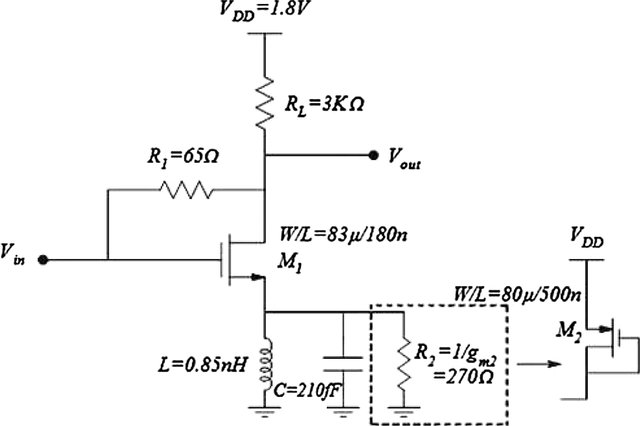
Ultra-low-power compact single-transistor all-pass filter with tunable delay capability
A novel first-order voltage-mode all-pass filter is introduced as a true-time delay (TTD) cell with tunable delay capability. The proposed filter consists of a single transistor, a varactor, and four resistors. The operation of the proposed filter is verified by post-layout simulations in 65-nm CMOS technology. The post-layout simulation results of a single stage of the proposed filter demonstrate a wideband operation range of 0.3-3 GHz and a continuously tunable delay in the range 12–40 ps. The circuit layout occupies 375 μm2 and the total power consumption of the circuit is 183.7 μW. © 2021
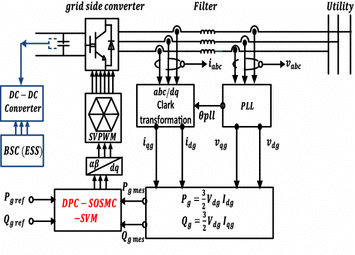
Effective supervisory controller to extend optimal energy management in hybrid wind turbine under energy and reliability constraints
One of the major factors that can increase the efficiency of wind turbines (WTs) is the simultaneous control of the different parts in several operating area. The main problem associated with control design in wind generator is the presence of asymmetric in the dynamic model of the system, which makes a generic supervisory control scheme for the power management of WT complicated. Consequently, supervisory controller can be utilized as the main building block of a wind farm controller (offshore), which meets the grid code requirements and can increased the efficiency and protection of WTs in
Hyperchaos and adaptive control of a novel hyperchaotic system with two quadratic nonlinearities
