Resource allocation for throughput enhancement in cellular shared relay networks
The downlink frame of a cellular relay network is considered, where a shared MIMO decode-and-froward relaying is used to serve the users at the edge of the cell. The relay employs zero-forcing beamforming to manage the interference among the mobile stations (MSs) at the edge of the cell. A non-cooperative scheme is considered where there is no coordination between the base stations (BSs) and the relay station (RS), and a power control algorithm for the RS is developed that maximizes the rate of the relayed users. A cooperative setting which allows the coordination of a power allocation between
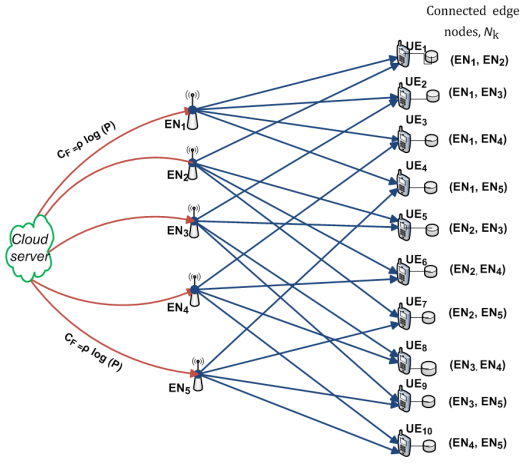
Cache-Aided Combination Networks with Interference
Centralized coded caching and delivery is studied for a radio access combination network (RACN), whereby a set of H edge nodes (ENs), connected to a cloud server via orthogonal fronthaul links with limited capacity, serve a total of K user equipments (UEs) over wireless links. The cloud server is assumed to hold a library of N files, each of size F bits; and each user, equipped with a cache of size μ R N F bits, is connected to a distinct set of r ENs each of which equipped with a cache of size μTNF bits, where μT , μ R in [{0,1}] are the fractional cache capacities of the UEs and the ENs
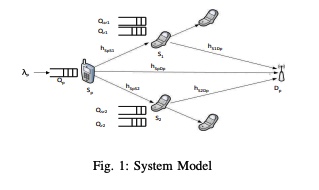
A dynamic relaying scheme for cognitive networks with multipacket reception capability
We study a cognitive radio system where the secondary users can relay the unsuccessful packets of the primary user. We study a model with one primary link and two secondary links with Multipacket Reception capability (MPR) added to the receivers. Secondary users relaying the primary unsuccessful packets are shown to increase the primary maximum stable throughput and increase the secondary user transmission opportunities. MPR capability is shown to further increase the secondary transmission opportunities as the secondary users can relay with a rate higher than 1 packets/slot as opposed to
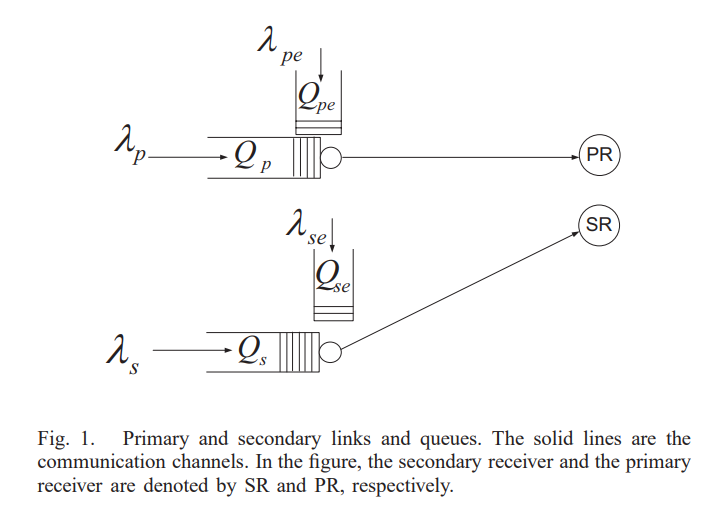
Optimal selection of spectrum sensing duration for an energy harvesting cognitive radio
In this paper, we consider a time-slotted cognitive radio (CR) setting with buffered and energy harvesting primary and CR users. At the beginning of each time slot, the CR user probabilistically chooses the spectrum sensing duration from a predefined set. If the primary user (PU) is sensed to be inactive, the CR user accesses the channel immediately. The CR user optimizes the sensing duration probabilities in order to maximize its mean data service rate with constraints on the stability of the primary and cognitive queues. The optimization problem is split into two subproblems. The first is a
Cooperative cognitive relaying with ordered cognitive multiple access
We investigate a cognitive radio system with two secondary users who can cooperate with the primary user in relaying its packets to the primary receiver. In addition to its own queue, each secondary user has a queue to keep the primary packets that are not received correctly by the primary receiver. The secondary users accept the unreceived primary packets with a certain probability and transmit randomly from either of their queues if both are nonempty. These probabilities are optimized to expand the maximum stable throughput region of the system. Moreover, we suggest a secondary multiple
