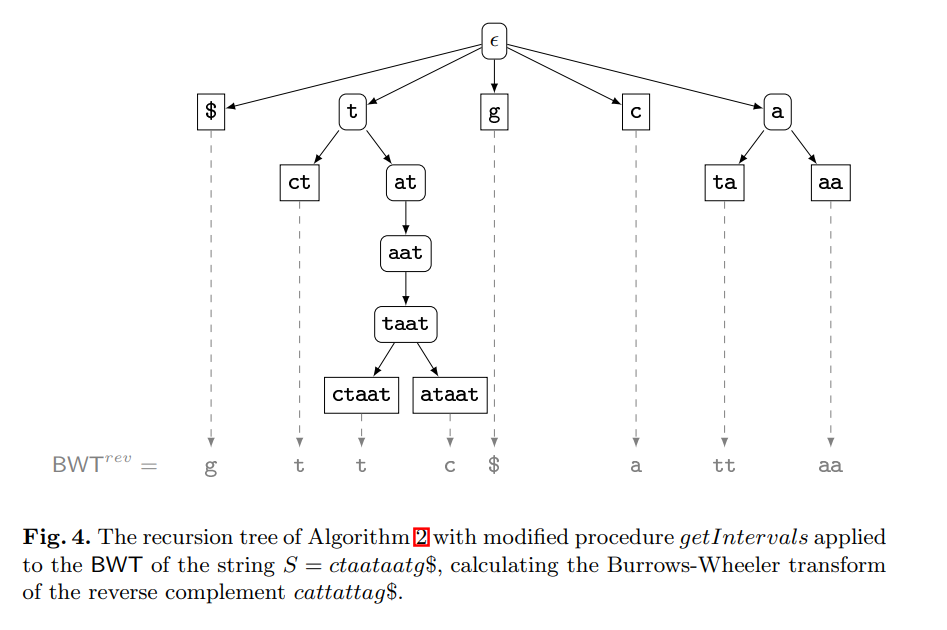
Computing the burrows-wheeler transform of a string and its reverse
The contribution of this paper is twofold. First, we provide new theoretical insights into the relationship between a string and its reverse: If the Burrows-Wheeler transform (BWT) of a string has been computed by sorting its suffixes, then the BWT and the longest common prefix array of the reverse string can be derived from it without suffix sorting. Furthermore, we show that the longest common prefix arrays of a string and its reverse are permutations of each other. Second, we provide a parallel algorithm that, given the BWT of a string, computes the BWT of its reverse much faster than all
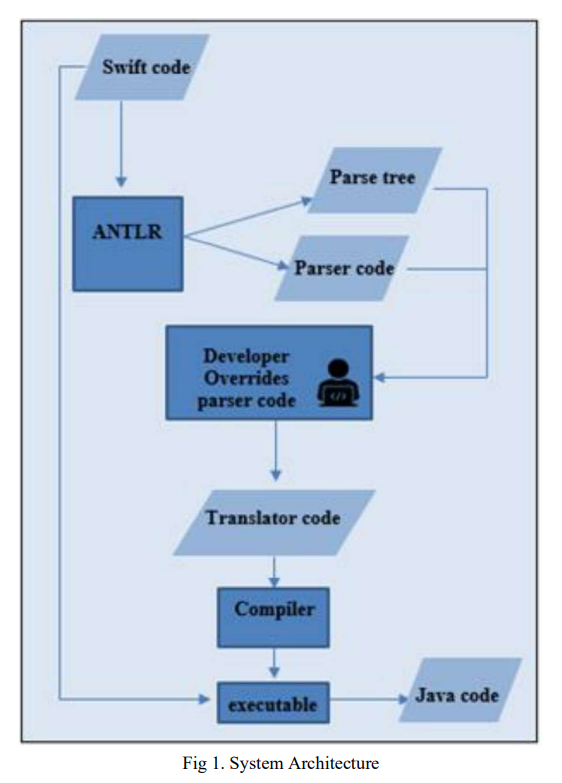
Trans-Compiler based Mobile Applications code converter: Swift to java
Numerous commercial tools like Xamarin, React Native and PhoneGap utilize the concept of cross-platform mobile applications development that builds applications once and runs it everywhere opposed to native mobile app development that writes in a specific programming language for every platform. These commercial tools are not very efficient for native developers as mobile applications must be written in specific language and they need the usage of specific frameworks. In this paper, a suggested approach in TCAIOSC tool to convert mobile applications from Android to iOS is used to develop the

Ambient and wearable sensing for gait classification in pervasive healthcare environments
Pervasive healthcare environments provide an effective solution for monitoring the wellbeing of the elderly where the general trend of an increasingly ageing population has placed significant burdens on current healthcare systems. An important pervasive healthcare system functionality is patient motion analysis where gait information can be used to detect walking behavior abnormalities that may indicate the onset of adverse health problems, for quantifying post-operative recovery, and to observe the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. The development of accurate motion analysis models
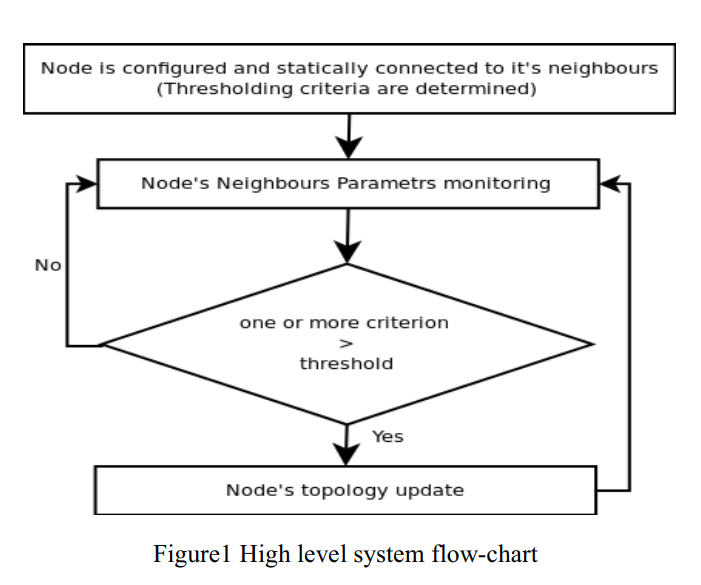
Janitor, certificate and jury (JCJ): Trust scheme for wireless ad-hoc networks
