Fractional canny edge detection for biomedical applications
This paper presents a comparative study of edge detection algorithms based on integer and fractional order differentiation. A performance comparison of the two algorithms has been proposed. Then, a soft computing technique has been applied to both algorithms for better edge detection. From the simulations, it shows that better performance is obtained compared to the classical approach. The noise performances of those algorithms are analyzed upon the addition of random Gaussian noise, as well as the addition of salt and pepper noise. The performance has been compared to peak signal to noise

Multistability Analysis and Function Projective Synchronization in Relay Coupled Oscillators
Regions of stability phases discovered in a general class of Genesio-Tesi chaotic oscillators are proposed. In a relatively large region of two-parameter space, the system has coexisting point attractors and limit cycles. The variation of two parameters is used to characterize the multistability by plotting the isospike diagrams for two nonsymmetric initial conditions. The parameters window in which the jerk system exhibits the unusual and striking feature of multiple attractors (e.g., coexistence of six disconnected periodic chaotic attractors and three-point attraction) is investigated. The
Fractional Order Sliding Mode PID Controller/Observer for Continuous Nonlinear Switched Systems with PSO Parameter Tuning
In this article a fractional order sliding mode PID controller and observer for the stabilization of continuous nonlinear switched systems is proposed. The design of the controller and observer is done following the separation principle, this means that the observer and controller are designed in a separate fashion, so a hybrid controller is implemented by designing the sliding mode controller part using an integral sliding mode surface along with a PIλDμ controller part which is the fractional order PID controller that is implemented to stabilizes the system. For the observer part, an
Trajectory control and image encryption using affine transformation of lorenz system
This paper presents a generalization of chaotic systems using two-dimensional affine transformations with six introduced parameters to achieve scaling, reflection, rotation, translation and/or shearing. Hence, the location of the strange attractor in space can be controlled without changing its chaotic dynamics. In addition, the embedded parameters enhance the randomness and sensitivity of the system and control its response. This approach overpasses performing the transformations as post-processing stages by applying them on the resulting time series. Trajectory control through dynamic
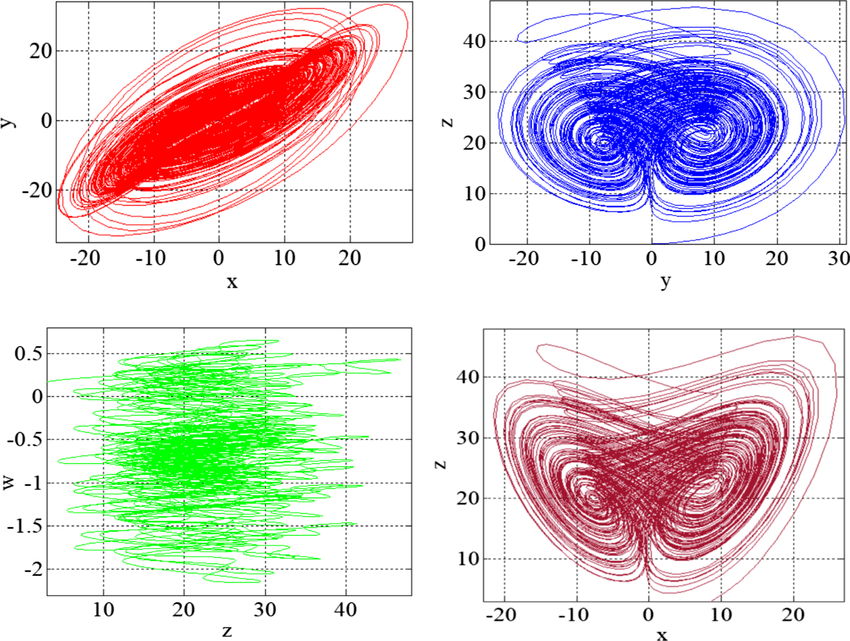
New hybrid synchronisation schemes based on coexistence of various types of synchronisation between master-slave hyperchaotic systems
In this paper, we present new approaches to study the co-existence of some types of synchronisation between hyperchaotic dynamical systems. The paper first analyses, based on stability theory of linear continuous-Time systems, the co-existence of the projective synchronisation (PS), the function projective synchronisation (FPS), the full state hybrid function projective synchronisation (FSHFPS) and the generalised synchronisation (GS) between general master and slave hyperchaotic systems. Successively, using Lyapunov stability theory, the coexistence of three different synchronisation types is
