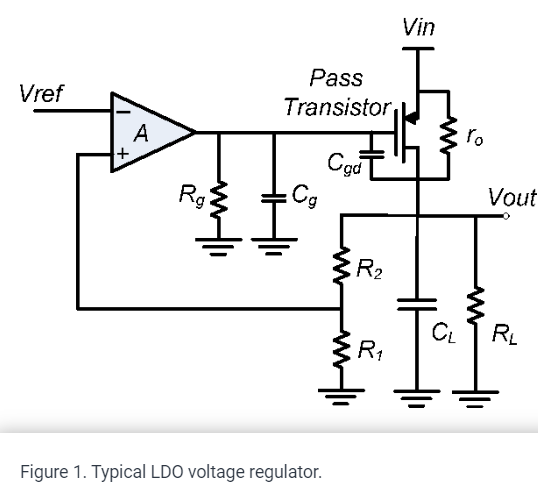
Parallel feedback compensation for LDO voltage regulators
A novel low dropout (LDO) voltage regulator compensation technique is demonstrated. A parallel feedback path is used to insert a zero at approximately three times the output pole. The parallel feedback consists of passive elements only and occupies small area. The proposed technique completely eliminates the output pole at different load conditions and results in high LDO bandwidth, which achieves fast output tracking of the input reference and fast recovery of sudden load changes. Moreover, the output pole elimination at different load conditions enables the potential scaling of the error
Multi-phase oscillator for higher-order PSK applications
Multi-phase oscillator is an essential block in digital communication systems especially phase shift keying PSK based systems. In this paper, a procedure for designing a multi-phase oscillator with any required phase shift is proposed, unlike the previous oscillator which generates equal phase shifts. This oscillator circuit is built using fractional-order elements to generate any distribution of phase shift. The general characteristics equation is studied where the condition for oscillation and oscillation frequency are derived. Finally, different examples are introduced with their
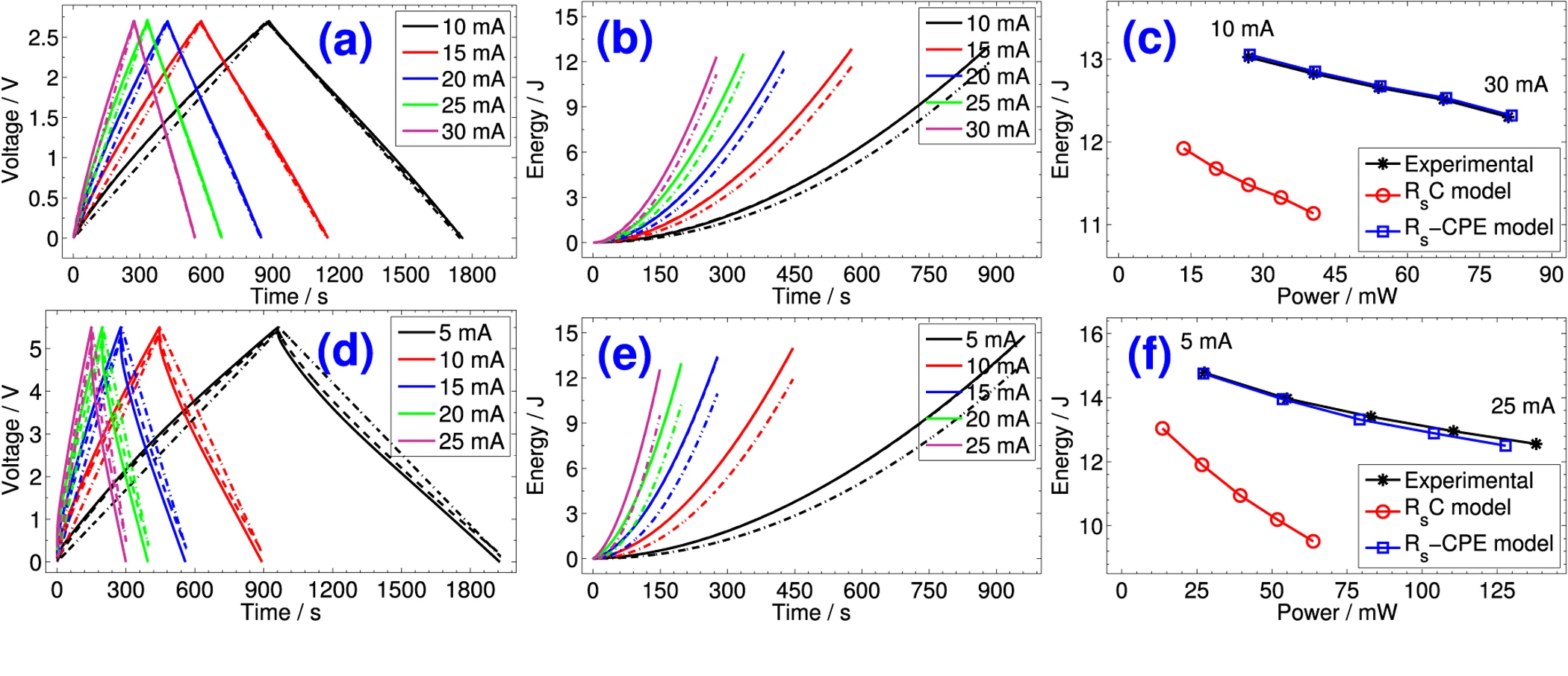
Reevaluation of Performance of Electric Double-layer Capacitors from Constant-current Charge/Discharge and Cyclic Voltammetry
The electric characteristics of electric-double layer capacitors (EDLCs) are determined by their capacitance which is usually measured in the time domain from constant-current charging/discharging and cyclic voltammetry tests, and from the frequency domain using nonlinear least-squares fitting of spectral impedance. The time-voltage and current-voltage profiles from the first two techniques are commonly treated by assuming ideal S s C behavior in spite of the nonlinear response of the device, which in turn provides inaccurate values for its characteristic metrics. In this paper we revisit the
Finite precision logistic map between computational efficiency and accuracy with encryption applications
Chaotic systems appear in many applications such as pseudo-random number generation, text encryption, and secure image transfer. Numerical solutions of these systems using digital software or hardware inevitably deviate from the expected analytical solutions. Chaotic orbits produced using finite precision systems do not exhibit the infinite period expected under the assumptions of infinite simulation time and precision. In this paper, digital implementation of the generalized logisticmap with signed parameter is considered. We present a fixed-point hardware realization of a Pseudo-Random
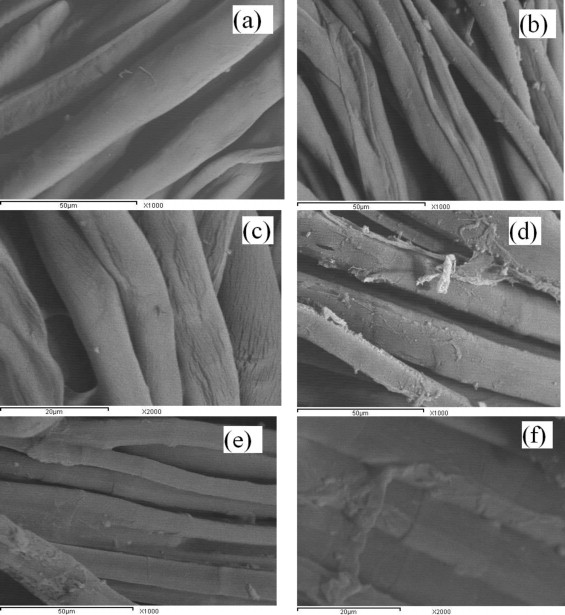
Novel chitosan-ZnO based nanocomposites as luminescent tags for cellulosic materials
Novel chitosan-ZnO composites have been synthesized as luminescent taggants for cellulosic materials. The synthesized chitosan-ZnO nanospheres (CS-ZnO NS), chitosan-ZnO-oleic acid quantum dots (CS-ZnO-oleic QD) and chitosan-ZnO-oleic acid:Eu3+ doped nanorods (CS-ZnO-oleic:Eu3+ NR) were characterized by X-ray diffraction, photoluminescence spectroscopy, FTIR spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The prepared luminescent CS-ZnO composites were used in printing paste and applied to different types of papers and textiles by using screen printing technique. The colorimetric values of
