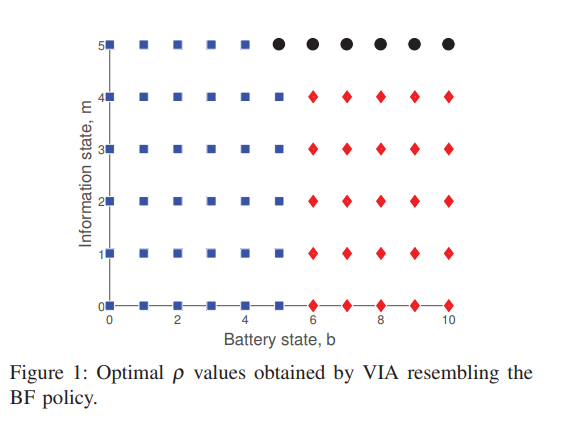
Wireless energy and information transfer in networks with hybrid ARQ
In this paper, we consider a class of wireless powered communication devices using hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) protocol to ensure reliable communications. In particular, we analyze the trade-off between accumulating mutual information and harvesting RF energy at the receiver of a point-to-point link over a time-varying independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) channel. The transmitter is assumed to have a constant energy source while the receiver relies, solely, on the RF energy harvested from the received signal. At each time slot, the incoming RF signal is split between
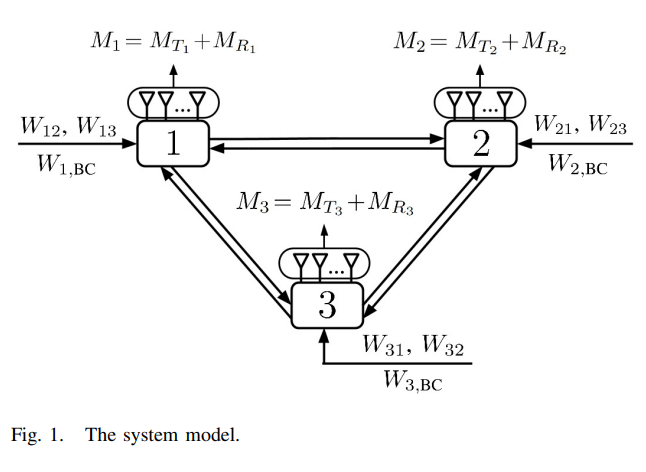
Degrees of Freedom of the Full-Duplex Asymmetric MIMO Three-Way Channel with Unicast and Broadcast Messages
In this paper, we characterize the total degrees of freedom (DoFs) of the full-duplex asymmetric multiple-input multiple- output (MIMO) three-way channel. Each node has a separate-antenna full-duplex MIMO transceiver with a different number of antennas, where each antenna can be configured for either signal transmission or reception. We study this system under two message configurations; the first configuration is when each node has two unicast messages to be delivered to the two other nodes, while the second configuration is when each node has two unicast messages as well as one broadcast
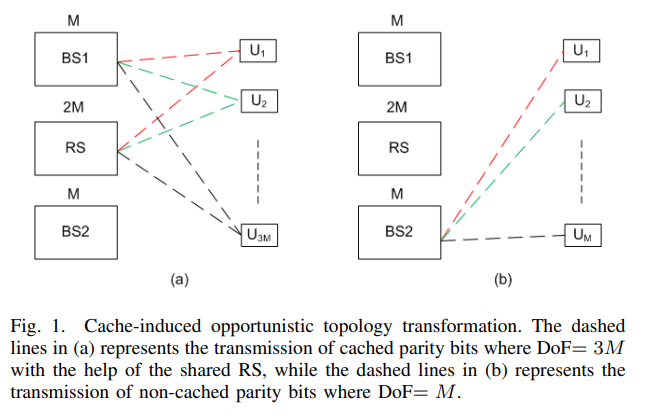
Degrees of freedom in cached MIMO relay networks with multiple base stations
