On the flow anonymity problem in network coding
In this paper, we aim at protecting the privacy of the communicating parties while ensuring the authenticity of source nodes. In particular, we exploit intra-flow network coding to preserve the anonymity of communicating parties. Towards this objective, we propose an anonymity preservation scheme, namely closed group anonymity (CGA) that preserves the anonymity of the communicating parties via mixing their flows. Afterwards, we explore an instance of the Authentication-Privacy Trade-off in the context of Network Coding. We analyze the trade-off with the aid of the proposed anonymity scheme and

Demo: O'BTW - An opportunistic, similarity-based mobile recommendation system
[No abstract available]
Cross-layer minimum-delay scheduling and maximum-throughput resource allocation for multiuser cognitive networks
A cognitive network is considered that consists of a base station (BS) communicating with multiple primary and secondary users. Each secondary user can access only one of the orthogonal primary channels. A model is considered in which the primary users can tolerate a certain average delay. A special case is also considered in which the primary users do not suffer from any delay. A novel cross-layer scheme is proposed in which the BS performs successive interference cancellation and thus a secondary user can coexist with an active primary user without adversely affecting its transmission. A
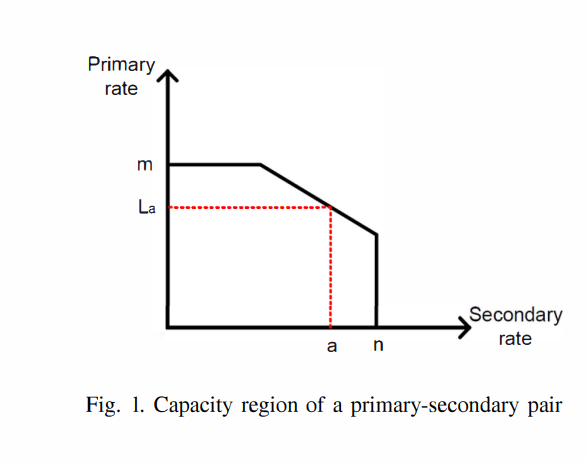
Cross-layer transmission rate/power policy for cognitive multi-access networks with imperfect sensing
We consider an underlay cognitive radio network with a primary user and a secondary user transmitting to a common receiver. The secondary user senses the primary user's channel to determine whether the primary user is active or idle. The secondary user's transmission policy is determined via a probabilistic cross-layer algorithm in which the secondary user's average packet delay is minimized subject to constraints on its average transmission power and the maximum probability of collision at the primary user. The proposed cross-layer algorithm determines the number of packets the secondary user
