
Quantitative assessment of Diabetic Macular Edema using fluorescein leakage maps
Diagnosis of Diabetic Macular Edema (DME) from Fundus Fluorescein Angiography (FFA) image sequences is a standard clinical practice. Nevertheless, current methods depend on subjective evaluation of the amount of fluorescein leakage in the images which lack reproducibility and require well-trained grader. In this work, we present a method for processing FFA images to generate a fluorescein leakage map that can be used for quantitative evaluation of DME. An essential step in the proposed method is to model the spatial distribution of the image intensity within the macula. This model, which
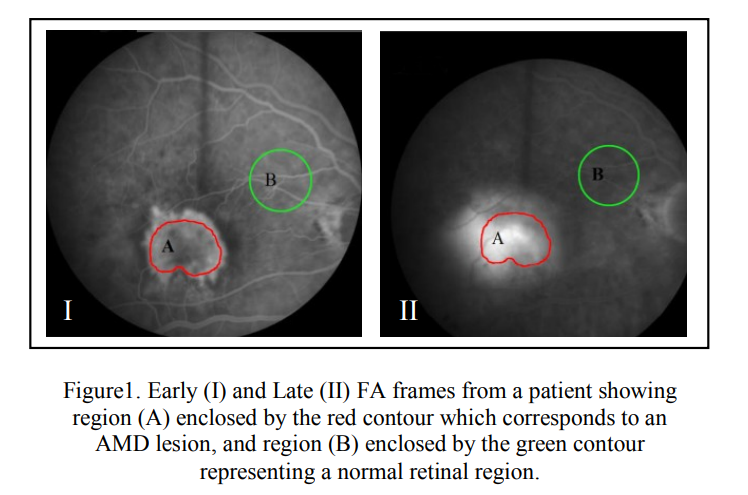
Quantitative assessment of age-related macular degeneration using parametric modeling of the leakage transfer function: Preliminary results
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a major cause of blindness and visual impairment in older adults. The wet form of the disease is characterized by abnormal blood vessels forming a choroidal neovascular membrane (CNV), that result in destruction of normal architecture of the retina. Current evaluation and follow up of wet AMD include subjective evaluation of Fluorescein Angiograms (FA) to determine the activity of the lesion and monitor the progression or regression of the disease. However, this subjective evaluation prevents accurate monitoring of the disease progression or regression
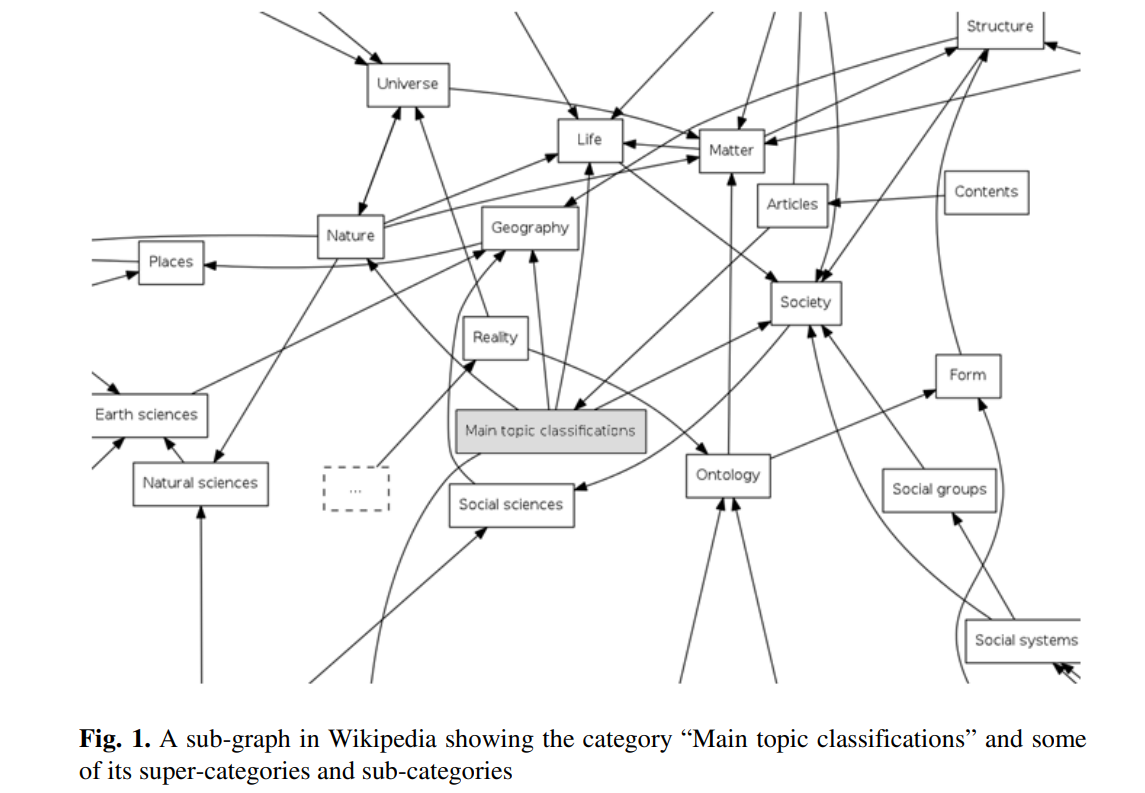
An approach for deriving semantically related category hierarchies from Wikipedia category graphs
