In silico identification of potential key regulatory factors in smoking-induced lung cancer
Background: Lung cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide and is the most commonly diagnosed cancer. Like other cancers, it is a complex and highly heterogeneous disease involving multiple signaling pathways. Identifying potential therapeutic targets is critical for the development of effective treatment strategies. Methods: We used a systems biology approach to identify potential key regulatory factors in smoking-induced lung cancer. We first identified genes that were differentially expressed between smokers with normal lungs and those with cancerous lungs, then integrated
Hadronization correspondence of Hawking-Unruh radiation from rotating and electrically charged black holes
The proposed correspondence between the Hawking-Unruh radiation mechanism in rotating, electrically-charged, and electrically-charged-rotating black holes and the hadronization process in high-energy collisions is assumed here. This allows us to determine the well-profound freezeout parameters characterizing the heavy-ion collisions. Furthermore, black holes thermodynamics is found analogous to a to that of the high-energy collisions. We also introduce a relation expressing the dependence of the angular momentum and the angular velocity deduced from rotating black holes on the chemical
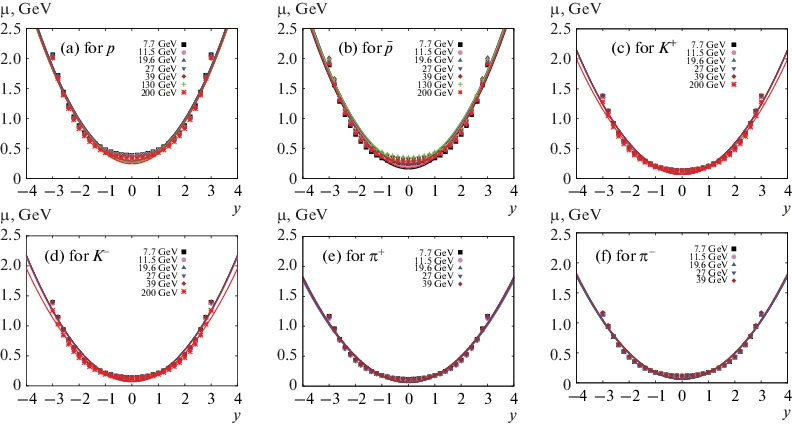
Almost Entirely Empirical Estimation for Chemical Potential
Abstract: Based on statistical thermal approaches, the transverse momentum distribution of the well-identified produced particles, π+, π–, K+, K–, p, and (Fromula presented.), is studied. We aim at introducing a novel almost entirely empirical estimation for the inclusive chemical potential μ. From the partition function of a grand-canonical ensemble, we propose a generic expression for the dependence of μ on the rapidity y. Then, by fitting this expression with the experimental results of the most central p⊥ and d2N/2πp⊥dp⊥dy, at 7.7, 11.5, 19.6, 27, 39, 130, 200 GeV, we introduce a generic
Guidance optimization for tactical homing missiles and air defense systems
The aim of this paper is to develop a functional approach to optimize the engagement effectiveness of the tactical homing missiles and air defense systems by utilizing the differential geometric concepts. In this paper the engagement geometry of the interceptor and the target is developed and expressed in differential geometric terms in order to demonstrate the possibilities of the impact triangles and specify the earliest interception based on the direct intercept geometry. Optimizing the missile heading angle and suitable missile velocity against the target velocity is then examined to
Assessment of cardiac mass from tagged magnetic resonance images
Purpose: Tagged and cine magnetic resonance imaging (tMRI and cMRI) techniques are used for evaluating regional and global heart function, respectively. Measuring global function parameters directly from tMRI is challenging due to the obstruction of the anatomical structure by the tagging pattern. The purpose of this study was to develop a method for processing the tMRI images to improve the myocardium-blood contrast in order to estimate global function parameters from the processed images. Materials and methods: The developed method consists of two stages: (1) removing the tagging pattern