The ability of physical layer relay caching to increase the degrees of freedom (DoF) of a single cell was recently illustrated. In this paper, we extend this result to the case of multiple cells in which a caching relay is shared among multiple non-cooperative base stations (BSs). In particular, we show that a large DoF gain can be achieved by exploiting the benefits of having a shared relay that cooperates with the BSs. We first propose a cache-assisted relaying protocol that improves the cooperation opportunity between the BSs and the relay. Next, we consider the cache content placement
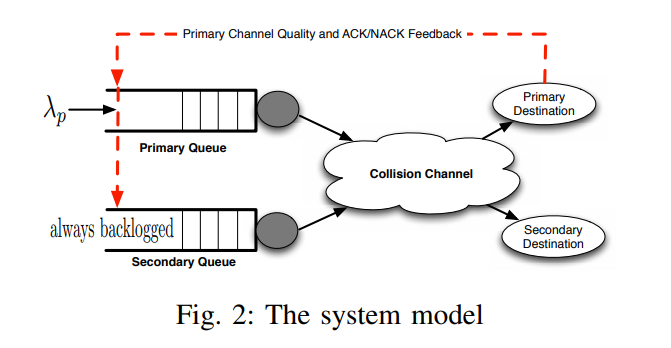
Hybrid feedback-based access scheme for cognitive radio systems
In this paper, a cognitive radio system is studied in which the secondary user (SU) leverages the primary user (PU) channel quality indicator feedback (CQI) and the PU automatic repeat request (ARQ). The SU randomly accesses the PU channel with access probabilities based on its spectrum sensing outcome and the PU feedbacks. The SU's access probabilities are selected though an optimization problem with the objective to maximize the SU's throughput while ensuring the stability of the PU's packet queue. This system is modeled using a multidimensional Markov chain. This model enabled us to derive
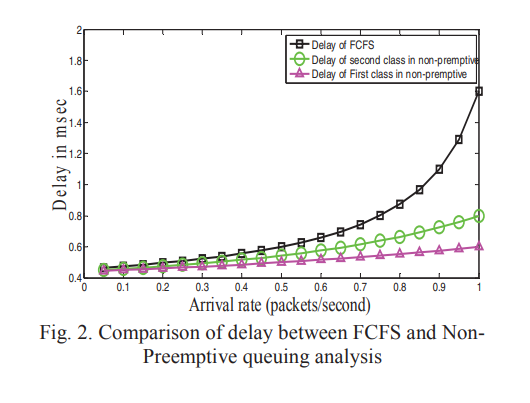
LTE dynamic scheduling scheme for massive M2M and H2H communication
Machine-to-Machine (M2M) has become a generally used term owing to the concept of the Internet of Things (IOT). M2M communications have numerous areas of implementation such as medicine, transportation, environmental monitoring, and smart grids. As the field of its implementation extends, the number of M2M equipment are projected to grow proportionally in the upcoming few years. Current cellular network technologies will not be able to cope with the expected increase in the number of M2M services while considering QoS as a major topic. Many applications of M2M are delay sensitive that will

