Resource Allocation and Interference Management Techniques for OFDM-Based VLC Atto-Cells
In this paper, a resource partitioning scheme combined with a new multi-carrier optical modulation technique for indoor visible light communication (VLC) system is proposed. In VLC systems, the coverage area is divided into multiple atto-cells. In each atto-cell, multiple LED arrays are used as access points (APs) serving the assigned users. The coverage area of APs might be overlapped to avoid service discontinuity for mobile users. The overlapped coverage zones result in co-channel interference (CCI). We develop a shared frequency reuse (SFR) technique combined with two resource allocation
Comparative Study of Vehicular Proactive Caching between Cellular and VLC Networks
The rapid growth of vehicle demand, such as information sharing, entertainment, and multimedia contents, overwhelms the back-haul network. Due to this nature of the network that suffers from high link disconnections and limited resources, it is challenging to develop a new strategy to satisfy users' requirements. Proactive caching is a useful technique to mitigate the load on core networks, and determining the best caching placement of data time to enhance the network is a significant issue. However, radiofrequency is spreading and supporting multiple channels communication, and has a licensed
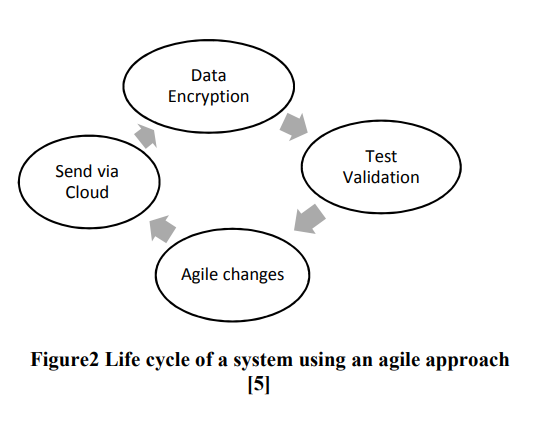
IoT Agile Framework Enhancement
Internet of Things (IoT) is considered as a trend nowadays. Devices connected to the internet interact with surrounding; this poses strong challenges in handling big data with a certain level of security. In this paper IoT devices will be divided in to two categories high vulnerability devices and low vulnerability devices. The classification depends on the ease of attacks. In order to ensure the security of IoT devices, an agile approach is used to secure high vulnerability devices as first step and then low vulnerability devices by applying encryption algorithms. © 2018 IEEE.
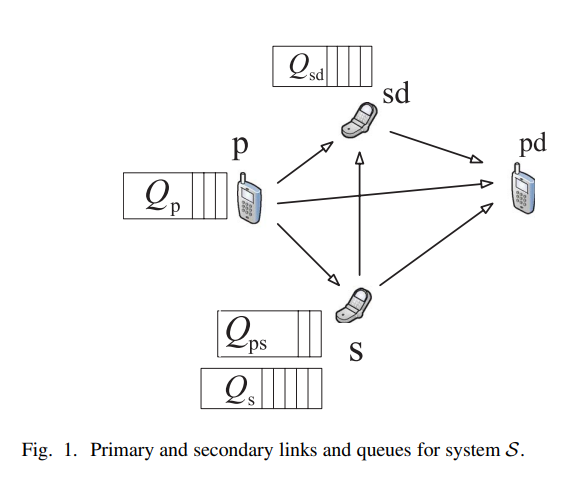
Maximum Secondary Stable Throughput of a Cooperative Secondary Transmitter-Receiver Pair: Protocol Design and Stability Analysis