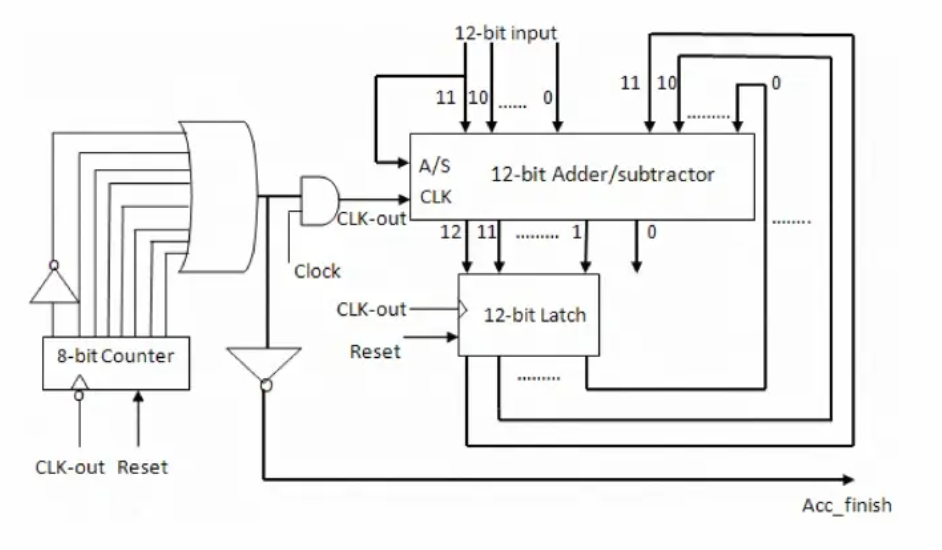
Synthesizable SVA protocol checker generation methodology based on TDML and VCD file formats
System Verilog Assertions (SVA) is widely used by hardware designers and verification engineers to apply Assertion Based Verification (ABV) methodology on their hardware designs. However, the complexity in understanding different protocol standards in general and JEDEC memory protocol standards in specific imposes numerous difficulties on designers and verification engineers when translating design specifications into SVA. This motivated us to devise new techniques that can be used to automatically generate SVA for DDR memory protocols with no ambiguity when capturing design requirements from
Real-Time Dorsal Hand Recognition Based on Smartphone
The integration of biometric recognition with smartphones is necessary to increase security, especially in financial transactions such as online payments. Vein recognition of the dorsal hand is superior to other methods such as palm, finger, and wrist, as it has a wide area to be captured and does not have any wrinkles. Most current systems that depend on dorsal hand vein recognition do not work in real-time and have poor results. In this paper, a dorsal hand recognition system working in real-time is proposed to achieve good results with a high frame rate. A contactless device consists of a
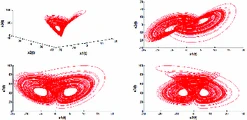
Control of new type of fractional chaos synchronization
Based on stability theory of linear fractional order systems and stability theory of linear integer order systems, the problem of coexistence of various types of synchronization between different dimensional fractional chaotic systems is investigated in this paper. Numerical and simulation results have clearly shown the effectiveness of the novel approach developed herein. © 2018, Springer International Publishing AG.
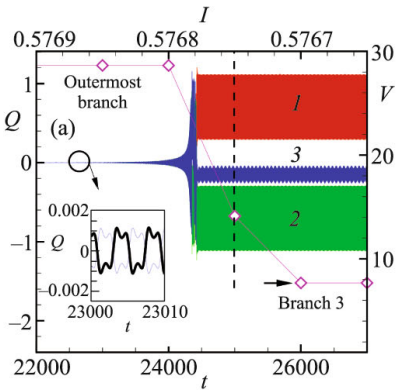
Breathing charge density waves in intrinsic Josephson junctions
We demonstrate the creation of a charge density wave (CDW) along a stack of coupled Josephson junctions (JJs) in layered superconductors. Electric charge in each superconducting layer oscillates around some average value, forming a breathing CDW. We show the transformation of a longitudinal plasma wave to CDW in the state corresponding to the outermost branch. Transition between different types of CDW's related to the inner branches of IV characteristic is demonstrated. The effect of the external electromagnetic radiation on the states corresponding to the inner branches differs crucially from
A simplification in integral frequency offset estimation based on joint detection algorithm for WiMAX 802.16e
Initial downlink synchronization for orthogonal frequency division multiple access ( OFDMA ) network access involves timing and frequency synchronization. The frequency offset is produced by oscillator drifts and time-varying Doppler shifts. In mobile WiMAX 802.16e carrier frequency offset (CFO) can be divided into: integral carrier frequency offset (ICFO) and fractional carrier frequency offset (FCFO). There are mainly three methods for CFO estimation: data-aided method, blind and semi-blind. This paper is based on the semi-blind method presented in "Joint detection of integral carrier
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 22
- Next page ››
