CNTFET design of a multiple-port ternary register file
Ternary number system offers higher information processing within the same number of digits when compared to binary systems. Such advantage motivated the development of ternary processing units especially with CNTFET which offers better power and delay results compared to CMOS-based realization. In this paper, we propose a variety of circuit realizations for the ternary memory elements that are needed in any processor including ternary D-latch, and ternary D-flip-flop. These basic building blocks are then used to design a ternary register file with multiple read and write ports. This paper is
Discretization of emperor penguins colony algorithms with application to modular product design
Modularity concepts attracted the attention of many researchers as it plays an important role in product design problems. Modularity requires dividing a product into a set of modules that are independent between each other and dependent within. The product is represented using Design Structure Matrix (DSM). DSM works as a system representation tool; it visualizes the interrelationship between product elements. In this research, a comparison is conducted between four optimization algorithms: Emperor Penguins Colony (EPC), First Modified Emperor Penguins Colony (MEPC1), Second Modified Emperor
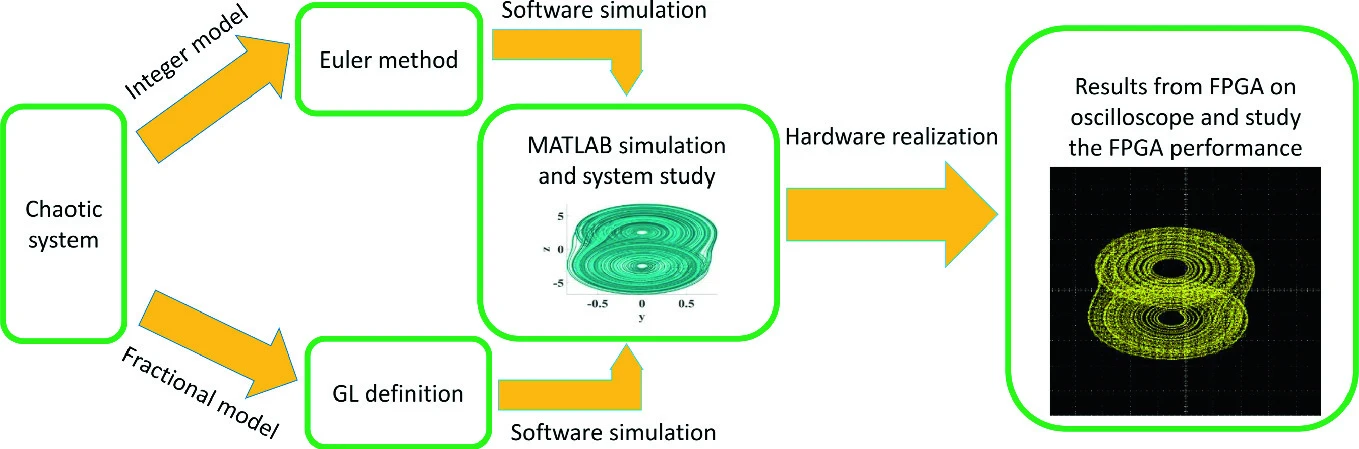
Fractional X-shape controllable multi-scroll attractor with parameter effect and FPGA automatic design tool software
This paper proposes a new fractional-order multi-scrolls chaotic system. More complex systems and flexible ranges of the chaotic behavior are obtained due to the extra parameters added by the fractional-order. The proposed system has novel complex chaotic behaviors. The effect of changing the system parameters on the system behavior is investigated and their bifurcation diagrams have been provided. The MLE for the proposed system in integer and fractional domain has been discussed. It shows that the proposed chaotic system is richer in the case of fractional-order. A novel FPGA design
Control of continuous-time chaotic (hyperchaotic) systems: F-M synchronisation