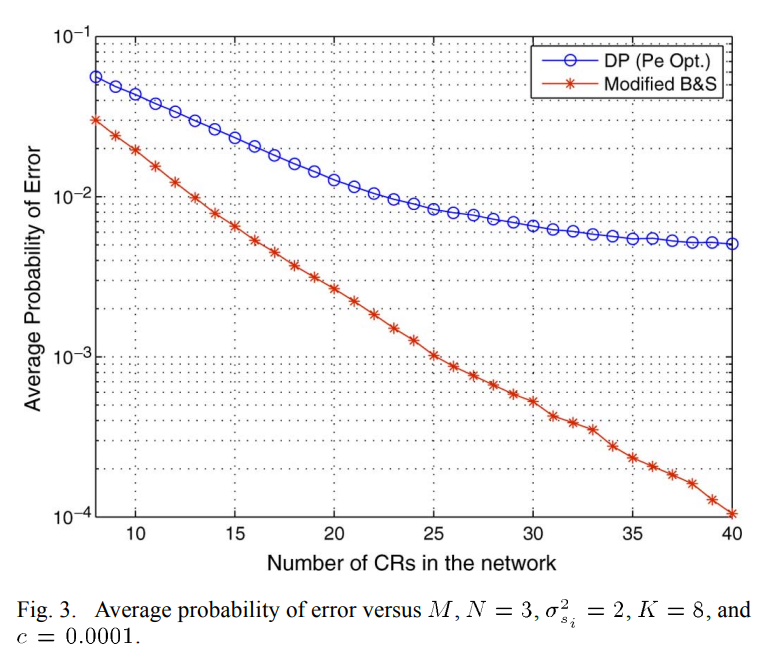
Distributed spectrum sensing with sequential ordered transmissions to a cognitive fusion center
Cooperative spectrum sensing is a robust strategy that enhances the detection probability of primary licensed users. However, a large number of detectors reporting to a fusion center for a final decision causes significant delay and also presumes the availability of unreasonable communication resources at the disposal of a network searching for spectral opportunities. In this paper, we employ the idea of sequential detection to obtain a quick, yet reliable, decision regarding primary activity. Local detectors take measurements, and only a few of them transmit the log likelihood ratios (LLR) to
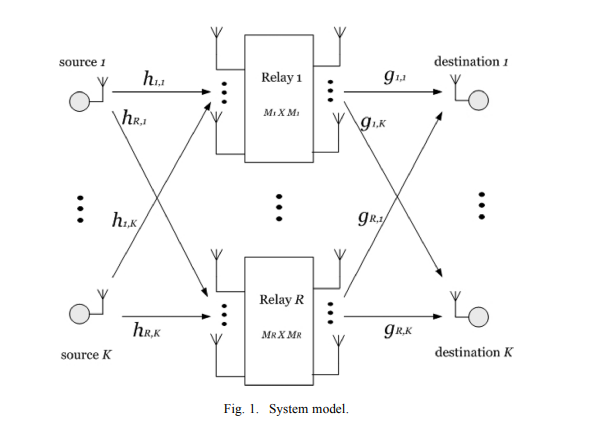
QOS-constrained multiuser peer-to-peer amplify-and-forward relay beamforming
A wireless communication scenario is considered with K single-antenna source-destination pairs communicating through several half-duplex amplify-and-forward MIMO relays where each source is targeting only one destination. The relay beamforming matrices are designed in order to minimize the total power transmitted from the relays subject to quality of service constraints on the received signal to interference-plus-noise ratio at each destination node. Due to the nonconvexity of this problem, several approximations have been used in the literature to find a computationally efficient solution. A
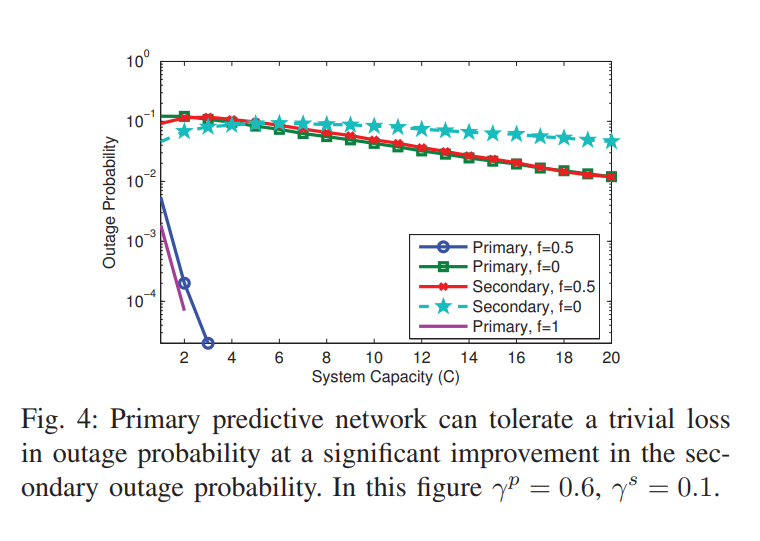
Proactive resource allocation in cognitive networks
Recently we have introduced the notion of proactive resource allocation and predictive wireless networks, where intelligent wireless networks are capable of tracking and exploiting the repetition patterns in human behavior while accessing the network resources. This predictability advantage grants the network more flexibility to schedule users' requests over a longer time horizon, and thereby significantly improves the quality of service (QoS) defined as outage probability. In this paper we extend our analysis to consider a network of two different QoS classes. The first is a primary class