In this paper, we investigate the impact of cooperation between a secondary transmitter-receiver pair and a primary transmitter on the maximum stable throughput of the primary-secondary network. Each transmitter, either primary or secondary, has a buffer for storing its own traffic. In addition to its own buffer, the secondary transmitter has a buffer for storing a fraction of the undelivered primary packets due to channel impairments. Moreover, the secondary destination has a relaying queue (buffer) for storing a fraction of the undelivered primary packets. In our proposed cooperative system
Degrees of freedom region of device-relaying cellular network
In this paper, we characterize the degrees of freedom (DoF) region of a MIMO device-relaying cellular network (DRCN) with three users and one base station (BS), where each user exchanges unicast messages with the BS. We assume that one of the users has no direct link to the BS, and hence, device-relaying is utilized to exchange data between this user and the BS, i.e., data is relayed via another user which has a direct link to the BS and a device to device (D2D) link to this user. We assume that each node operates in perfect full-duplex mode. Cut-set and genie-aided bounds are utilized to
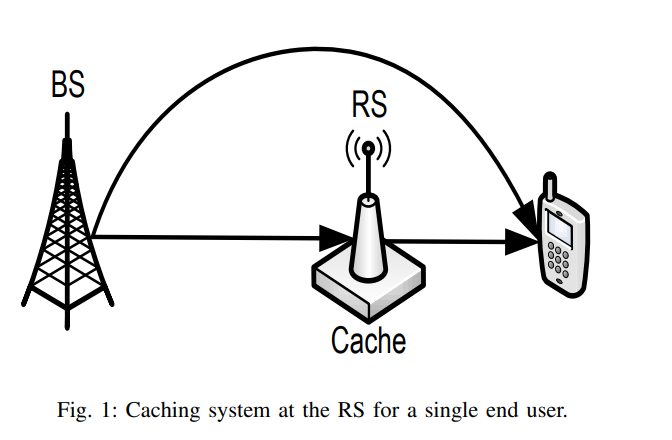
On Optimal Dynamic Caching in Relay Networks
We investigate dynamic content caching in relay networks where an intermediate relay station (RS) can adaptively cache data content based on their varying popularity. With the objective of minimizing the time average cost of content delivery, we formulate and study the problem of optimal RS cache allocation when the popularities of data content are unknown apriori to the network. While optimal dynamic cache control suffers the curse of dimensionality, we develop a fundamental lower bound on the achievable cost by any caching policy. Inspired by the structure of such lower bound, we develop a
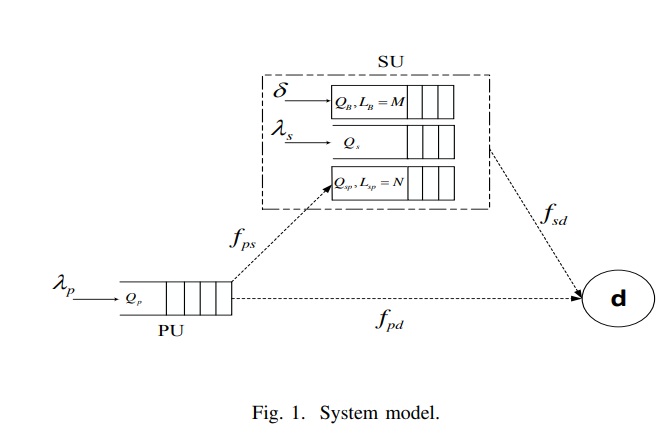
On the role of finite queues in cooperative cognitive radio networks with energy harvesting
This paper studies the problem of cooperative communications in cognitive radio networks where the secondary user is equipped with finite length relaying queue as well as finite length battery queue. The major hurdle towards fully characterizing the stable throughput region stems from the sheer complexity associated with solving the two-dimensional Markov Chain (MC) model for both finite queues. Motivated by this, we relax the problem and focus on two energy constrained systems, namely, finite battery queue with infinite relay queue and finite relay queue with infinite battery queue. We
