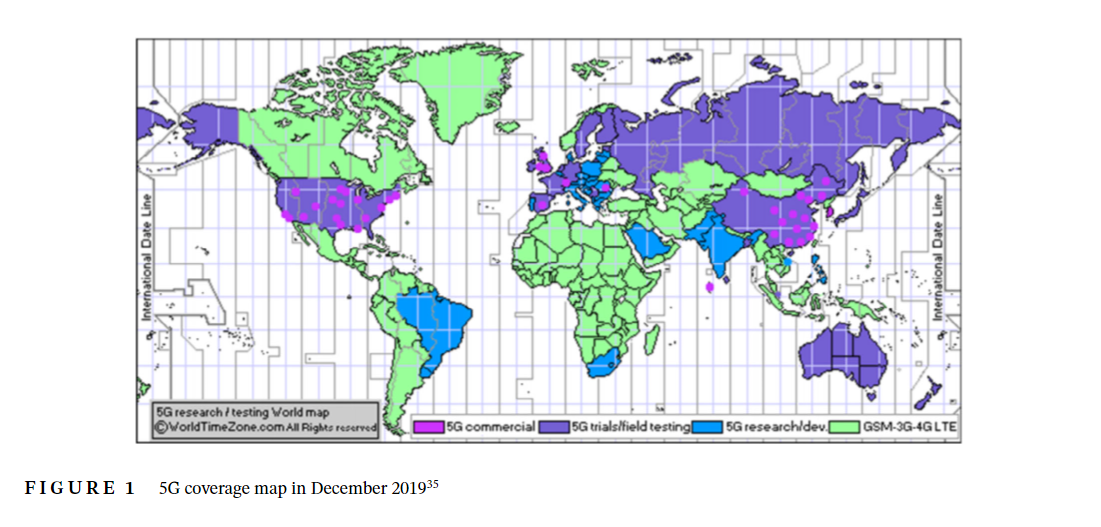
6G: A comprehensive survey on technologies, applications, challenges, and research problems
The inherent limitations of the network keep on going to be revealed with the continuous deployment of cellular networks. The next generation 6G is motivated by these drawbacks to properly integrate important rate-hungry applications such as extended reality, wireless brain-computer interactions, autonomous vehicles, and so on. Also, to support significant applications, 6G will handle large amounts of data transmission in smart cities with much lower latency. It combines many state-of-the-art trends and technology to provide higher data rates for ultra-reliable and low latency communications
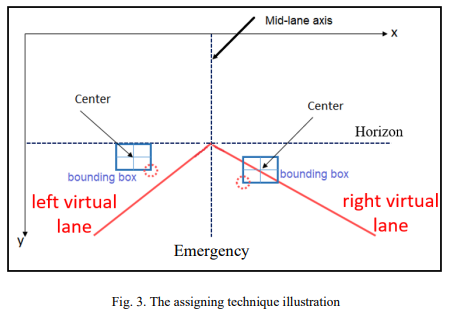
Demonstration of Forward Collision Warning System Based on Real-Time Computer Vision
This paper demonstrates the software and hardware of a forward-collision warning system using techniques of realtime computer vision which helps self-driving cars and autonomous vehicles systems to merge with the road environment safely and ensure the reliability of these systems. The software approach of the paper consists of five parts: car detection, depth estimation, lane assignation, the relative speed of other cars and their corresponding speed limit and finally ultrasonic sensors which completes the front of the vehicle as the camera can't cover it alone. Besides these five objectives
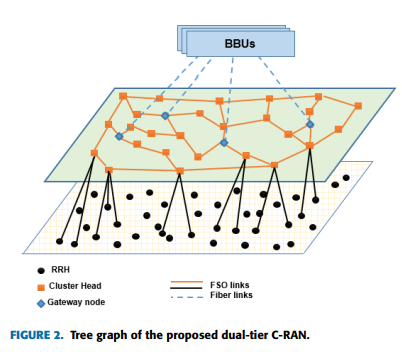
Dynamic Traffic Model with Optimal Gateways Placement in IP Cloud Heterogeneous CRAN
In this paper, topology design, optimal routing, and gateways placement selection algorithms are proposed in Heterogeneous Cloud Radio Access Network (C-RAN) with exploiting Free Space Optical (FSO) communication. The proposed network consists of two tiers; the lower tier concerns with clustering Remote Radio Heads (RRHs) based on traffic demands. The upper tier consists of transceivers along with the Cluster Heads (CHs) and gateways. Algorithms are proposed to achieve the lowest number of edges and the highest possible throughput based on the presented optimization problem. Moreover, route
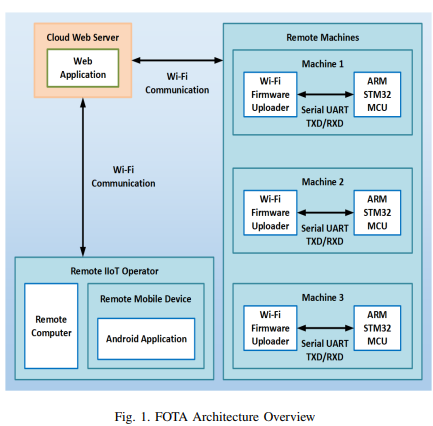
A Scalable Firmware-Over-The-Air Architecture suitable for Industrial IoT Applications