Practical provably secure communication for half-duplex radios
In this paper, we present a practical and provably secure two-way wireless communication scheme in the presence of a passive eavesdropper. The scheme implements a randomized scheduling and power allocation mechanism, where each legitimate node transmits in random time slots and with random transmit power. Such randomization results in ambiguity at the eavesdropper with regard to the origin of each transmitted frame. The scheme is analyzed in a time-varying binary block erasure channel model and secrecy outage probabilities are derived and empirically evaluated. The scheme is implemented over
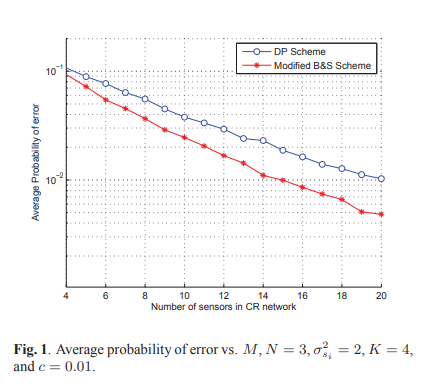
Cooperative sensing with sequential ordered transmissions to secondary fusion center
Successful spectrum sharing in a cognitive radio network depends on the correct and quick detection of primary activity. Cooperative spectrum sensing is therefore suggested to enhance the reliability of such detection. However, it renders another significant problem of increased detection delay and traffic burden. Moreover, efficient schemes for multi-sensor data fusion should be designed. In this paper, we employ sequential detection scheme together with ordered transmissions from cognitive detectors. We derive two sequential schemes, one that is capable of achieving the minimum probability
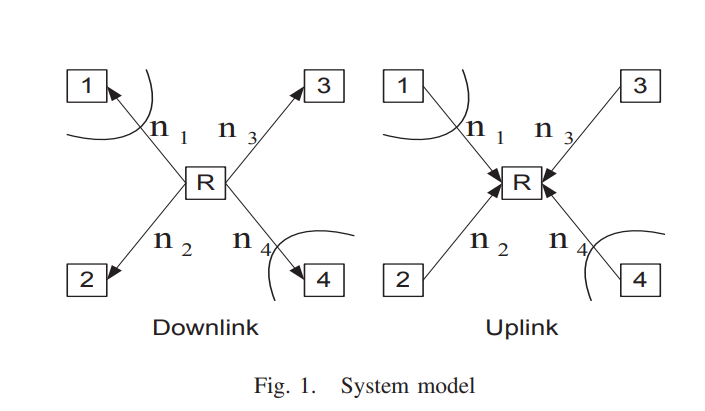
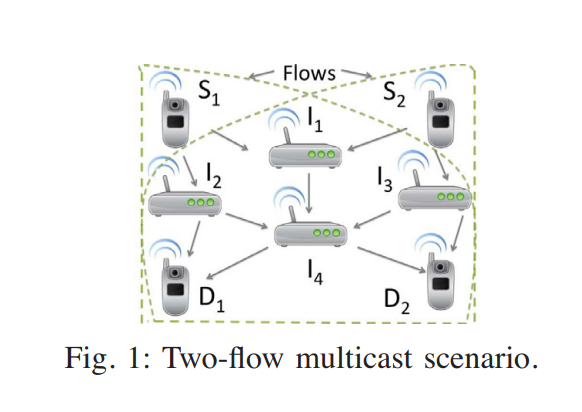
On the deterministic multicast capacity of bidirectional relay networks
In this paper, we completely characterize the deterministic multicast capacity region of the symmetric two-pair bidirectional half duplex relay network with private messages. Towards this end, we first develop a new upper bound on the deterministic capacity region, based on the notion of a one-sided genie. We then proceed to construct novel detour schemes that achieve the upper bound by routing the bits intended for a certain receiver through the network rather than sending it directly. To the best of the authors' knowledge, this scenario corresponds to one of the rare cases where coding
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 40
- Next page ››