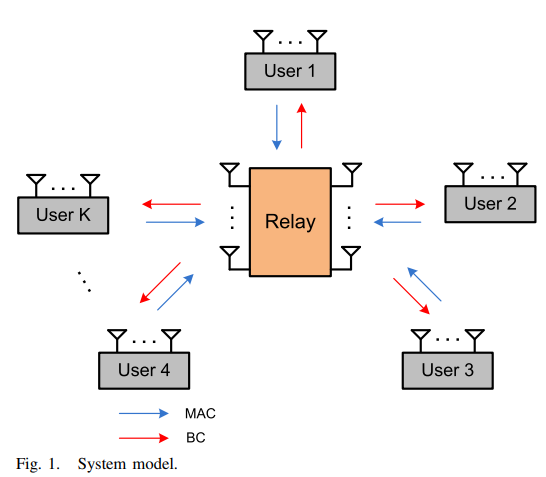
Degrees of Freedom for the MIMO Multi-Way Relay Channel with Common and Private Messages
In this paper, we study the general multiple input multiple output (MIMO) multi-way relay channel, i.e., MIMO Y channel, with common and private messages. In this channel, K users exchange messages through a common relay. Each user transmits a private message to each user in addition to a common message to all the other users. The i th user and the relay are equipped with Mi and N antennas, respectively. First, we derive the degrees of freedom (DoF) region of the symmetric three-user MIMO Y channel, where Mi = M and i ∈ {1,2,3}. Due to the symmetry of the network, we focus on the case where
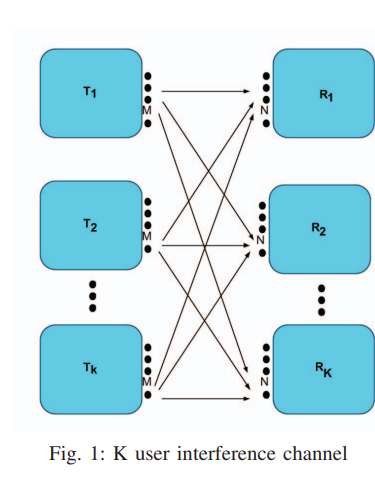
On the degrees of freedom region of the M × N Interference Channel
In this paper, the K-user MIMO interference channel is considered. The asymmetric DoF region for the channel is studied. The asymmetric DoF represent the set of all achievable DoF combinations {d1, d2,..., dK}. For the three user channel, two cases are presented, the first is when all transmitters and receivers have equal number of antennas M, the other is when each transmitter has M antennas, while each receiver has N antennas. For the K user channel, we extend our achievable scheme for the M × N case. It is assumed that the channel coefficients are constant and known to all transmitters and
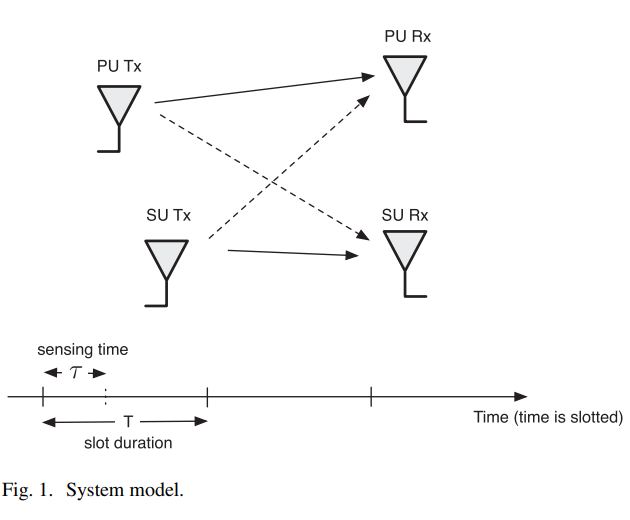
Effective capacity of delay-constrained cognitive radio links exploiting primary feedback
In this paper, we study the effective capacity (EC) of cognitive radio (CR) networks operating under statistical quality-of-service (QoS) constraints in an attempt to support real-time applications at the secondary users (SUs). In particular, we analyze the performance gains, in terms of EC and average transmitted power, attributed to leveraging the primary user (PU) feedback overheard at the SU, at no additional complexity or hardware cost. We characterize the EC performance improvement for the SU, in the presence of a feedback-based sensing scheme, under the signal-to-interference-plus-noise
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 30
- Next page ››