Ad hoc networks are peer mobile nodes that self configure to form a network. In these types of networks there is no routing infrastructure, and usually nodes have limited resources. This imposes a serious problem due to some nodes' selfishness and willingness to preserve their resources. Many approaches have been proposed to deal with this problem and mitigate the selfishness; amongst these approaches are reputation systems. This paper proposes a reputation system scheme that helps isolating misbehaving nodes and decreasing their ability to launch an attack on the network. The idea of this
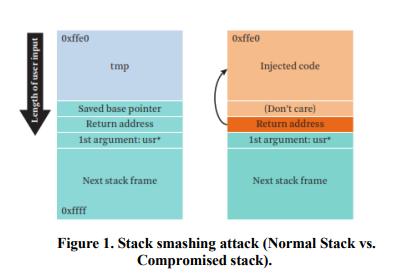
Survey of Code Reuse Attacks and Comparison of Mitigation Techniques
Code-Reuse Attacks (CRAs) are solid mechanisms to bypass advanced software and hardware defenses. Due to vulnerabilities found in software which allows attackers to corrupt the memory space of the vulnerable software to modify maliciously the contents of the memory; hence controlling the software to be able to run arbitrary code. The CRAs defenses either prevents the attacker from reading program code, controlling program memory space directly or indirectly through the usage of pointers. This paper provides a thorough evaluation of the current mitigation techniques against CRAs with regards to
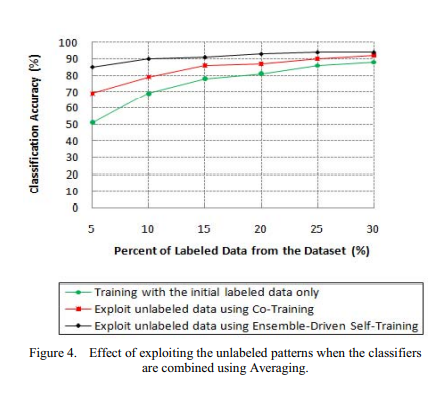
A semi-supervised learning approach for soft labeled data
In some machine learning applications using soft labels is more useful and informative than crisp labels. Soft labels indicate the degree of membership of the training data to the given classes. Often only a small number of labeled data is available while unlabeled data is abundant. Therefore, it is important to make use of unlabeled data. In this paper we propose an approach for Fuzzy-Input Fuzzy-Output classification in which the classifier can learn with soft-labeled data and can also produce degree of belongingness to classes as an output for each pattern. Particularly, we investigate the
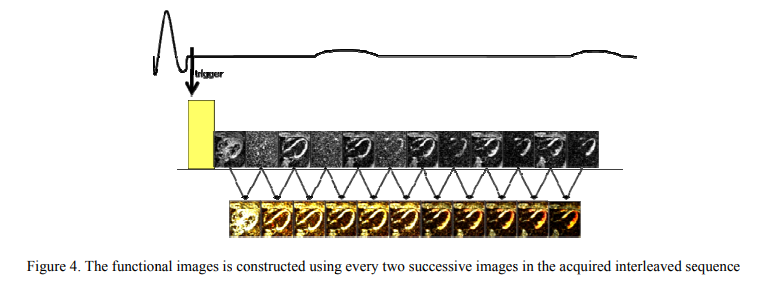
Strain correction in interleaved strain-encoded (SENC) cardiac MR