This paper proposes a reliable and scalable architecture for firmware-over-the-air updates, which provides remote cloud real-time distribution of new firmware versions on industrial machines in an efficient simultaneous manner. The architecture comprises remotely interconnected software and hardware systems for handling the procedures of firmware distribution over a wireless network. The main contributions are developing a special boot-loader for ARM micro-controllers and an Android application for performing FOTA updates. A simulation is performed using Web and Android applications showing
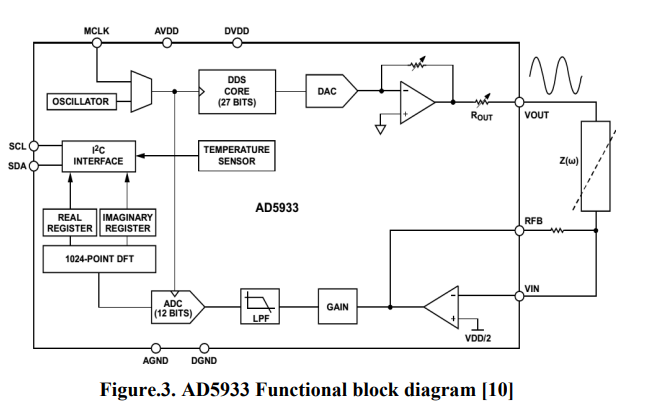
Aging effect on apples bio-impedance using AD5933
In this paper, the effect of the fruits aging on bio-impedance is experimentally studied. Bio-impedance analysis, as accurate and fast method is used to investigate and monitor group of apples properties during aging. This method provides an alternative method for investigating apples physical properties that are highly related to chemical properties. AD5933 impedance analyzer chip within the frequency range (5 KHz-100 KHz) and NI-ELVIS board within the frequency range (300 Hz-5 KHz) are used to investigate the changes in apple's properties during aging. According to experimental results, the
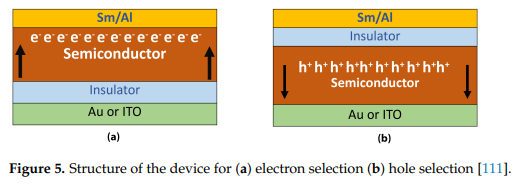
Review organic solar cells parameters extraction and characterization techniques
Organic photovoltaic research is continuing in order to improve the efficiency and stability of the products. Organic devices have recently demonstrated excellent efficiency, bringing them closer to the market. Understanding the relationship between the microscopic parameters of the device and the conditions under which it is prepared and operated is essential for improving performance at the device level. This review paper emphasizes the importance of the parameter extraction stage for organic solar cell investigations by offering various device models and extraction methodologies. In order
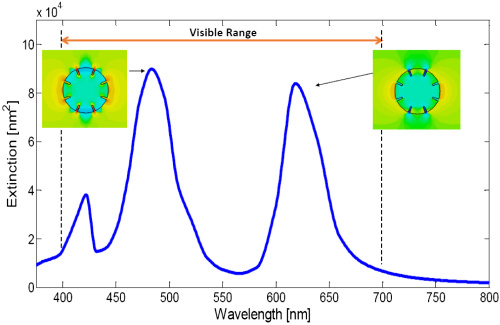
Enhanced plasmonic photovoltaic using embedded novel gear-shaped nanoparticles
In this paper, novel gear-shaped nanoparticles are introduced for the first time to enhance the photovoltaic (PV) efficiency. This has been achieved via increasing the overall power absorption by the PV semiconductor material in both visible and near-infrared ranges. The modes of the new gear-shaped nanoparticles are investigated. A parametric study has been performed which demonstrates how the design parameters of the proposed nanoparticles can be engineered for best overall power absorption within a Si surrounding medium. A figure of merit (FoM) is defined that takes into account all
