
On the role of vehicular mobility in cooperative content caching
In this paper, we analyze the performance of cooperative content caching in vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETs). In particular, we characterize, using analysis and simulations, the behavior of the probability of outage (i.e. not finding a requested data chunk at a neighbor) under freeway vehicular mobility. First, we introduce a formal definition for the probability of outage in the context of cooperative content caching. Second, we characterize, analytically, the outage probability under vehicular and random mobility scenarios. Next, we verify the analytical results using simulations and

MIMO VANETs: Research challenges and opportunities
In this paper, we provide a review of the benefits of employing multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) processing techniques in vehicular ad hoc networks VANETs. These benefits include increasing the range of communication via beamforming, improving the reliability of communication via spatial diversity, increasing the throughput of the network via spatial multiplexing, and managing multiuser interference due to the presence of multiple transmitting terminals. We also present a number of key research challenges facing MIMO VANETs. The first one is deriving statistical MIMO-V2V channel models
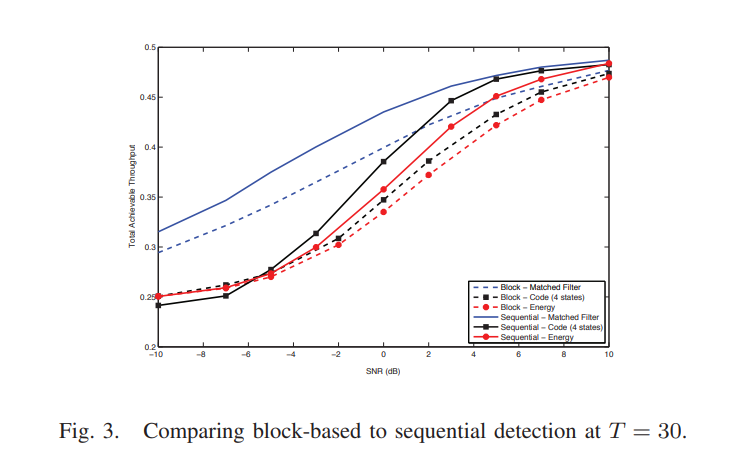
On the utility of primary side information in cognitive sensing
In this paper, we study the impact of the knowledge of primary side information on the efficiency of spectrum sensing for cognitive radio networks. In particular, assuming that the secondary transmitter knows the modulation and/or coding scheme used in the primary transmissions, we evaluate the efficiency of spectrum sensing in terms of maximizing the overall achievable throughput of the system. We present the results for both block-based and sequential detection techniques. We show that in sequential detection, and when the cognitive transmitter has knowledge of the primary codebook, the
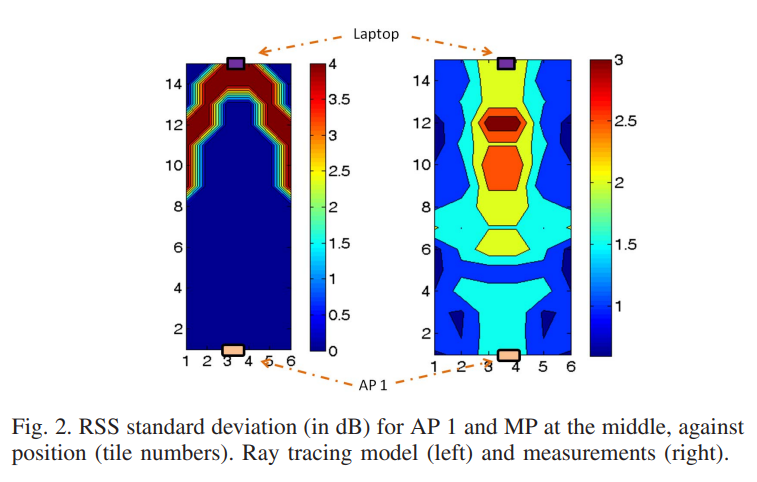
Impact of the human motion on the variance of the received signal strength of wireless links
