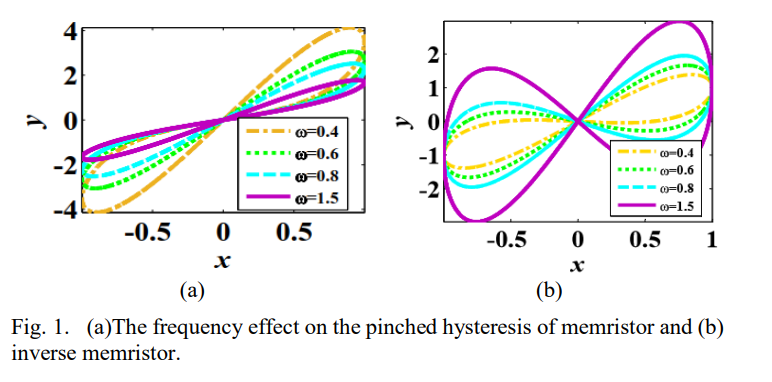
Inverse memrsitor emulator active Realizations
The paper aims to propose three different inverse memristor emulators based on serveral active blocks. One of the presented emulator realizes employing second generation current conveyor (CCII) andcanalog voltage multiplier with passive elements. The other two introduced emulators are designed using cureent feedback operational amplifier (CFOA) with two switches or two BJT transistor. One of the proposed emulators has the advantages that it switches between the inverse and memristor at the same time but in different frequency with less number of components. The introduced circuitry are
IoT ethics challenges and legal issues
IoT systems have different technologies such as: RIFD, NFC, 3G, 4G, and Sensors. Their function is to transfer very large sensitive and private data. There are many ethical challenges that need to be taken into consideration by individuals and companies that use this technology. Amongst the challenges is the user awareness of attack risks. This paper discusses different ethical and legal challenges that need to be taken in account for IoT health care applications during the near future. © 2017 IEEE.
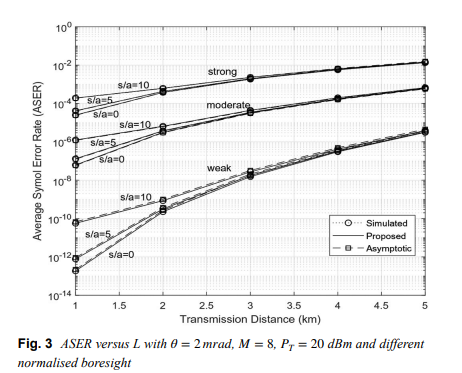
Generic evaluation of FSO system over Málaga turbulence channel with MPPM and non-zero-boresight pointing errors
Free space optical (FSO) communication channels are affected by fluctuations in irradiance due to atmospheric turbulence and pointing errors. Recently, a generalized statistical model knows as Málaga (M) was developed to describe irradiance fluctuations of the beam propagating through a turbulent medium. In this paper, an approximate finite-series probability density function (PDF) for composite M turbulence with pointing errors is verified. Considering multiple pulseposition- modulation (MPPM) with intensity modulation and direct detection, specific closed-form expressions for average symbol
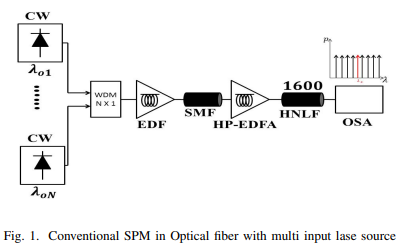
Generation of OFC by Self-Phase Modulation and Multiple Laser Sources in HNLF
Self-Phase Modulation (SPM) is a non-linear phenomenon relating to the self-induced phase shift encountered by the optical field during its transmission into the optical fiber. It is the most popular technique for generating an optical frequency comb (OFC) with different frequency spacing values. The SPM is regulated by many parameters such as fiber length, input optical power, and the non-linearity of the optical fiber. The OFC distinguishes between a high spectral flatness level, a high optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) and a wide range of wavelengths. In this paper, The SPM uses to
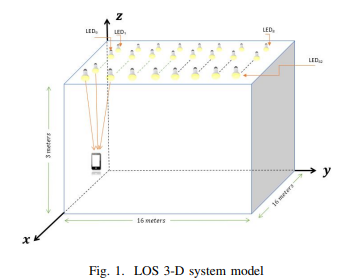
Visible Light Communications Localization Error Enhancement using Parameter Relaxation
In this paper, we propose applying a parameter relaxation technique to the location estimation algorithm that is based on the Received Signal Strength (RSS) of Visible Light Communications (VLC). A hybrid system of localization balancing is introduced, where the localization algorithm is developed with and without this efficient parameter relaxation. The results show that applying the parameter relaxation reduces the localization Root Mean Square (RMS) error by 43% of that without relaxation; and the processing time is reduced by 18% of that without relaxation. Moreover, the parameter
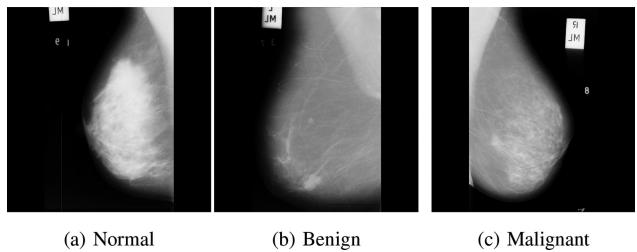
Early breast cancer diagnostics based on hierarchical machine learning classification for mammography images
