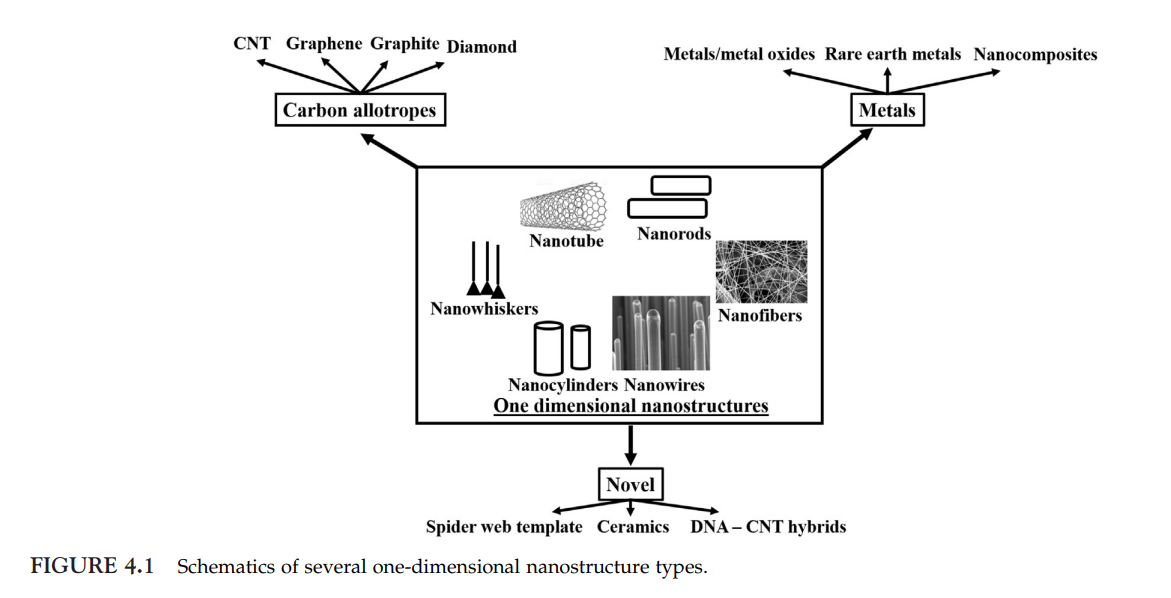
Sustainability of one-dimensional nanostructures: Fabrication and industrial
[No abstract available]
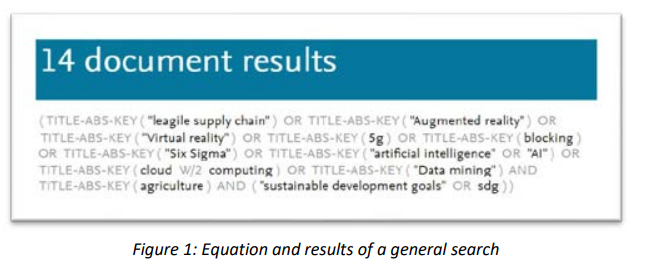
Logistics 4.0 technologies in agriculture systems: Potential impacts in the sdg
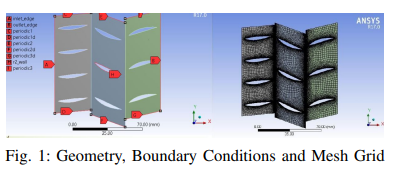
Optimized Preliminary Design of a Multistage Low-Speed Axial FLow Compressor
This paper proposes a technique based on a MAT-LAB code capable of getting an optimized preliminary design of an efficient low-speed compressor qualified for laboratory experiments with relatively low cost. The code was made to design five repeated compressor stages on two steps conducted iteratively, namely 'mean line and radial design' to determine the optimum compressor geometry and then the 'off-design' to test the stability of the design in other working conditions. The optimization tool minimizes a flexible cost function which can be changed if needed to get different designs. A certain
Improved Semantic Segmentation of Low-Resolution 3D Point Clouds Using Supervised Domain Adaptation
One of the key challenges in applying deep learning to solve real-life problems is the lack of large annotated datasets. Furthermore, for a deep learning model to perform well on the test set, all samples in the training and test sets should be independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.), which means that test samples should be similar to the samples that were used to train the model. In many cases, however, the underlying training and test set distributions are different. In such cases, it is common to adapt the test samples by transforming them to their equivalent counterparts in the
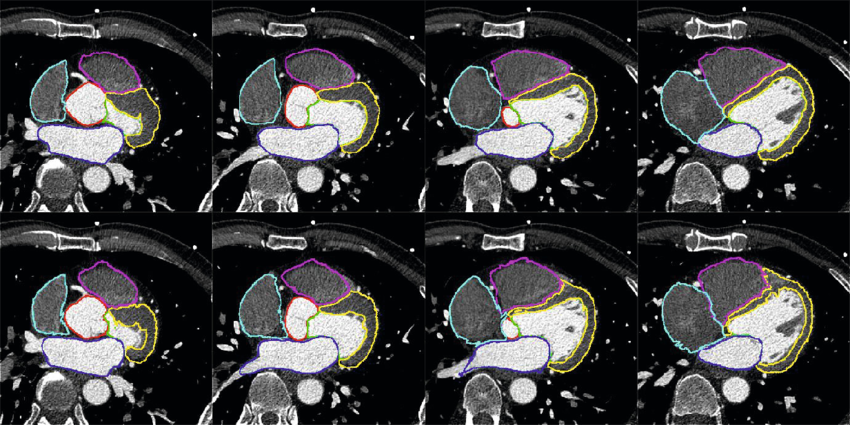
Myocardial segmentation using constrained multi-seeded region growing
Multi-slice short-axis acquisitions of the left ventricle are fundamental for estimating the volume and mass of the left ventricle in cardiac MRI scans. Manual segmentation of the myocardium in all time frames per each cross-section is a cumbersome task. Therefore, automatic myocardium segmentation methods are essential for cardiac functional analysis. Region growing has been proposed to segment the myocardium. Although the technique is simple and fast, non uniform intensity and low-contrast interfaces of the myocardium are major challenges of the technique that limit its use in myocardial
In-silico development and assessment of a Kalman filter motor decoder for prosthetic hand control
Up to 50% of amputees abandon their prostheses, partly due to rapid degradation of the control systems, which require frequent recalibration. The goal of this study was to develop a Kalman filter-based approach to decoding motoneuron activity to identify movement kinematics and thereby provide stable, long-term, accurate, real-time decoding. The Kalman filter-based decoder was examined via biologically varied datasets generated from a high-fidelity computational model of the spinal motoneuron pool. The estimated movement kinematics controlled a simulated MuJoCo prosthetic hand. This clear-box