Liu-Su-Liu chaotic system (2007) is one of the classical 3-D chaotic systems in the literature. By introducing a feedback control to the Liu-Su-Liu chaotic system,we obtain a novel hyperchaotic system in this work, which has two quadratic nonlinearities. The phase portraits of the novel hyperchaotic system are displayed and the qualitative properties of the novel hyperchaotic system are discussed. We show that the novel hyperchaotic system has a unique equilibrium point at the origin, which is unstable. The Lyapunov exponents of the novel 4-D hyperchaotic system are obtained as L1 = 1.1097, L2
Hyperchaos and adaptive control of a novel hyperchaotic system with two quadratic nonlinearities
Liu-Su-Liu chaotic system (2007) is one of the classical 3-D chaotic systems in the literature. By introducing a feedback control to the Liu-Su-Liu chaotic system,we obtain a novel hyperchaotic system in this work, which has two quadratic nonlinearities. The phase portraits of the novel hyperchaotic system are displayed and the qualitative properties of the novel hyperchaotic system are discussed. We show that the novel hyperchaotic system has a unique equilibrium point at the origin, which is unstable. The Lyapunov exponents of the novel 4-D hyperchaotic system are obtained as L1 = 1.1097, L2
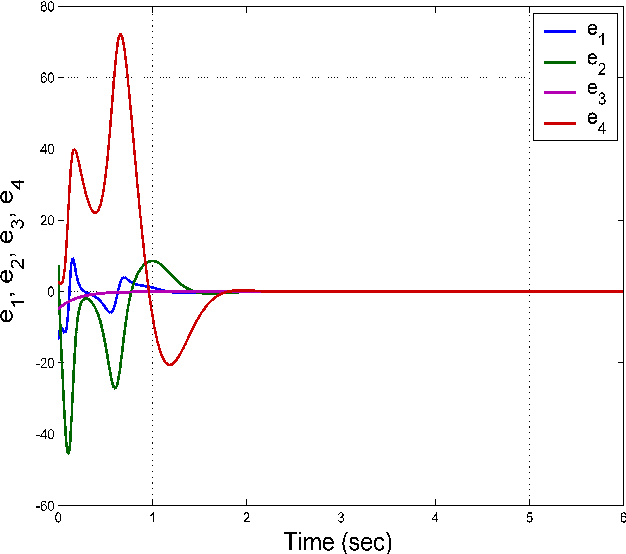
A novel 4-D hyperchaotic system with two quadratic nonlinearities and its adaptive synchronisation
This work announces an eleven-term novel 4-D hyperchaotic system with two quadratic nonlinearities. A qualitative analysis of the properties of the novel 4-D hyperchaotic system is presented. A special feature of our novel hyperchaotic system is that it has three equilibrium points of which two are unstable and one is locally asymptotically stable. The Lyapunov exponents of the novel hyperchaotic system are obtained as L1 = 1.5146, L2 = 0.2527, L3 = 0 and L4 = −12.7626. The Kaplan-Yorke dimension of the novel hyperchaotic system is derived as DKY = 3.1385. Next, this work describes the design
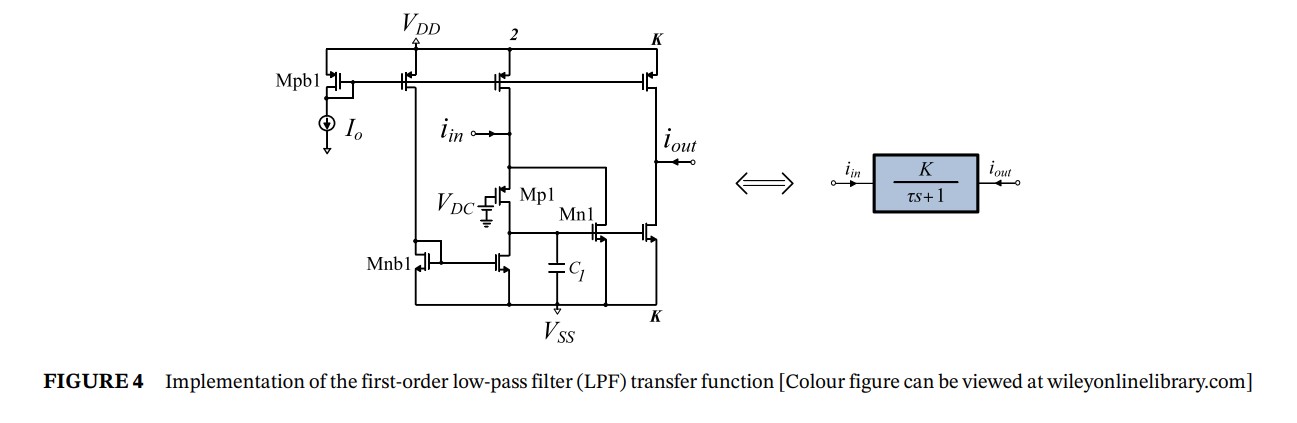