Human motion has strong impact on the received signal strength (RSS) of indoor wireless links that can be exploited for variance-based device-free positioning. In this paper, we investigate the effect of human motion on the variance of the RSS of wireless local area networks (WLAN) operating at 2.4 GHz. Using measurements, the RSS variance for human in-place motion is determined as a function of the human position in a corridor setting. We provide ray tracing and empirical models to capture this effect. The accuracy of the different models is compared under different scenarios. Furthermore, we
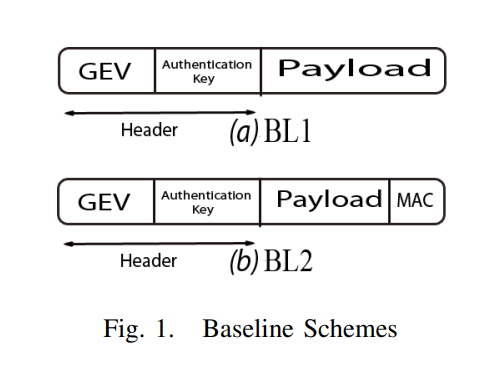
SANC: Source authentication using network coding
In this paper, we explore the security merits of network coding and potential trade-offs with the widely accepted throughput benefits, especially in multicast scenarios. In particular, we propose a novel Source Authentication using Network Coding (SANC) scheme that can either complement state-of-the-art application-layer authentication schemes proposed in the literature or be used as a stand-alone scheme in network coding-based networks. Towards this objective, we propose a general framework for embedding the authentication information within the network coding Global Encoding Vector. This is
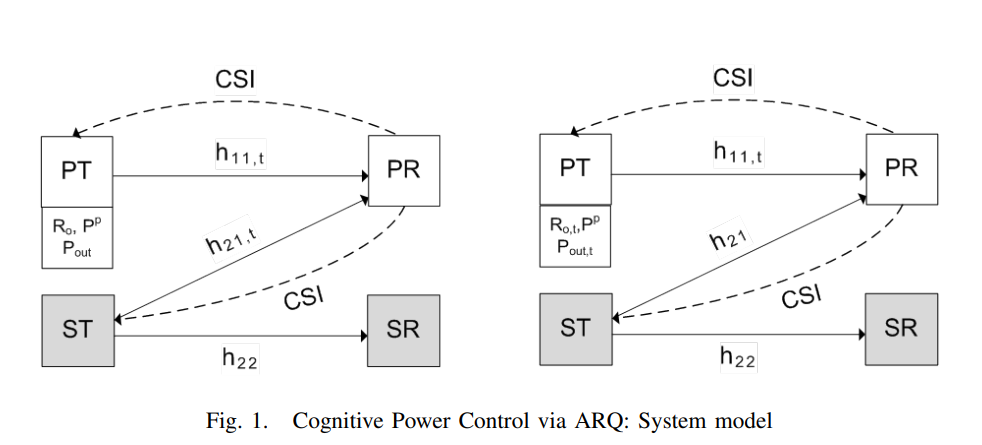
Throughput maximization over temporally correlated fading channels in cognitive radio networks
We consider a primary link and a secondary link, each composed of a transmitter and a receiver. The primary channel and the channel between the secondary transmitter and the primary receiver follow a first-order Markov model for channel variation over time. Under this assumption of temporal correlation and via exploiting the channel state information (CSI) feedback, we pose the cognitive power control problem as the maximization of secondary throughput subject to a constraint on the primary outage. To solve this problem, we assume that the primary transmitter sends with a constant-rate and
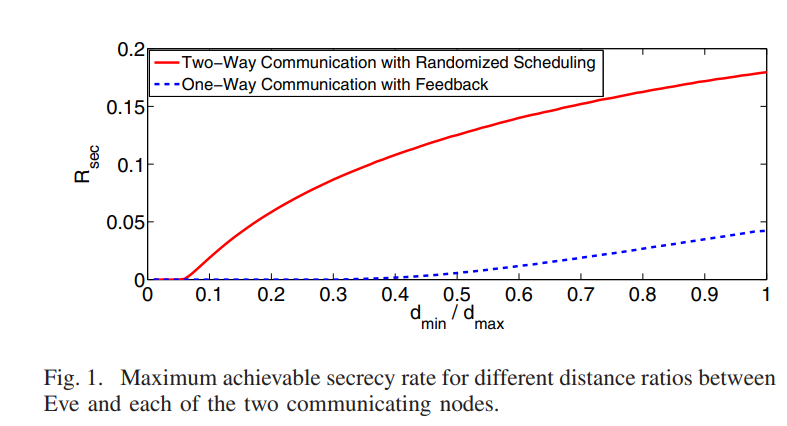
Randomization for security in half-duplex two-way Gaussian channels
This paper develops a new physical layer framework for secure two-way wireless communication in the presence of a passive eavesdropper, i.e., Eve. Our approach achieves perfect information theoretic secrecy via a novel randomized scheduling and power allocation scheme. The key idea is to allow Alice and. Bob to send symbols at random time instants. While Alice will be able to determine the symbols transmitted by Bob, Eve will suffer from ambiguity regarding the source of any particular symbol. This desirable ambiguity is enhanced, in our approach, by randomizing the transmit power level. Our
