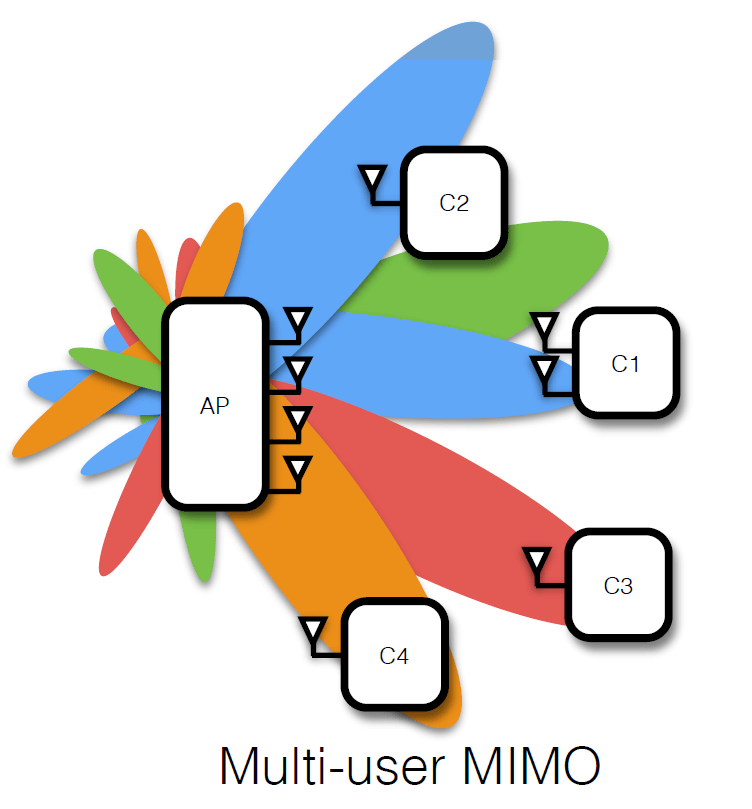
Multiuser MIMO relaying under quality of service constraints
We consider a wireless communication scenario with K source-destination pairs communicating through several half-duplex amplify-and-forward relays. We design the relay beamforming matrices by minimizing the total power transmitted from all the relays subject to quality of service constraints on the received signal to interference-plus-noise ratio at each destination node. We propose a novel method for solving the resulting nonconvex optimization problem in which the problem is decomposed into a group of second-order cone programs (SOCPs) parameterized by K real parameters. Grid search or
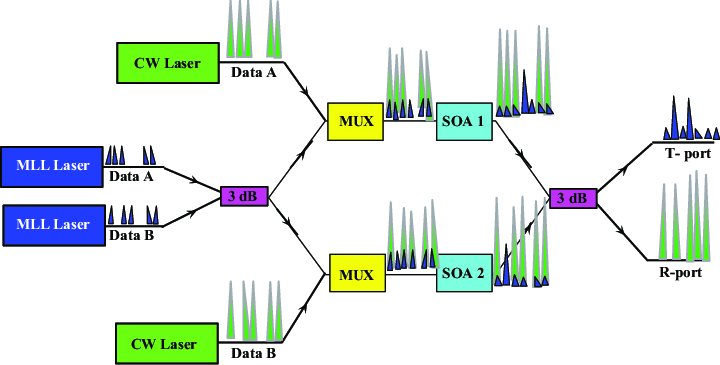
Network Coded Cooperation Receiver with Analog XOR Mapping for Enhanced BER
In this paper, we propose a novel physical layer decoding technique for Device-to-Device Network Coded Cooperation (NCC) receivers in the Two Way Relay Channel (TWRC) scenario. The proposed technique is efficiently applicable either when Channel State Information (CSI) are available at the receiver or not. It first employs XOR arithmetic analog mapping to extract a distorted version of the intended signal from the network-coded signal received from the relay. The obtained signal is then combined with the direct signal received from the source, resulting in a higher SNR version of the intended
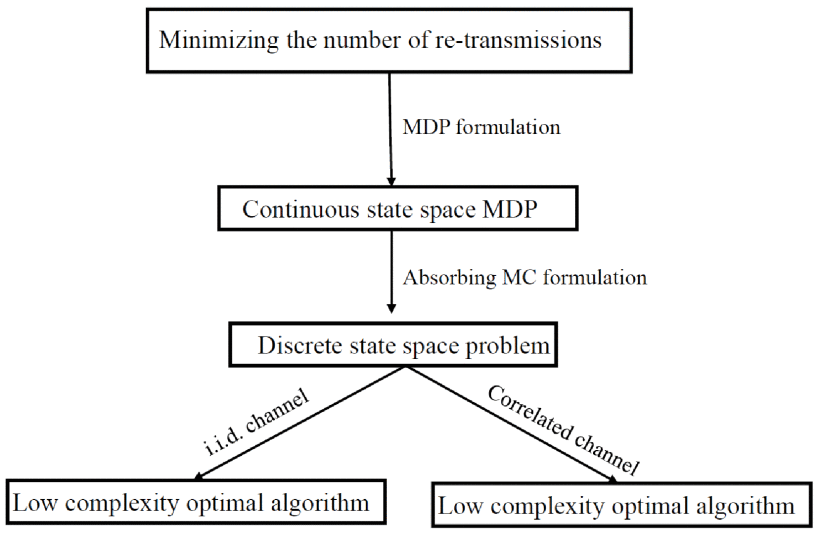
SWIPT Using Hybrid ARQ over Time Varying Channels
We consider a class of wireless powered devices employing hybrid automatic repeat request to ensure reliable end-to-end communications over a two-state time-varying channel. A receiver, with no power source, relies on the energy transferred by a simultaneous wireless information and power transfer enabled transmitter to receive and decode information. Under the two-state channel model, information is received at two different rates while it is only possible to harvest energy in one of the states. The receiver aims to decode its messages with minimum expected number of re-transmissions. Dynamic
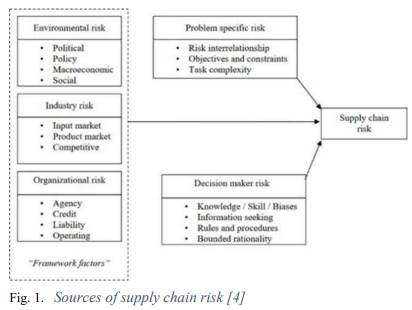