Weighted sum degrees of freedom of the asymmetric MIMO y channel with common and private messages
This paper investigates the weighted sum degrees of freedom (DoF) of the MIMO Y channel that consists of three users, where the j-Th user is equipped with Mj antennas, and a relay equipped with N antennas. In this network, each user conveys two private messages to the other two users in addition to a common message directed to both of them. As there is no direct link between the users, communication occurs through the relay. We define a weighted sum DoF metric that integrates all the network messages and weights the common message by a factor of α. Then, we study the weighted sum DoF
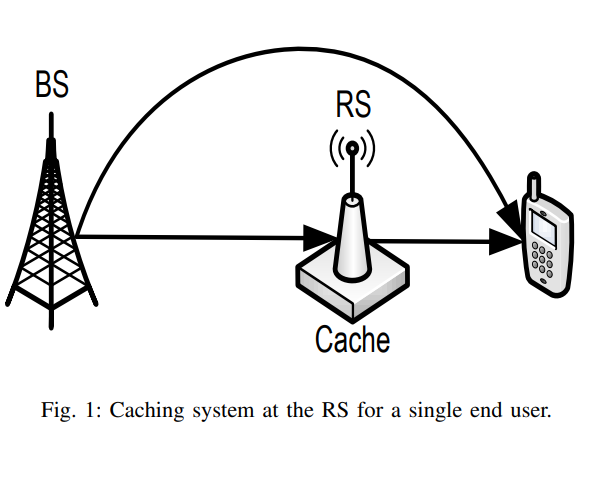
Dynamic proactive caching in relay networks
We investigate the performance of dynamic proactive caching in relay networks where an intermediate relay station caches content for potential future use by end users. A central base station proactively controls the cache allocation such that cached content remains fresh for consumption for a limited number of time slots called proactive service window. With uncertain user demand over multiple data items and dynamically changing wireless links, we consider the optimal allocation of relay stations cache to minimize the time average expected service cost. We characterize a fundamental lower
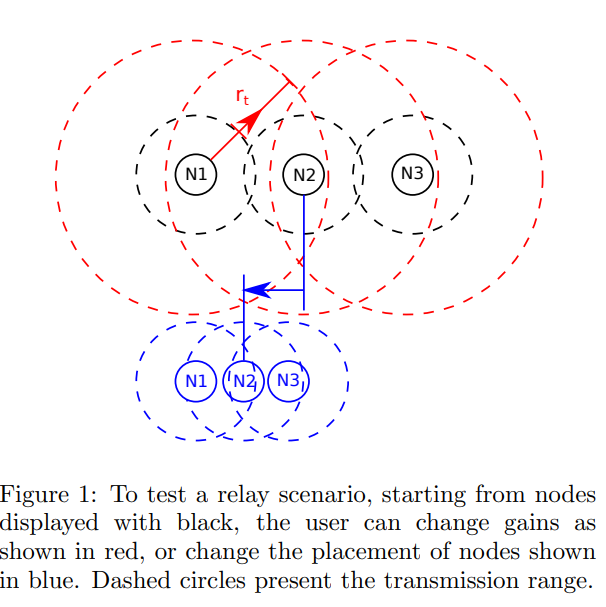
Topology realization using gain control for wireless testbeds
Wireless testbeds present a convenient and cost effective option for researchers in communications to validate their work. The main drawback of these testbeds is their reliance on nodes with fixed placement; this limits experimenters ability to test protocols that depend on a complex connectivity between