In this paper, a new type of chaos synchronisation between different dimensional chaotic systems is proposed. The novel scheme is called F-M synchronisation, since it combines the inverse generalised synchronisation with the matrix projective synchronisation. In particular, the proposed approach enables F-M synchronisation to be achieved between n-dimensional master system and m-dimensional slave system in different dimensions. The technique, which exploits nonlinear controllers, stability property of integer-order linear continuous-time dynamical systems and Lyapunov stability theory, proves
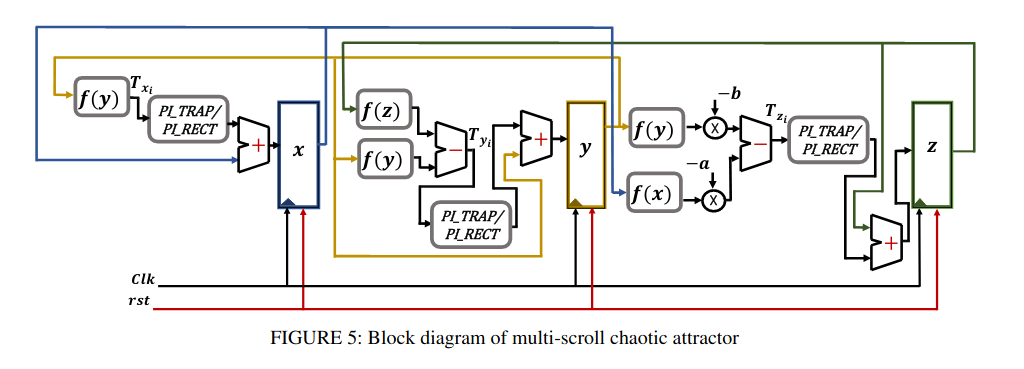
FPGA implementation of integer/fractional chaotic systems
Chaotic systems have remarkable importance in capturing some complex features of the physical process. Recently, fractional calculus becomes a vigorous tool in characterizing the dynamics of complex systems. The fractional-order chaotic systems increase the chaotic behavior in new dimensions and add extra degrees of freedom, which increase system controllability. In this chapter, FPGA implementation of different integer and fractional-order chaotic systems is presented. The investigated integer-order systems include Chua double scroll chaotic system and the modified Chua N-scroll chaotic
Numerical Simulations and FPGA Implementations of Fractional-Order Systems Based on Product Integration Rules
Product integration (PI) rules are well known numerical techniques that are used to solve differential equations of integer and, recently, fractional orders. Due to the high memory dependency of the PI rules used in solving fractional-order systems (FOS), their hardware implementation is very difficult and resources-demanding. In this paper, modified versions of the PI rules are introduced to facilitate their digital implementations. The studied rules are PI rectangular, PI trapezoidal, and predict-evaluate-correct-evaluate (PECE) rules. The three modified versions of the PI rules are
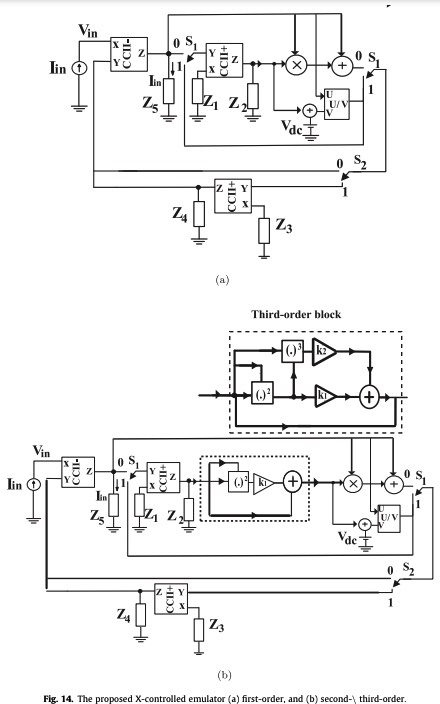
A general emulator for fractional-order memristive elements with multiple pinched points and application
In this paper, X-controlled universal fractional-order memelements (FOMEs) emulator is proposed. The emulation circuit is realized using second-generation current conveyor (CCII) and analog voltage multiplier (AVM)/divider block with two switches to control the type of memelements and emulator mode. The effect of the fractional-order capacitor (FOC) on the pinched hysteresis loop (HL) area and the range of frequency is discussed at different fractional-order α. Additionally, the higher-order meminductor, memristor, memcapacitor, and inverse memristor are discussed presenting multiple pinched