Supply Chain Risk Assessment Using Fuzzy Logic
Business's strength arises from the strength of its supply chain. Therefore, a proper supply chain management is vital for business continuity. One of the most challenging parts of SCM is the contract negotiation, and one main aspect of the negotiation is to know the risk associated with each range of quantity agreed on. Currently Managers assess the quantity to be supplied based on a binary way of either full or 0 supply, This paper aims to assess the corresponding quantities risks of the suppliers on a multilayer basis. The proposed approach uses fuzzy logic as an artificial intelligence
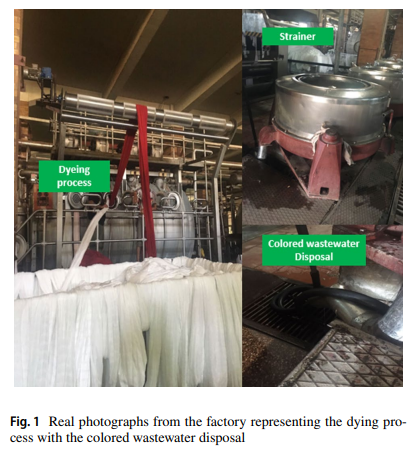
Sustainable Evaluation of Using Nano Zero-Valent Iron and Activated Carbon for Real Textile Effluent Remediation
In this study, the performance of using two different adsorbents, nano-zero-valent iron (nZVI) and activated carbon (AC), was examined for the treatment of real textile effluents. The porous structure and chemical composition of the synthesized nZVI were detected via X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and EDX analysis. Batch adsorption studies were conducted to investigate the optimal operating conditions including pH, adsorbent dose, contact time and stirring rate for the removal of COD, TSS and color from real textile wastewater. At same optimal operating conditions, pH 6, dose
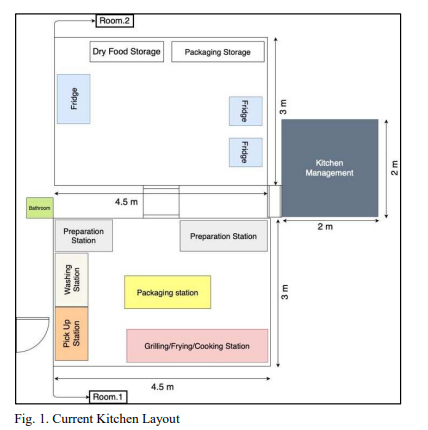
Facility layout and supply chain management of food service industries: A case study
Although there is a massive number of food tech enabled startups all over the world only few of them can succeed globally, determining the main factors which affect success or failure are still a challenge. In this paper, industrial engineering fundamentals are used to develop the startup structure and workplace design in two main areas; layout design to improve the work environment as well as flow of workers and flow of materials, supply chain management to design push-pull hybrid system and demand forecasting using non-stationary exponential smoothing method. © 2021 IEEE.