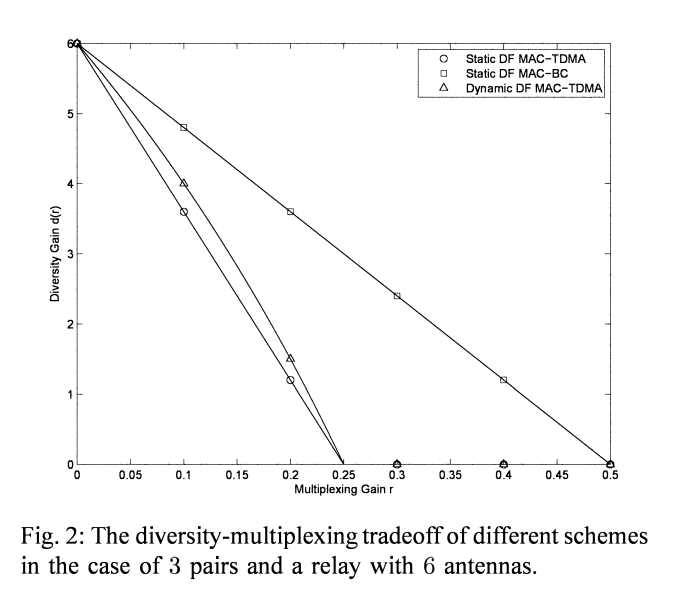
The MIMO wireless switch: Relaying can increase the multiplexing gain
This paper considers an interference network composed of K half-duplex single-antenna pairs of users who wish to establish bi-directional communication with the aid of a multiinput-multi-output (MIMO) half-duplex relay node. This channel is referred to as the "MIMO Wireless Switch" since, for the sake of simplicity, our model assumes no direct link between the two end nodes of each pair implying that all communication must go through the relay node (i.e., the MIMO switch). Assuming a delay-limited scenario, the fundamental limits in the high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) regime is analyzed using
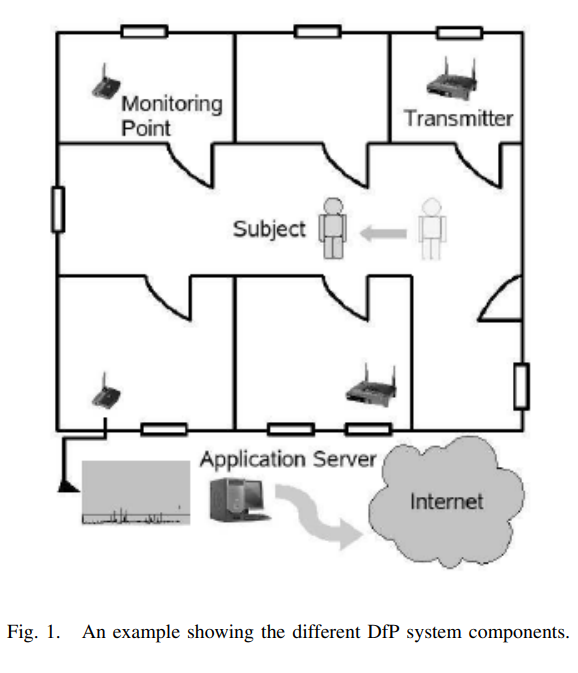
Smart devices for smart environments: Device-free passive detection in real environments
Device-free Passive (DfP) localization is a system envisioned to detect, track, and identify entities that do not carry any device, nor participate actively in the localization process. A DfP system allows using nominal WiFi equipment for intrusion detection, without using any extra hardware, adding smartness to any WiFi-enabled device. In this paper, we focus on the detection function of the DfP system in a real environment. We show that the performance of our previously developed algorithms for detection in a controlled environments, which achieved 100% recall and precision, degrades
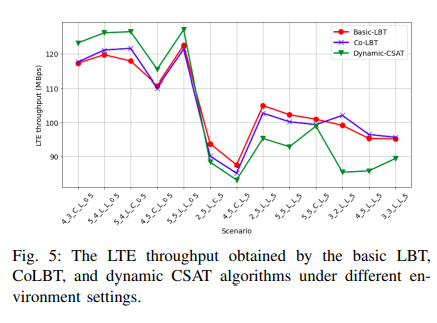
Machine Learning-based Module for Monitoring LTE/WiFi Coexistence Networks Dynamics
Long-Term Evolution (LTE) technology is expected to shift some of its transmissions into the unlicensed band to overcome the spectrum scarcity problem. Nevertheless, in order to effectively use the unlicensed spectrum, several challenges have to be addressed. The most important of which is how to coexist with the incumbent unlicensed WiFi networks. Incorporating the "intelligence"component into the network radios is foreseen to resolve the intrinsic network challenges, rather than conventional non-adaptive action plans. Specifically, an intelligent cognitive engine (CE) that continuously
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 32
- Next page ››