Wikipedia is the largest online encyclopedia known to date. Its rich content and semi-structured nature has made it into a very valuable research tool used for classification, information extraction, and semantic annotation, among others. Many applications can benefit from the presence of a topic hierarchy in Wikipedia. However, what Wikipedia currently offers is a category graph built through hierarchical category links the semantics of which are un-defined. Because of this lack of semantics, a sub-category in Wikipedia does not necessarily comply with the concept of a sub-category in a
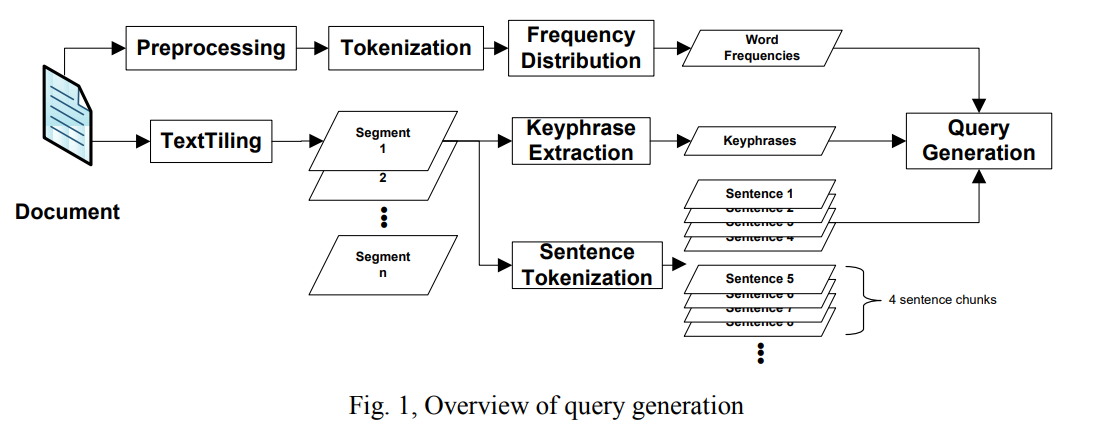
Plagiarism candidate retrieval using selective query formulation and discriminative query scoring: Notebook for PAN at CLEF 2013
This paper details the approach of implementing an English plagiarism source retrieval system to be presented at PAN 2013. The system uses the TextTiling algorithm to break a given document into segments that are centered around certain topics within the document. From these segments, keyphrases are generated using the KPMiner keyphrase extraction system. These keyphrases and segments are then used in generating queries indicative of the segment, and consequently the document. The queries are submitted to ChatNoir for finding plagiarism sources in the ClueWeb09 corpus from which the pan13
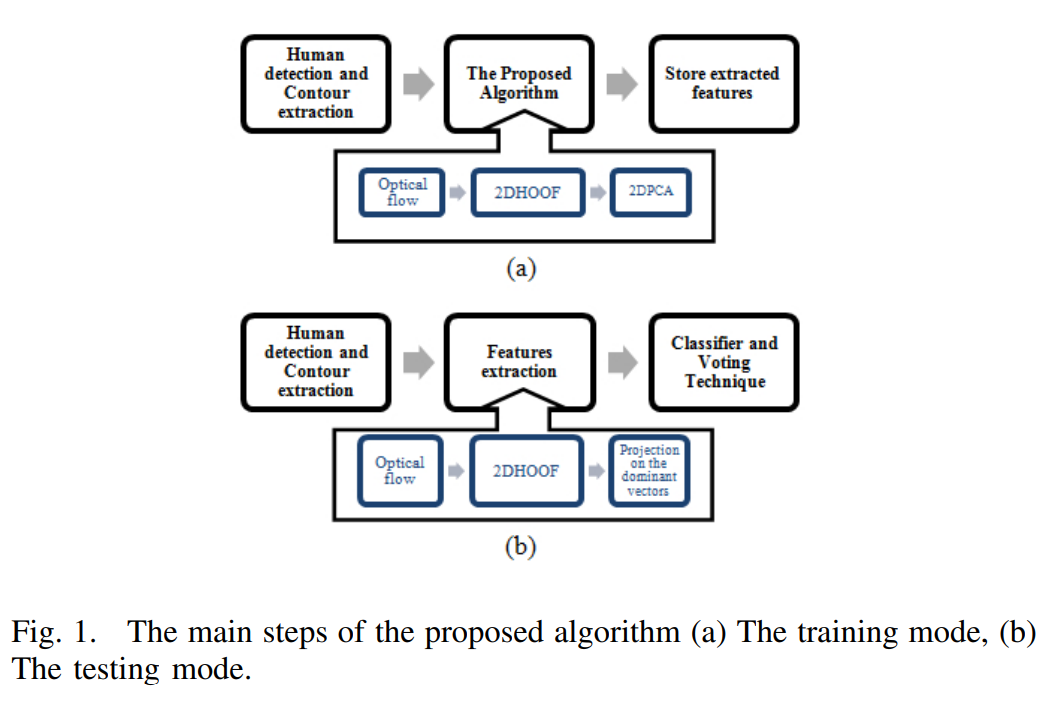
2DHOOF-2DPCA contour based optical flow algorithm for human activity recognition
A novel algorithm for human activity recognition is presented in this paper. This approach is based on a new 2D representation for the Histogram of Oriented Optical Flow (2DHOOF) describing the motion of the actor's contour, where one multi-layer 2D-histogram per video is constructed. Each histogram layer consists of 2D bins (layers) that represent different range of angles. Applying our 2DHOOF features descriptors on the actor's contour reduces the storage requirement and the computation complexity since a sparse optical flow is calculated instead of dense optical flow. In addition, it is
