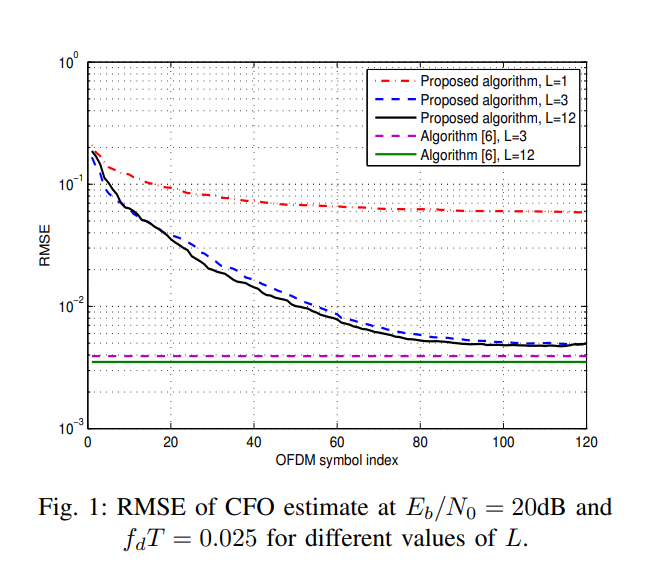
Low-complexity Kalman filter-based carrier frequency offset estimation and tracking for OFDM systems
In this paper, an iterative blind estimator for fractional carrier frequency offset (CFO) in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems is proposed. The estimator utilizes the null subcarriers transmitted at the edge of the spectrum and does not require any training. In addition, the proposed estimator does not require any prior knowledge of the frequency response of the channel. The problem is formulated using a state-space model, and an extended Kalman filter (EKF) is employed to estimate the CFO iteratively. Simulation results illustrate the enhanced ability of the proposed
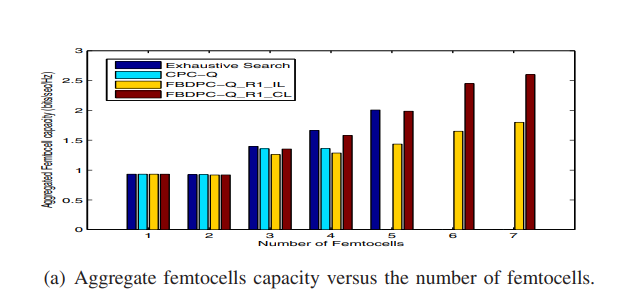
A cooperative Q-learning approach for online power allocation in femtocell networks
In this paper, we address the problem of distributed interference management of cognitive femtocells that share the same frequency range with macrocells using distributed multiagent Q-learning. We formulate and solve three problems representing three different Q-learning algorithms: namely, centralized, femto-based distributed and subcarrier-based distributed power control using Q-learning (CPC-Q, FBDPC-Q and SBDPCQ). CPC-Q, although not of practical interest, characterizes the global optimum. Each of FBDPC-Q and SBDPC-Q works in two different learning paradigms: Independent (IL) and
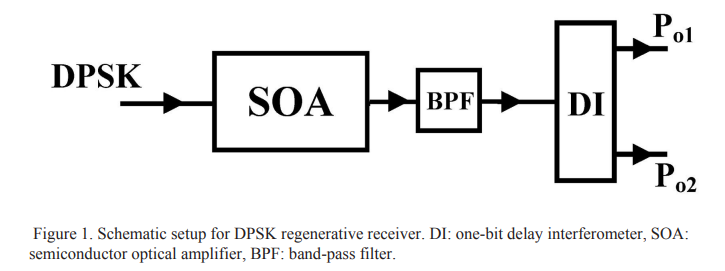
DPSK receiver-sensitivity enhancement using an SOA in front of the receiver
