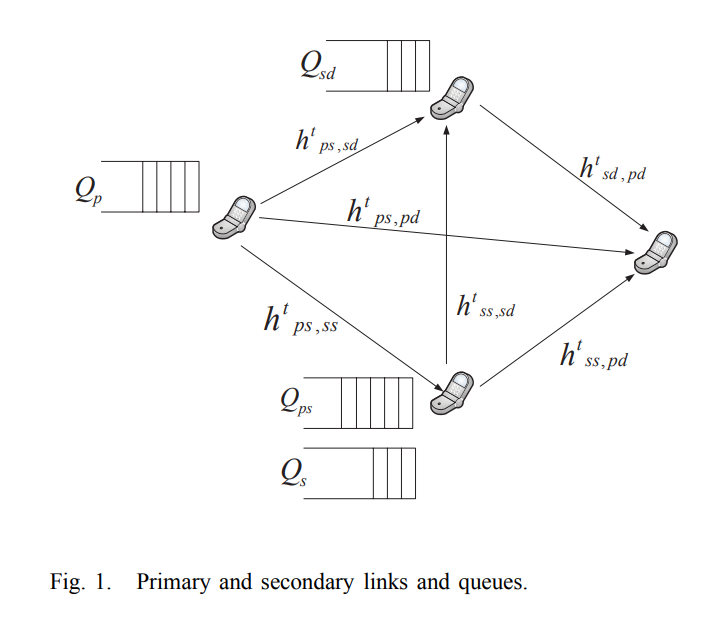
Transmit and receive cooperative cognition: Protocol design and stability analysis
In this paper, we investigate the stability of a cooperative cognitive system. We propose a cooperative secondary transmitter-receiver system (CSTR), where, the secondary transmitter (ST) and the secondary receiver (SR) increase the spectrum availability for the ST packets by relaying the unsuccessfully transmitted packets of the primary transmitter (PT). We assume receiving nodes with multipacket reception capability (MPR). We provide two inner bounds and two outer bounds on the stability region of the considered system. © 2013 ICST - The Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics
Self-Driving Car Lane-keeping Assist using PID and Pure Pursuit Control
Detection of lane boundaries is the primary role for monitoring an autonomous car's trajectory. Three lane identification methodologies are explored in this paper with experimental illustration: Edge detection, Hough transformation, and Birds eye view. The next step after obtaining the boundary points is to add a regulation rule to effectively trigger the regulation of steering and velocity to the motors. A comparative analysis is made between different steering controllers like PID or by using PID with a pure pursuit controller for the Lane Keeping Assist (LKA) system. A camera that sends
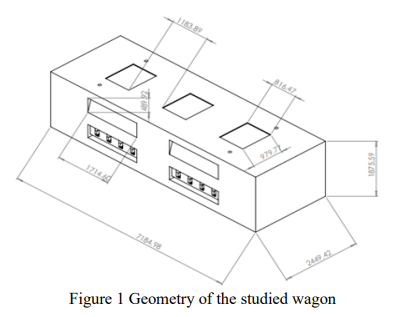
Regression Modeling for the Ventilation Effect on COVID-19 Spreading in Metro Wagons
The effect of different ventilation parameters on the infection potential of COVID-19 in a metro wagon is numerically studied. Two key indicators are used to quantify this potential. Based on the numerical results a regression analysis is performed to come up with the most suitable regression model for these key parameters. The proposed regression models are helpful in quantifying the infection risk at different ventilation scenarios. © 2021 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 23
- Next page ››