The strain encoding (SENC) technique directly encodes regional strain of the heart into the acquired MR images and produces two images with two different tunings so that longitudinal strain, on the short-axis view, or circumferential strain on the long-axis view, are measured. Interleaving acquisition is used to shorten the acquisition time of the two tuned images by 50%, but it suffers from errors in the strain calculations due to inter-tunings motion of the heart. In this work, we propose a method to correct for the inter-tunings motion by estimating the motion-induced shift in the spatial
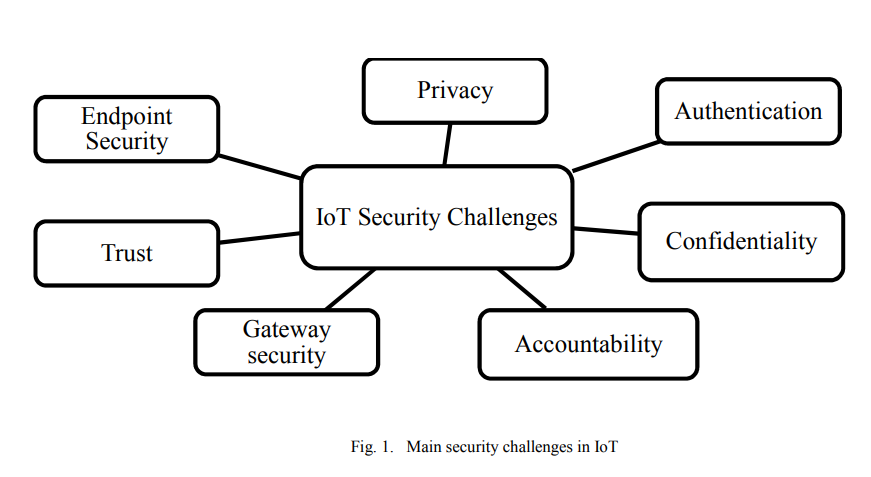
Internet of Things security framework
For the past decade, Internet of Things (IoT) had an important role in our lives. It connects a large number of embedded devices. These devices fulfill very difficult and complicated tasks, which facilitate our work. Till now the security of IoT faces many challenges such as privacy, authentication, confidentiality, trust, middleware security, mobile security and policy enforcement. In order to provide a secure environment for IoT, this paper proposes a framework for IoT devices. © 2017 IEEE.
Replica placement in peer-assisted clouds: An economic approach
We introduce NileStore, a replica placement algorithm based on an economical model for use in Peer-assisted cloud storage. The algorithm uses storage and bandwidth resources of peers to offload the cloud provider's resources. We formulate the placement problem as a linear task assignment problem where the aim is to minimize time needed for file replicas to reach a certain desired threshold. Using simulation, We reduce the probability of a file being served from the provider's servers by more than 97.5% under realistic network conditions. © 2011 IFIP International Federation for Information
Cloud-based parallel suffix array construction based on MPI
Massive amount of genomics data are being produced nowadays by Next Generation Sequencing machines. The suffix array is currently the best choice for indexing genomics data, because of its efficiency and large number of applications. In this paper, we address the problem of constructing the suffix array on computer cluster in the cloud. We present a solution that automates the establishment of a computer cluster in a cloud and automatically constructs the suffix array in a distributed fashion over the cluster nodes. This has the advantage of encapsulating all set-up details and execution of
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 27
- Next page ››