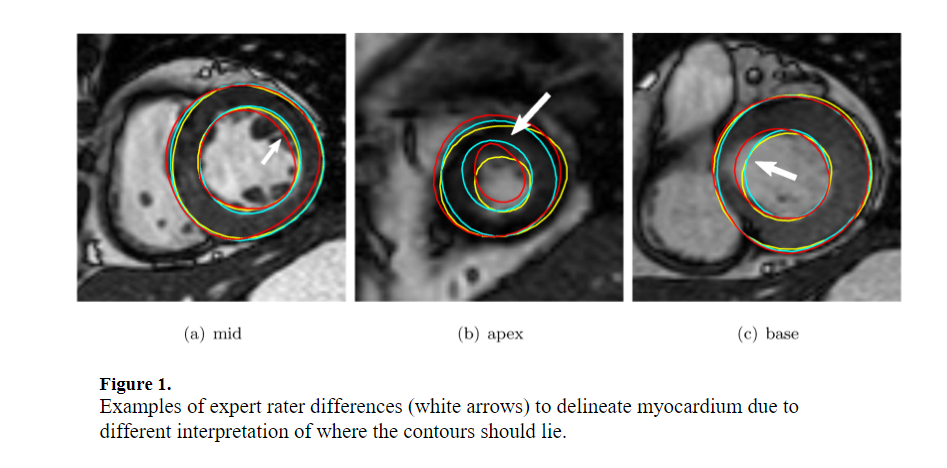
A collaborative resource to build consensus for automated left ventricular segmentation of cardiac MR images
A collaborative framework was initiated to establish a community resource of ground truth segmentations from cardiac MRI. Multi-site, multi-vendor cardiac MRI datasets comprising 95 patients (73 men, 22 women; mean age 62.73. ±. 11.24. years) with coronary artery disease and prior myocardial infarction, were randomly selected from data made available by the Cardiac Atlas Project ( Fonseca et al., 2011). Three semi- and two fully-automated raters segmented the left ventricular myocardium from short-axis cardiac MR images as part of a challenge introduced at the STACOM 2011 MICCAI workshop (
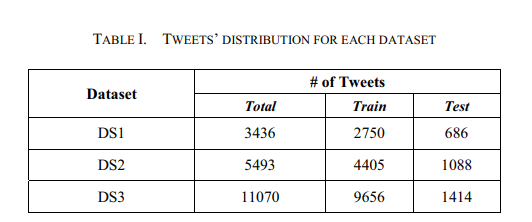
Which configuration works best? an experimental study on supervised Arabic twitter sentiment analysis
Arabic Twitter Sentiment Analysis has been gaining a lot of attention lately with supervised approaches being exploited widely. However, to date, there has not been an experimental study that examines how different configurations of the Bag of Words model, text representation scheme, can affect various supervised machine learning methods. The goal of the presented work is to do exactly that. Specifically, this work examines which configurations work best for each of three machine learning approaches that have shown good results when applied on the task of sentiment analysis, namely: Support
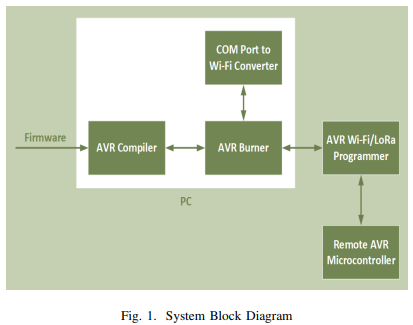
On Flashing over the Air 'FOTA' for IoT Appliances - An ATMEL Prototype