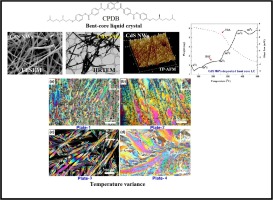
Reliable optoelectronic switchable device implementation by CdS nanowires conjugated bent-core liquid crystal matrix
Enhancing the performance of high luminescent and dielectrically capable cadmium sulfide nanowire (CdS NW) is of great importance, because of their promising ability in analyzing the dimensionality and size. The tuned physical characteristics of semiconductor CdS NWs allowed the manipulation of both electronic and optoelectronic devices at the nanoscale by dispersing a new bent core (BC) liquid crystal (LC) compound. This was derived from a 4-chlororesorcinol central core unit with two terephthalate based rod-like units carrying chiral (S)-3, 7-dimethyloctyloxy (namely ‘CPDB’) terminal chains
Comparative Study of Two Level and Three Level PWM-Rectifier with Voltage Oriented Control
This article presents performance evaluation and comparison between Voltage Oriented Control (VOC) methods for PWM-rectifiers, two levels and three levels, in order to demonstrate the great advantages of using a three-level Neutral Point Clamped (NPC). The control of the DC bus voltage is carried out using the PI controller. The effectiveness of this approach is illustrated by simulation results using MATLAB/Simulink. © Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2019.
Reconfigurable FPGA Realization of Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems
This paper proposes FPGA realization of an IP core for generic fractional-order derivative based on Grünwald-Letnikov approximation. This generic design is applied to achieve reconfigurable realization of fractional-order chaotic systems. The fractional-order real-time configuration boosts the suitability of this particular realization for different applications, including dynamic switching, synchronization, and encryption. The proposed design targets optimized utilization of the FPGA internal resources and efficient employment of the external peripherals: switches and I/O ports in the FPGA
Architectures and Challenges Towards Software Defined Cloud of Things (SDCoT)
Last decade witnessed a growth on developing of IoT architecture models to cope with various challenges and domains requirements. This leads to rapid increasing the number of the connected devices, which means large amount of data are needed to be stored and processed. Form this context, Cloud Computing is emerged as a solution to enable centrally unlimited storage of data and programs with the ability to access anytime from anywhere. The integration between IoT and cloud brings the concept of Cloud of Things (CoT) to support different types of data and multiple services with data ubiquity
Fractional chaos maps with flower pollination algorithm for chaotic systems’ parameters identification
Meta-heuristic optimization algorithms are the new gate in solving most of the complicated nonlinear systems. So, improving their robustness, reliability, and convergence speed is the main target to meet the requirements of various optimization problems. In the current work, three different fractional-order chaos maps (FC-maps), which have been introduced recently, are incorporated with the fundamental flower pollination algorithm to tune its parameters adaptively. These maps are fractional logistic map, fractional sine map, fractional tent map, and their integer-order versions. As a result
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 50
- Next page ››