Partial fraction expansion–based realizations of fractional-order differentiators and integrators using active filters
Approximations of the fractional-order differentiator and integrator operators s±r are proposed in this work. These approximations target the realization of these operators using standard active filter transfer functions. Hence, circuit implementations in integrated circuit form or in discrete component form are significantly facilitated. Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) realizations of the proposed approximations are given and validated via simulations using the AMS 0.35 μm CMOS technology, while experimental results using operational amplifier circuits are tested and confirm
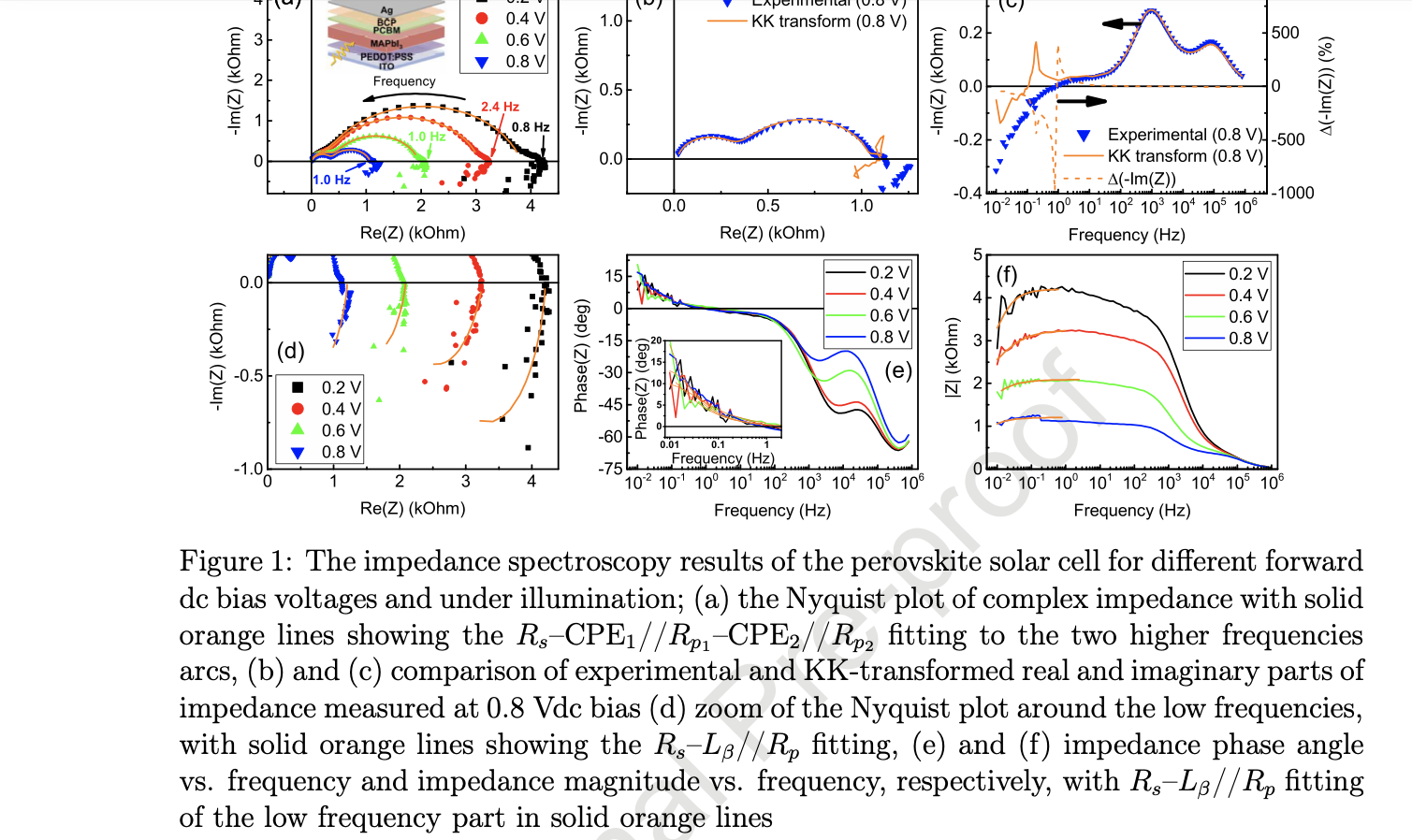
Active circuit model of low-frequency behavior in perovskite solar cells
The low-frequency impedance hook in perovskite solar cells (PSC) is a feature that has been frequently associated with the behavior of passive circuits of inductors or negative capacitances. However, if the experimental impedance data do not transform according to the Kramers-Kronig (KK) relations, the system does not fulfill the conditions of linearity, stability, causality and finiteness necessary for validating the impedance measurements and fitting it using passive circuit elements. In this study, we found that the impedance hook in a standard PSC configuration is not compliant with the KK
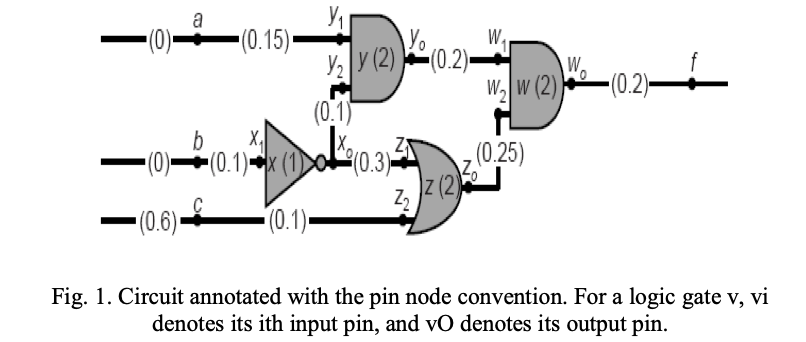
Accurate timing analysis of combinational logic cells engine using adaptive technique based on current source model