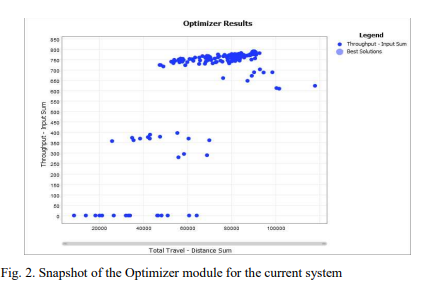
FlexSim Simulation to Enhance Productivity of a Production Cell : A Case Study
The use of modelling and simulation as a decision-making tool has increasingly been recognized to solve industrial problems. Modeling and simulation are utilized in this study to assess, analyze, and provide recommendations for improving the performance of an existing production cell in a manufacturing plant. To analyze the performance of the assembly line under investigation, multiple key performance indicators (KPIs) are determined. With the aid of FlexSim simulation tool, an improved system is recommended after running more than 90 different scenarios to enhance the productivity. The
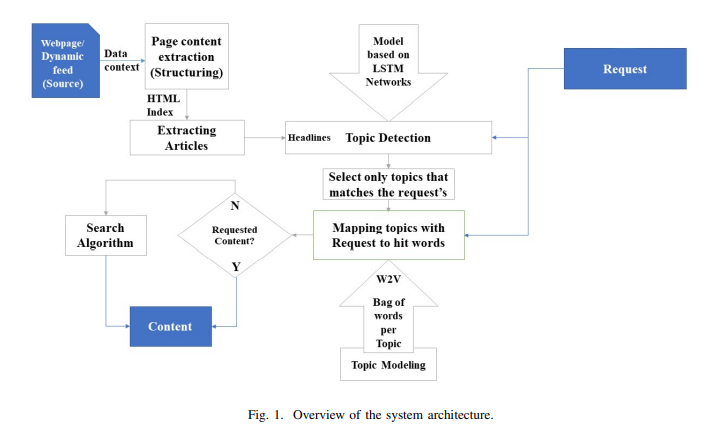
Towards Intelligent Web Context-Based Content On-Demand Extraction Using Deep Learning
Information extraction and reasoning from massive high-dimensional data at dynamic contexts, is very demanding and yet is very hard to obtain in real-time basis. However, such process capability and efficiency might be affected and limited by the available computational resources and the consequent power consumption. Conventional search mechanisms are often incapable of real-time fetching a predefined content from data source, without concerning the increased number of connected devices that contribute to the same source. In this work, we propose and present a concept for an efficient approach
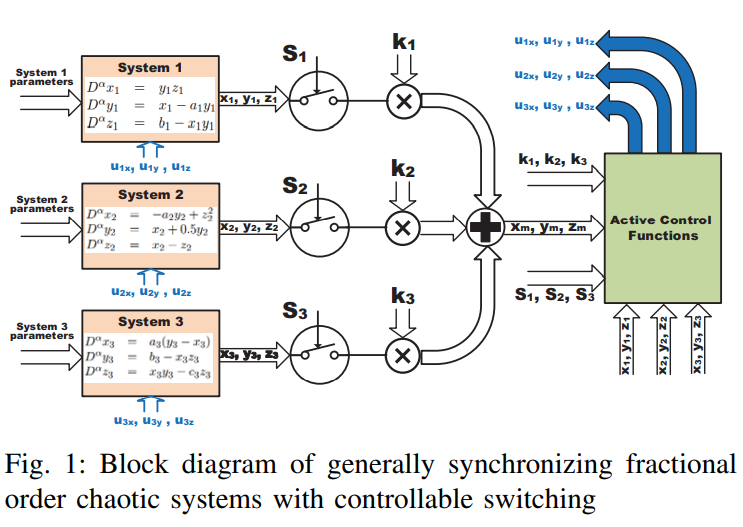
Switched active control synchronization of three fractional order chaotic systems
This paper discusses the continuous effect of fractional order parameter on two chaotic systems. Switched synchronization of three different fractional order chaotic systems is presented as an extension for synchronizing two different systems using active control. The proposed technique, which is based on the switching parameters and the scaling factors that control the choices of master and slave systems, is explained. The NonStandard Finite Difference method is used for the numerical solution of the fractional order master and slave systems. Four cases and many numeric simulations are
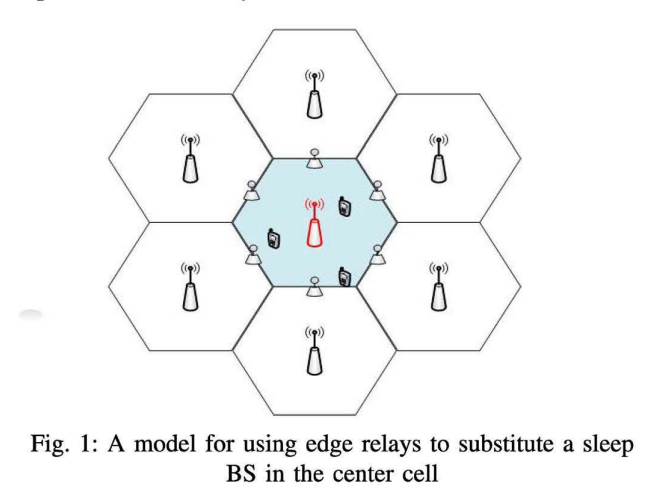
Joint relay assignment and adaptive modulation for energy-efficient cellular networks
Energy efficient operation of cellular systems becomes a core design goal for economic and environment-friendly network operation. Several studies have shown that the energy consumed in base stations represents 60-80% of the energy consumption in cellular networks. In this paper, we develop an optimization framework that exploits several energy efficient techniques including switching power modes of base stations, Adaptive Modulation (AM), and the use of relays. Our main objective is to reduce both, transmitted and circuit power, subject to satisfying the quality of service constraints. To
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