Wireless flashing over the air is a challenging task. Appliances are required to update its flash or EEPROM via a remote system update. However, direct connectivity via a wire is not available. Within the application of consumer electronics, such as utility meters or other appliances, there is always a room to update the appliance remotely for optimal operation. In this paper, we present a new system for remotely flashing all models of ATMEL AVR microcontrollers via Wi-Fi and LoRa technologies. Also, we will demonstrate an experimental work to prove our new methodology as well as applying it
Correlation between protocol selection and packet drop attack severity in ad hoc networks
Mobile Ad hoc Network (MANET) are self-configuring, dynamic, networks that consist of nodes with various capabilities communicating through a wide spectrum of frequencies. Such flexibility in infrastructure and design comes with great risks in form of attacks on its nodes and the routing protocols that connect the network together. The aim of this paper is to explore the correlation between the attack severity and the protocol used. In this paper, the comparison will be mainly between the Dynamic Source Routing (DSR) protocol, and the Ad-Hoc On-Demand Distance Vector (AODV) protocol and how
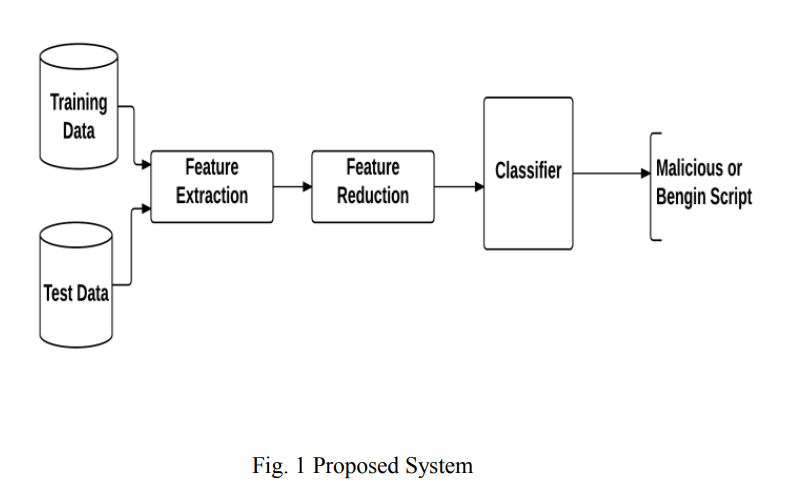
Malicious VBScript detection algorithm based on data-mining techniques
Malware attacks are amongst the most common security threats. Not only malware incidents are rapidly increasing, but also the attack methodologies are getting more complicated. Moreover malware writers expand in using different platforms and languages. This raises the need for new detection methods which support more reliable, low resource consuming and fast solutions. In this paper, a new algorithm has been proposed based on machine learning techniques and static analysis features to detect malicious scripts specifically for VBScript files. Experimental results show that the proposed
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 19
- Next page ››