As the usage of very large scale integration (VLSI) in computers continues to increase, debugging of timing problems on actual hardware becomes more and more difficult. The post-layout gate-level simulation constitutes a critical design step for timing closure. The major drawback of traditional post-layout gate-level simulation is its long analysis time, which increases as design complexity increases. An alternative method is static timing analysis (STA), which can reduce analysis time. Going deeper through the nanometer technology, new STA techniques have to be present to provide more

A new signaling technique for a low power on-chip SerDes transceivers
This paper represents a new self timed signaling technique for low power SerDes transceiver. A three level coding technique enables extracting the clock from the data using simple phase detector rather than using complex power hungry blocks such as Clock Data Recovery (CDR) or a Phase Locked Loop (PLL). This SerDes transceiver was implemented using 90nm TSMC technology. The transmitter serializes 8 parallel bits at 1.125GHz, and multiplexes the 10Gbps serial data stream with a 20GHz clock on a single line using three level signaling. The total power consumed in the Tx/Rx pair with the
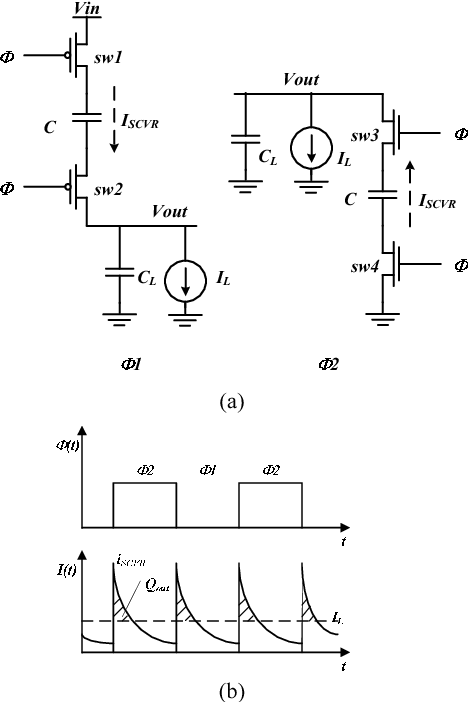
A novel control technique to eliminate output-voltage-ripple in switched-capacitor DC-DC converters
A novel ripple mitigation technique is proposed for switched-capacitor voltage regulators (SCVR), which eliminates the output voltage ripple without using multi-phase interleaving. An inner control loop matches the SCVR's switch current to the load current on a cycle by cycle basis. A 2-phase 32 SCVR is designed in 45-nm CMOS process with the proposed control. For a 1.8 V to 1.05 V /40 mA converter, the proposed mitigation loop reduces the peak-to-peak output ripple from 330 mVp-p to 17 mVp-p, using total output capacitance of 4 nF/A. In addition, the proposed technique yields excellent
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 44
- Next page ››