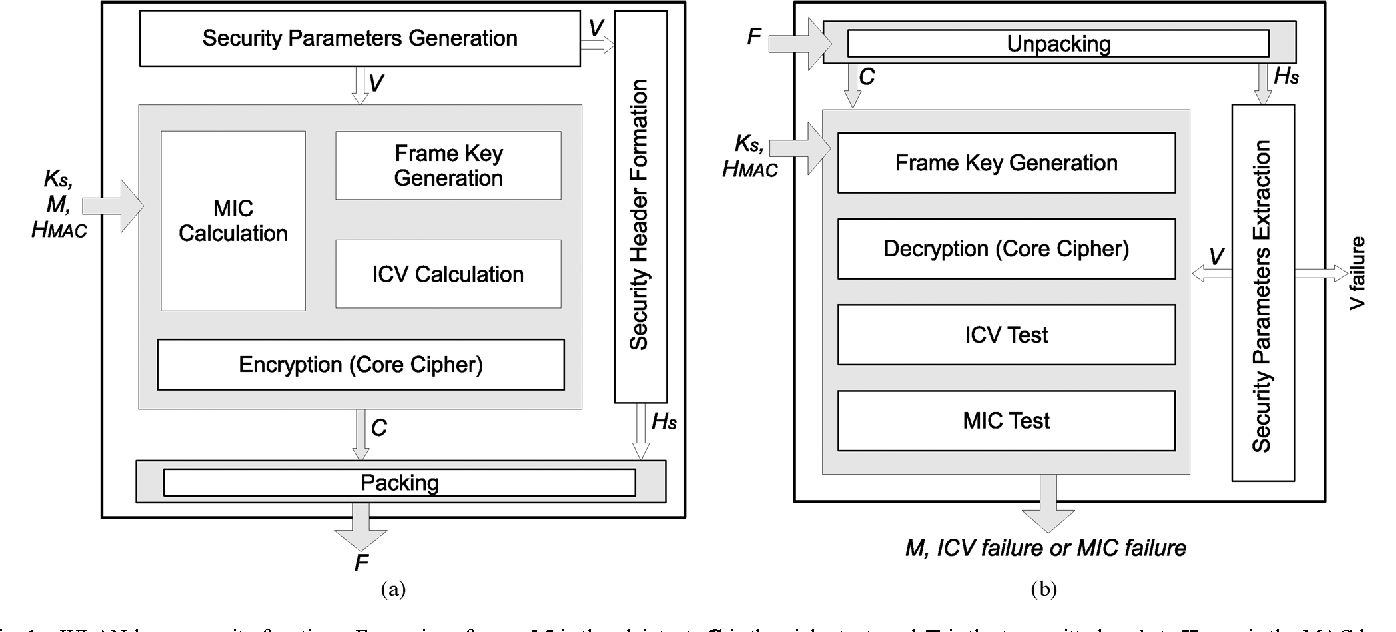
Keys through ARQ: Theory and practice
This paper develops a novel framework for sharing secret keys using the Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) protocol. We first characterize the underlying information theoretic limits, under different assumptions on the channel spatial and temporal correlation function. Our analysis reveals a novel role of dumb antennas in overcoming the negative impact of spatial correlation on the achievable secrecy rates. We further develop an adaptive rate allocation policy, which achieves higher secrecy rates in temporally correlated channels, and explicit constructions for ARQ secrecy coding that enjoy low

Multi-reader RFID tag identification using bit tracking (MRTI-BT)
In this paper we study the problem of tag identification in multi-reader RFID systems. In particular, we propose a novel solution to the reader-to-reader collisions and tag collisions in multi-reader systems, using the concept of bit tracking [1]. Towards this objective, we propose the multi-reader RFID tag identification using bit tracking (MRTI-BT) algorithm which allows concurrent tag identification, by neighboring RFID readers, as opposed to time-consuming scheduling. First, MRTI-BT identifies tags exclusive to different RFIDs, concurrently. Second, the concept of bit tracking and the
Analytical Markov model for slotted ALOHA with opportunistic RF energy harvesting
In this paper, we investigate the performance of an ALOHA random access wireless network consisting of nodes with and without RF energy harvesting capability. We develop and analyze a Markov model for the system when nodes with RF energy harvesting capability are infinitely backlogged. Our results indicate that the network throughput is improved when the conventional nodes are underloaded. On the contrary, when all types of nodes have finite backlogs, we numerically demonstrate that the network throughput and delay are improved when the overall system is overloaded. We show that there exists a
Integrated VLC/RF Wireless Technologies for Reliable Content Caching System in Vehicular Networks
In a vehicular communications environment, the need for information sharing, entertainment, and multimedia will increase, leading to congestion of backhaul networks. The major challenge of this network is latency and resource limitations. Proactive caching can be obtained from local caches rather than from remote servers, which can avoid long delays resulting from limited backhaul capacity and resources. Therefore, proactive caching reduces latency and improves the quality of services. Determining which files should be cached in memory is a critical issue. The paper proposes various placement
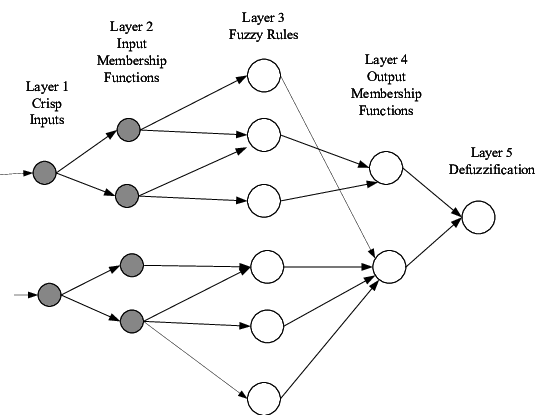
Neuro-fuzzy system for 3-dof parallel robot manipulator
Planar Parallel manipulators (PPMs) are widely used these days, as they have many advantages compared to their serial counterparts. However, their inverse and direct kinematics are hard to obtain, due to the complexity of the manipulators' behavior. Therefore, this paper provides a comparative analysis for two methods that were used to obtain the inverse kinematics of a 3-RRR manipulator. Instead of the conventional algebraic and graphical methods used for attaining the mathematical models for such manipulators, an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference structure (AFNIS) model was alternatively
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