the nodes such as relaying. In this work, we present a way to overcome this limitation; this method attempts to realize a given topology between a set of nodes by adjusting each node's transmit power and receive gain in a manner to connect and disconnect the links between the nodes as desired
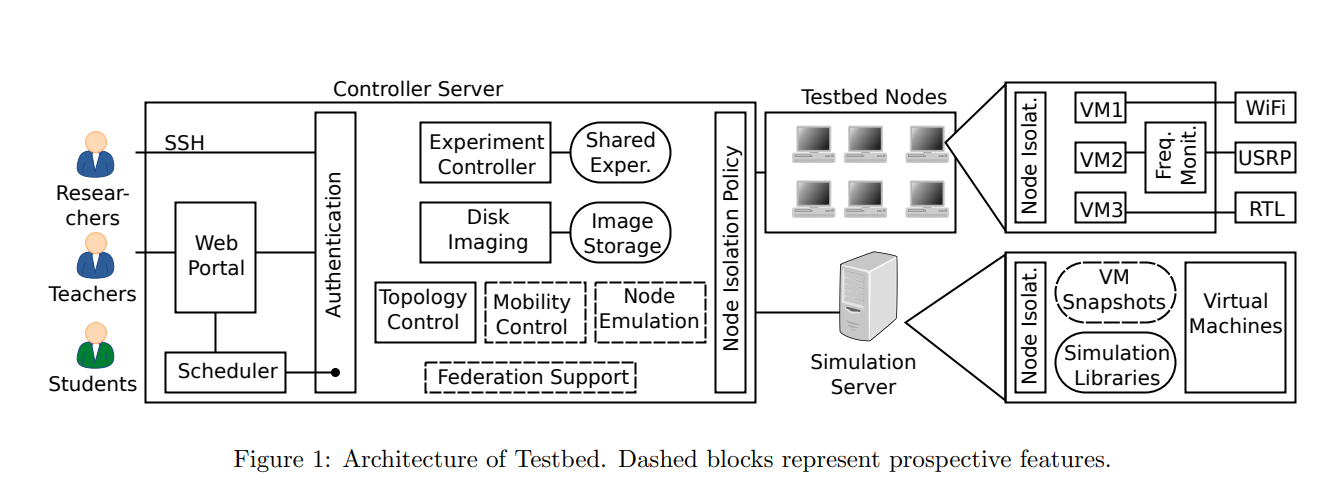
CRC: Collaborative research and teaching testbed for wireless communications and networks
The validation of wireless communications research, whether it is focused on PHY, MAC or higher layers, can be done in several ways, each with its limitations. Simulations tend to be simplified. Equipping wireless labs requires funding and time. Remotely accessible testbeds present a good option to validate research. The existing testbeds have gone a long way in building the infrastructure for managing and operating themselves. Yet, there is still space to improve the administration of resources whether it is nodes, frequency spectrum or storage space. In this work, we present the
Protocol design and stability analysis of cooperative cognitive radio users
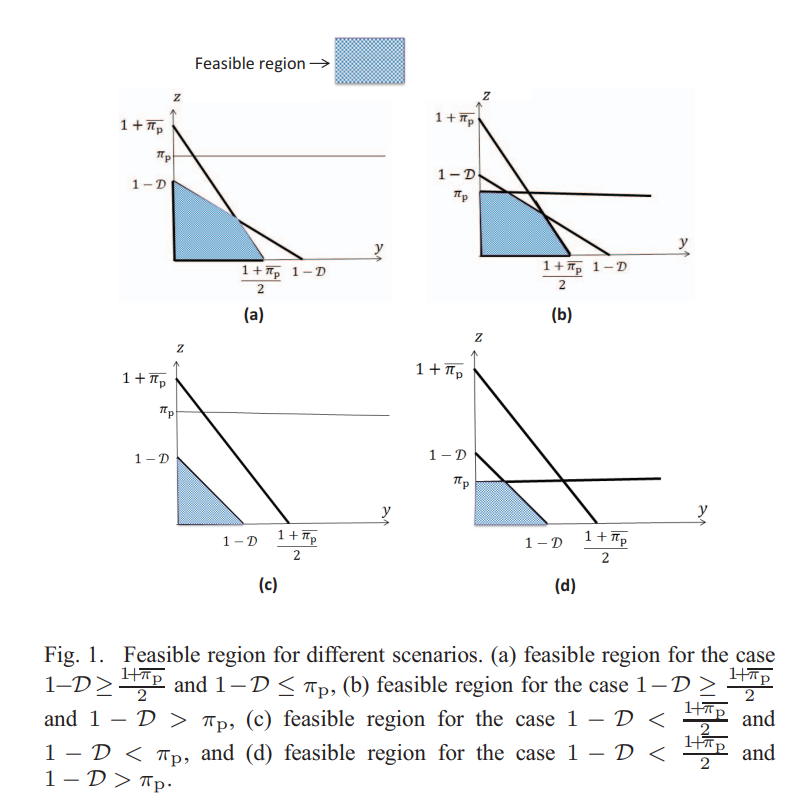
A single cognitive radio transmitter-receiver pair shares the spectrum with two primary users communicating with their respective receivers. Each primary user has a local traffic queue, whereas the cognitive user has three queues; one storing its own traffic while the other two are relaying queues used to store primary relayed packets admitted from the two primary users. A new cooperative cognitive medium access control protocol for the described network is proposed, where the cognitive user exploits the idle periods of the primary spectrum bands. Traffic arrival to each relaying queue is
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 38
- Next page ››