Improved strain measuring using fast strain-encoded cardiac MR
The strain encoding (SENC) technique encodes regional strain of the heart into the acquired MR images and produces two images with two different tunings so that longitudinal strain, on the short-axis view, or circumferential strain on the long-axis view, are measured. Interleaving acquisition is used to shorten the acquisition time of the two tuned images by 50%, but it suffers from errors in the strain calculations due to inter-tunings motion of the heart, which is the motion between two successive acquisitions. In this work, a method is proposed to correct for the inter-tunings motion by
Improved technique to detect the infarction in delayed enhancement image using k-mean method
Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging is an important technique for cardiac diagnosis. Measuring the scar in myocardium is important to cardiologists to assess the viability of the heart. Delayed enhancement (DE) images are acquired after about 10 minutes following injecting the patient with contrast agent so the infracted region appears brighter than its surroundings. A common method to segment the infarction from DE images is based on intensity Thresholding. This technique performed poorly for detecting small infarcts in noisy images. In this work we aim to identify the best threshold
Inherent fat cancellation in complementary spatial modulation of magnetization
An efficient fat suppression method is presented for MR tagging with complementary spatial modulation of magnetization (CSPAMM). In this method, the complementary modulation is applied to the water content of the tissues, while in-phase modulation is applied to the fat content. Therefore, during image reconstruction, the subtraction of the acquired images increases the tagging contrast of the water while cancels the tagging lines of the fat. Compared with the existing fat suppression techniques, the proposed method allows imaging with higher temporal resolution and shorter echo-time without
In-Silico Comparative Analysis of Egyptian SARS CoV-2 with Other Populations: A Phylogeny and Mutation Analysis
In the current SARS-CoV2 pandemic, identification and differentiation between SARS-COV2 strains are vital to attain efficient therapeutic targeting, drug discovery and vaccination. In this study, we investigate how the viral genetic code mutated locally and what variations is the Egyptian population most susceptible to in comparison with different strains isolated from Asia, Europe and other countries in Africa. Our aim is to evaluate the significance of these variations and whether they constitute a change on the protein level and identify if any of these variations occurred in the conserved
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