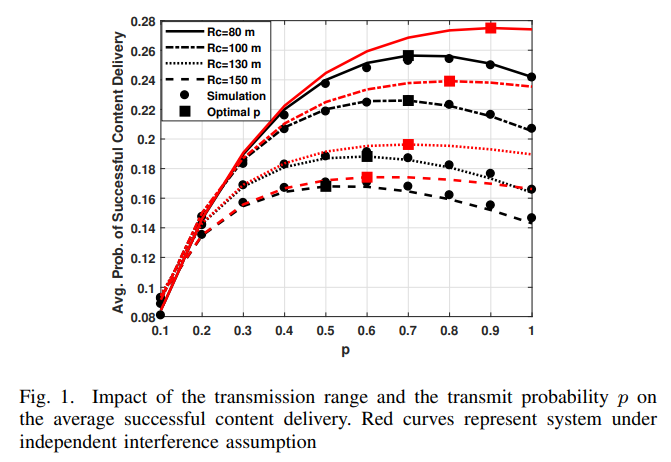
Impact of Temporally Correlated Nakagami-m Interferers in D2D Cache-Aided Networks
In this paper, we exploit tools from stochastic geometry to characterize the average probability of successful content delivery in a cache-enabled device-to-device (D2D) network under Nakagami- m fading. Specifically, we focus on the impact of temporal interference correlation due to erroneous packets retransmissions. The aggregate network interference is characterized under a slotted Aloha scheme in a homogeneous Poisson field of static interferers. In addition, the effect of different system parameters, such as the content popularity, intensity of devices, and D2D communication range, on the
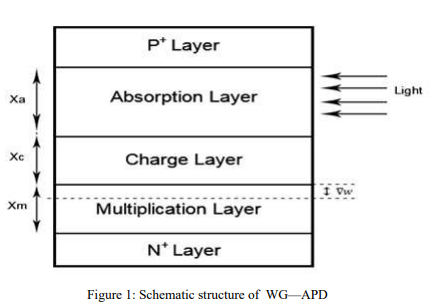
A Stochastic Modeling of the Gain in Waveguide Avalanche Photodetectors (WG-APDs)
Waveguide photodetectors are considered as a promising candidate for high speed photodetection where the tradeoff between the transit time bandwidth and the quantum efficiency is overcome as the incident optical signal and the photogenerated carriers move in perpendicular directions. In WG-Avalanche Photodetectors (WG-APDs), the avalanche multiplication gain enhances the photocurrent of the photodiodes. In these photodiodes, the inaccuracies in the ionizations coefficients of the photogenerated electrons and holes and in the dimensions of the multiplication layer affect the multiplication gain
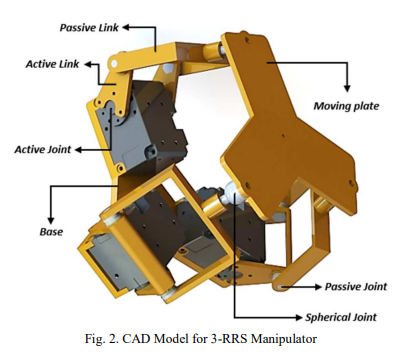
Design, simulation, and kinematics of 9-DOF Serial-Parallel Hybrid Manipulator Robot
Serial manipulator robot is one of the most advanced robots in the last decade. The demand for this type of robot leads the researchers to develop and improve the robot to increase its workspace, speed and to minimize the control complexity. This paper presents a novel robot configuration that combines a 6 DOF serial manipulator with a 3 DOF spherical parallel wrist. The serial manipulator is KUKA kr6 R900 type, which is a real industrial robot. At the same time, the parallel spherical wrist is 3-RRS type (Revolute- Revolute-Spherical Joint), which can support one translation movement in the Z
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 34
- Next page ››