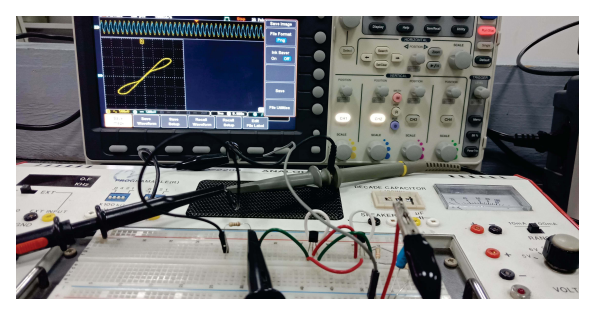
A Simple BJT Inverse Memristor Emulator and Its Application in Chaotic Oscillators
A generalized inverse memristor emulator is proposed based on two BJT transistors as a diode connected with a first order parallel RC filter. The mathematical model of the circuit is presented where the pinched hysteresis loops (PHLs) with different periodic stimuli are analyzed. The numerical, P-Spice simulations and experimental results are presented indicating that the introduced emulator is a simple voltage-controlled generalized inverse memristor. The results show that the PHLs area is increased with increasing the applied frequency. In addition, the proposed emulator is employed in a
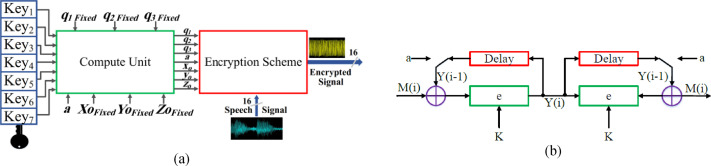
FPGA implementation of sound encryption system based on fractional-order chaotic systems
This paper introduces design and FPGA implementation of sound encryption system based on a fractional-order chaotic system. Also, it presents the FPGA implementation of Tang, Yalcin, and Özoǧuz fractional order chaotic systems. The Grunwald-Letnikov (GL) definition is used to generalize the investigated systems into the fractional-order domain. Also, the variation of parameters for each system is investigated against the window size of the GL definition. Xilinx ISE 14.5 is used to simulate the proposed design. Also, some hardware reduction techniques are applied to decrease hardware
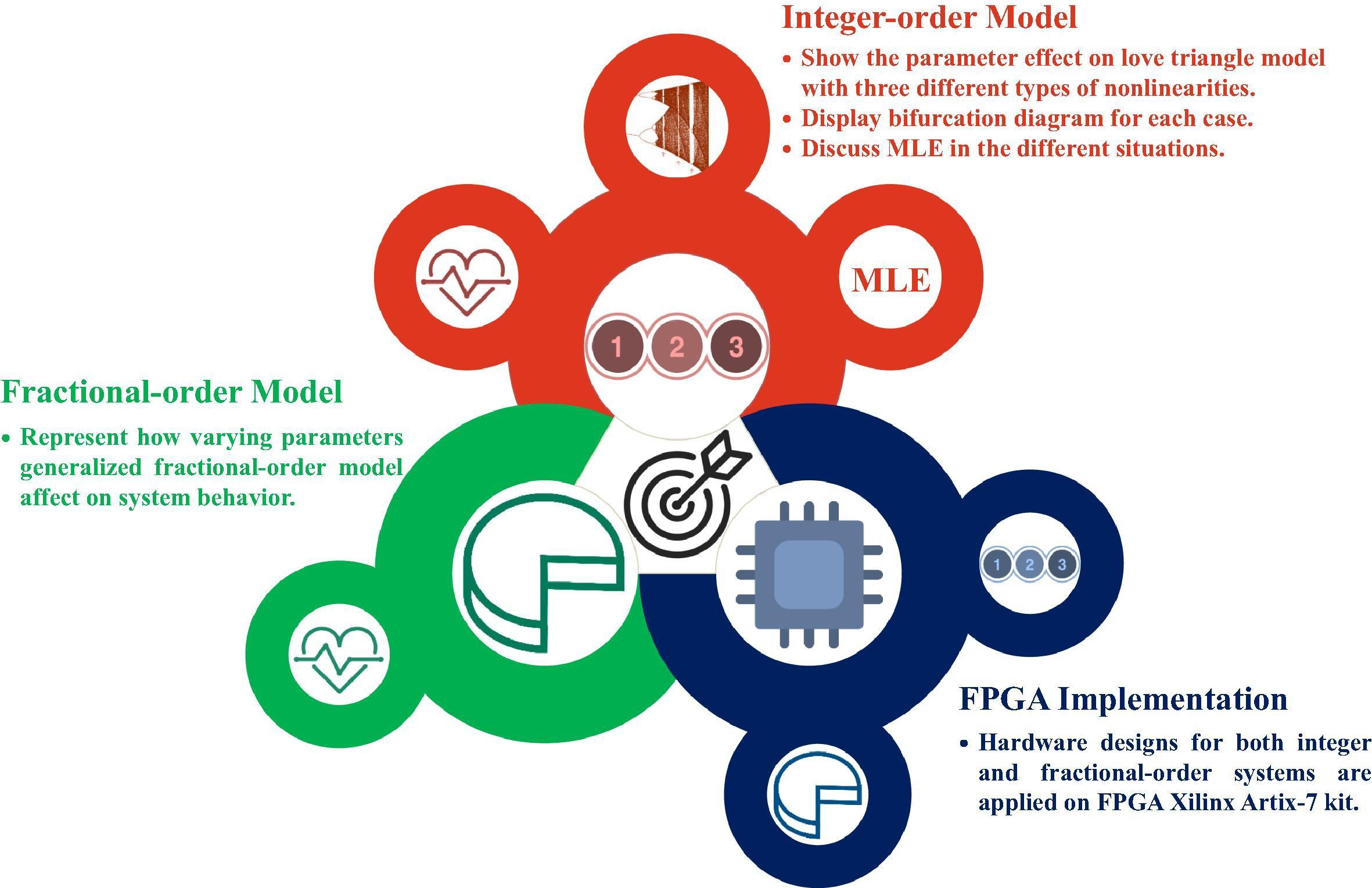
A study of the nonlinear dynamics of human behavior and its digital hardware implementation
This paper introduces an intensive discussion for the dynamical model of the love triangle in both integer and fractional-order domains. Three different types of nonlinearities soft, hard, and mixed between soft and hard, are used in this study. MATLAB numerical simulations for the different three categories are presented. Also, a discussion for how the kind of personalities affects the behavior of chaotic attractors is introduced. This paper suggests some explanations for the complex love relationships depending on the impact of memory (IoM) principle. Lyapunov exponents, Kaplan-Yorke
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 46
- Next page ››