A technique for DPSK receiver-sensitivity improvement is demonstrated using numerical simulations. It is based on reshaping and reamplifying of received 80 Gbit/s DPSK using an SOA before a one bit delay interferometer. The SOA re-amplifies data without adding amplitude or differential phase noise due to its gain-compression. The system is tested using 231-1 PRBS RZ-DPSK (NRZ-DPSK) loaded with both phase and amplitude noise. It shows 2dB (1.7dB) quality-factor improvement. The estimated BER by error-counting shows receiver-sensitivity improvement of ≅3dB in case of single-ended detection and
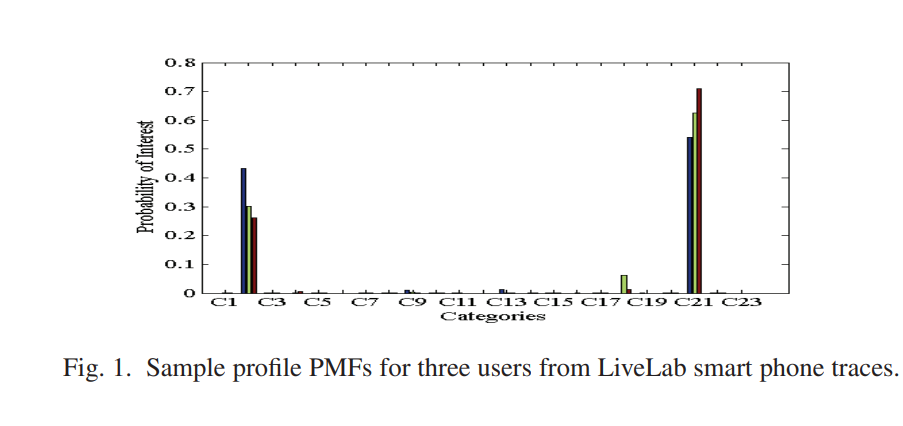
The quest for user similarity in mobile societies
In this paper we explore the notion of mobile users' similarity as a key enabler of innovative applications hinging on opportunistic mobile encounters. In particular, we analyze the performance of known similarity metrics, applicable to our problem domain, as well as propose a novel temporal-based metric, in an attempt to quantify the inherently qualitative notion of similarity. Towards this objective, we first introduce generalized profile structures, beyond mere location, that aim to capture users interests and prior experiences, in the form of a probability distribution. Afterwards, we
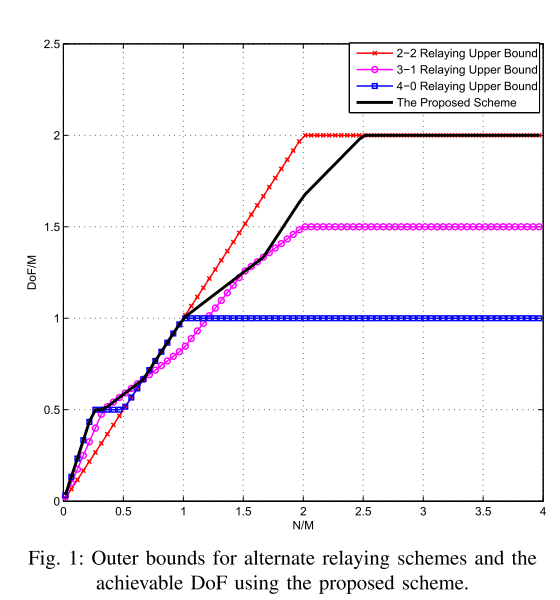
Degrees of freedom for a two-cell relay network with soft handoffs
In this paper we investigate the degrees of freedom of a cellular relay network that consists of two base stations, two mobile stations and four decode-and-forward relays. The base stations and the mobile stations are equipped with M antennas each, whereas the relays are equipped with N antennas each. In addition, each base station has an independent message to each mobile station. The relays are used to froward the messages from the base stations to the mobile station as there is no direct link. We consider three different relaying architectures where the two relays associated with each base
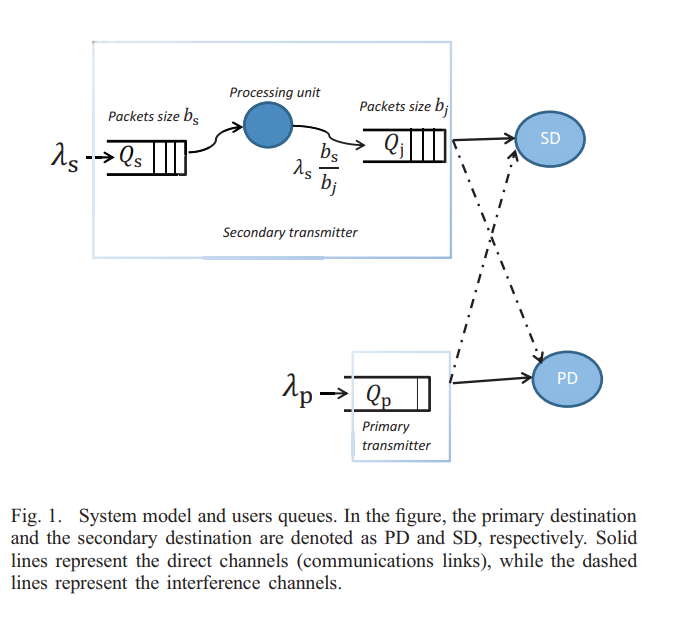