Cognitive access protocol for alleviating sensing errors in cognitive multiple-access systems
This letter studies a time-slotted multiple-access system with a primary user (PU) and a secondary user (SU) sharing the same channel resource. We propose a novel secondary access protocol which alleviates sensing errors and detects the availability of primary channels with the highest ability of detection. Under the proposed protocol, the SU may access the channel at one of a predefined instants within the time slot each of which associated with a certain access probability that changes based on the sensing outcome. There is also a possibility of accessing the channel at the beginning of the
CellNet:A bottom-up approach to network design
The ever-increasing dependence on the Internet is challenged by several factors impeding the smooth transition to the nomadic and ubiquitous future communications. These hindering factors are primarily attributed to the top-down approach in designing computer networks that resulted in adopting a layered architecture for abstracting network functionalities as well as for engineering protocols; a methodology that proved to be neither adaptable nor evolvable in response to changes in network operational requirements and technological advancements. This paper presents a bottom-up1 strategy for
Cooperative D2D communication in downlink cellular networks with energy harvesting capability
Device-to-Device (D2D) communications have been highlighted as one of the promising solutions to enhance spectrum utilization of LTE-Advanced networks. In this paper, we consider a D2D transmitter cooperating with a cellular network by acting as a relay to serve one of the cellular users. We consider the case in which the D2D transmitter is equipped with an energy harvesting capability. We investigate the trade-off between the amount of energy used for relaying and the energy used for decoding the cellular user data at the relaying node. We formulate an optimization problem to maximize the
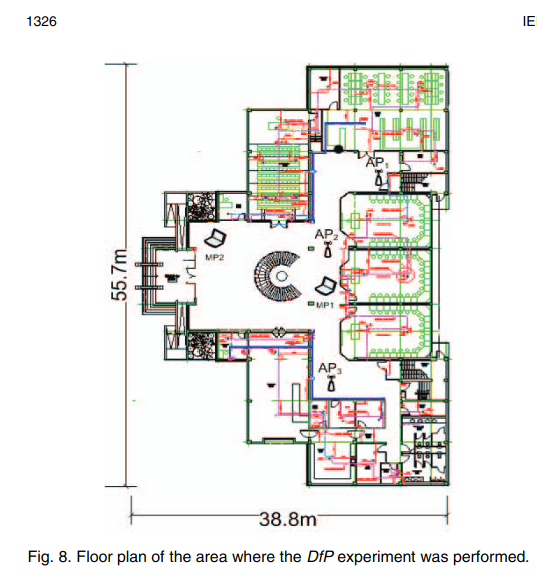
Nuzzer: A large-scale device-free passive localization system for wireless environments
The widespread usage of WLANs and mobile devices has fostered the interest in localization systems for wireless environments. The majority of research in the context of wireless-based localization systems has focused on device-based active localization, in which devices are attached to tracked entities. Recently, device-free passive localization (DfP) has been proposed where the tracked entity is neither required to carry devices nor to participate actively in the localization process. Previous studies have focused on small areas and/or controlled environments. In this paper, we present the
CellSense: An accurate energy-efficient GSM positioning system
Context-aware applications have been gaining huge interest in the last few years. With cell phones becoming ubiquitous computing devices, cell phone localization has become an important research problem. In this paper, we present CellSense, which is a probabilistic received signal strength indicator (RSSI)-based fingerprinting location determination system for Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) phones. We discuss the challenges of implementing a probabilistic fingerprinting localization technique in GSM networks and present the details of the CellSense system and how it addresses
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 29
- Next page ››