Breast cancer constitutes a significant threat to women’s health and is considered the second leading cause of their death. Breast cancer is a result of abnormal behavior in the functionality of the normal breast cells. Therefore, breast cells tend to grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor that can be felt like a breast lump. Early diagnosis of breast cancer is proved to reduce the risks of death by providing a better chance of identifying a suitable treatment. Machine learning and artificial intelligence play a key role in healthcare systems by assisting physicians in diagnosing early, better
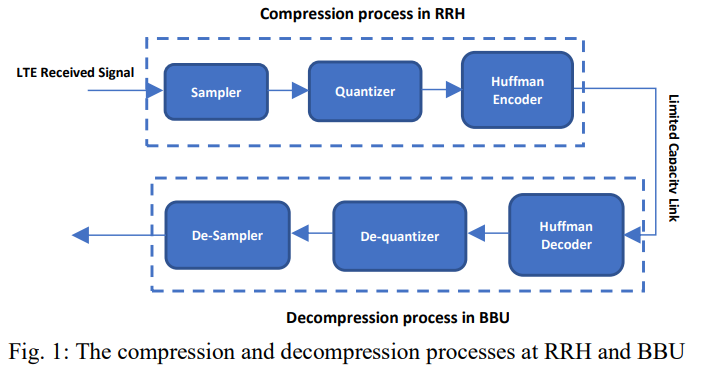
CPRI data compression using non-uniform quantized huffman technique in c-RAN
The long-term evolution (LTE) transports complex-baseband samples between the remote radio head and baseband processing unit. Common public radio interface (CPRI) protocol is used in practice and enables flexible radio head deployments and distributed antenna systems. Current wireless links (FSO and mmWave) have a few Gb/p transmissions which insufficient capacity are to support 20 MHz bandwidth LTE with multiple sectors. In this presented work, we propose a compression algorithm uses non-quantized Huffman. The proposed technique achieves 78% compression ratio while maintaining with EVM less
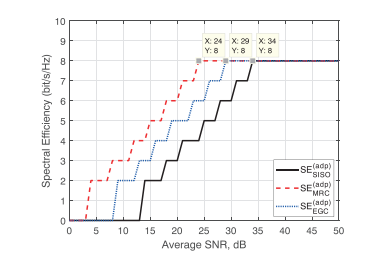
Spectral efficiency improvement with SISO and SIMO in M-QAM over millimeter-wave links
This paper proposes a spectral efficiency improvement technique for millimeter wave (mmWave) links. The proposed technique provides an efficient utilization of the mmWave link capacity. This technique is applied in three cases the single-input single-output (SISO), single-input multiple-output (SIMO) with the maximal ratio combining and with the equal gain combining. The M-ary quadrature amplitude modulation scheme is used in our work. The power series expansion is used for deriving closed-form expressions for bit error rate (BER) performances in all studied cases. The BER closed-form
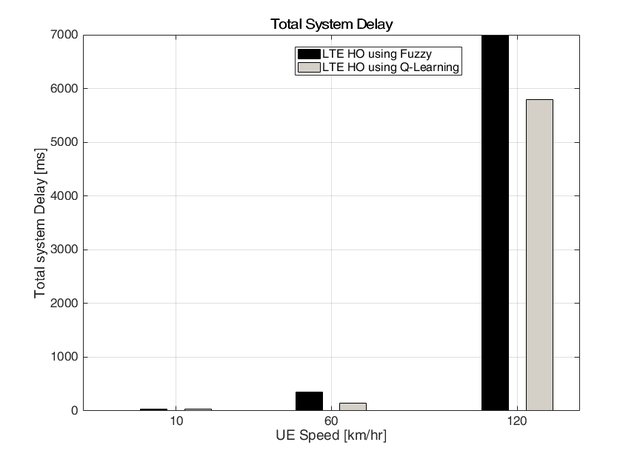
Type-2 Fuzzy Technique for LTE Handover Optimization Based on Cooperated Multi-Point
A seamless and fast handover from one cell to another is one of the main goals of long term evolution (LTE). Hence, the decision of handover is a critical part of the design process of handover. Then the selection of handover parameters must be in a careful and optimal way to have an efficient and successful handover. In this paper, a new optimized CoMP handover algorithm (CoMP HO) for LTE network based on type-2 fuzzy logic is presented. CoMP HO's were implemented by considering the cell-edge users and how to serve them without handover. It is shown via simulation that the proposed CoMP HO's

Fully balanced LED driving circuit for optogenetics stimulation
Implantable probes with built-in light emitters have a promising potential for a range of applications, in particular optogenetic neural stimulation. However, where soft encapsulation methods are used, lifetime will be a function of the quality of encapsulation and the driving mechanism. We have found that a balanced driving mechanism - whereby the integral voltage on encapsulated contacts, can significantly prolong lifetimes. As such, in this work, we have designed a driving circuit that drives current but ensures balanced electric fields with an error of less than 1%. The circuit has been
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 25
- Next page ››