Throughput maximization via adjusting packet size of a buffered cognitive radio user
In this paper, we investigate a cognitive scenario with one secondary user and one primary user. Users are assumed to be buffered terminals. Each user has certain arrival rate with certain packet size. We propose a scheme where the cognitive radio user (secondary user) may combine some of the arrived packets into a single larger packet or split each of them into smaller packets to increase its maximum mean stable arrival rate. We consider sensing errors and study two channel models; namely, collision channel model, where concurrent transmissions cause definite packets loss, and multi-packet
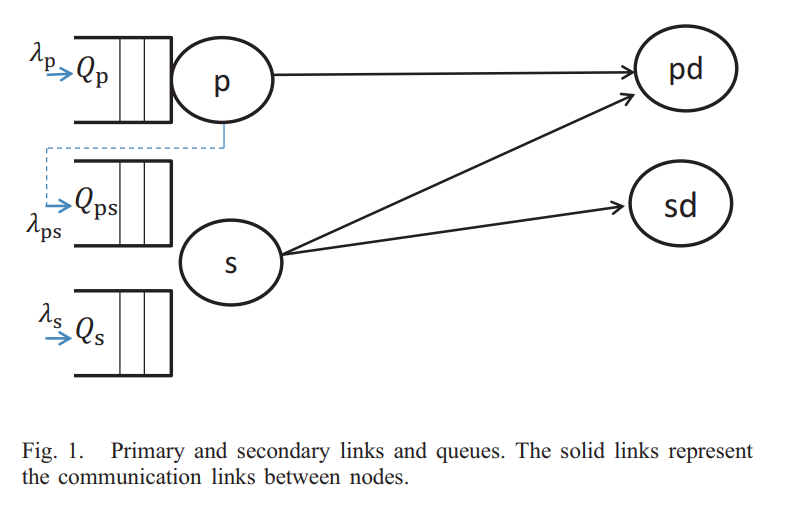
Probabilistic band-splitting for a buffered cooperative cognitive terminal
In this paper, we propose a cognitive protocol that involves cooperation between the primary and secondary users. In addition to its own queue, the secondary user (SU) has a queue to store, and then relay, the undelivered primary packets. When the primary queue is nonempty, the SU remains idle and attempts to decode the primary packet. When the primary queue is empty, the SU splits the total channel bandwidth into two orthogonal subbands and assigns each to a queue probabilistically. We show the advantage of the proposed protocol over the prioritized cognitive relaying (PCR) protocol in which
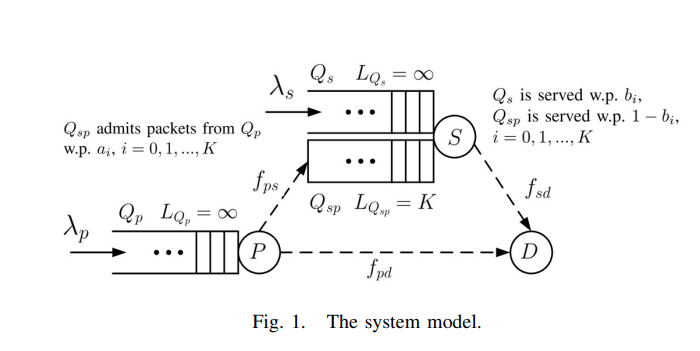
On the stable throughput of cooperative cognitive radio networks with finite relaying buffer
In this paper, we study the problem of cooperative communications in cognitive radio systems where the secondary user has limited relaying room for the overheard primary packets. More specifically, we characterize the stable throughput region of a cognitive radio network with a finite relaying buffer at the secondary user. Towards this objective, we formulate a constrained optimization problem for maximizing the secondary user throughput while guaranteeing the stability of the primary user queue. We consider a general cooperation policy where the packet admission and queue selection
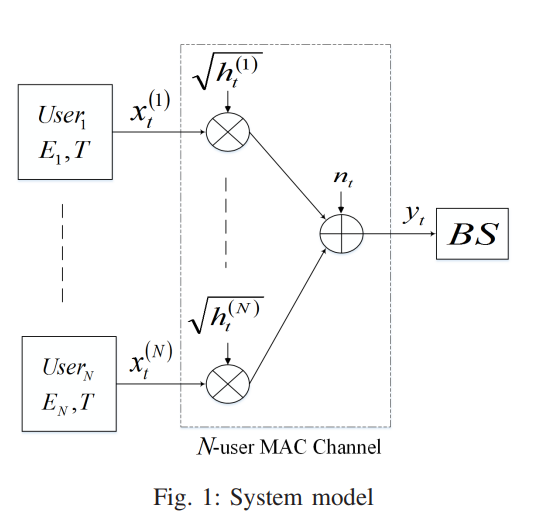
Optimal energy allocation for delay-constrained traffic over fading multiple access channels
In this paper, we consider a multiple-access fading channel where N users transmit to a single base station (BS) within a limited number of time slots. We assume that each user has a fixed amount of energy available to be consumed over the transmission window. We derive the optimal energy allocation policy for each user that maximizes the total system throughput under two different assumptions on the channel state information. First, we consider the offline allocation problem where the channel states are known a priori before transmission. We solve a convex optimization problem to maximize the
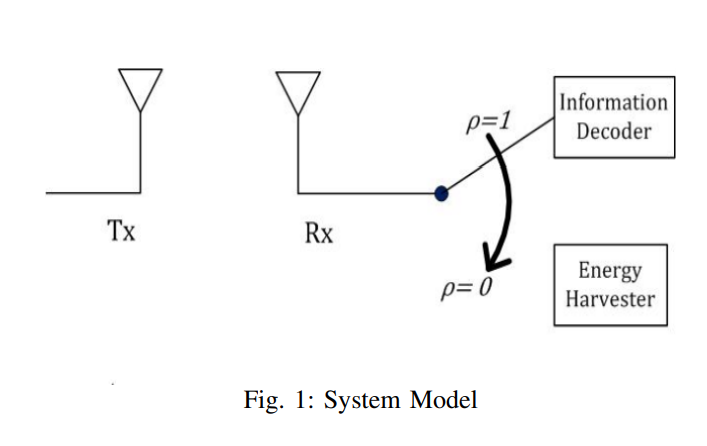
RF energy harvesting in wireless networks with HARQ
In this paper, we consider a class of wireless powered communication networks using data link layer hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) protocol to ensure reliable communications. In particular, we analyze the trade-off between accumulating mutual information and accumulating RF energy at the receiver of a point-to-point link using HARQ with incremental redundancy over a Rayleigh fading channel. The transmitter is assumed to have a constant energy source while the receiver relies, solely, on the RF energy harvested from the received signal. First, we target the optimal time switching (TS)
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 19
- Next page ››
