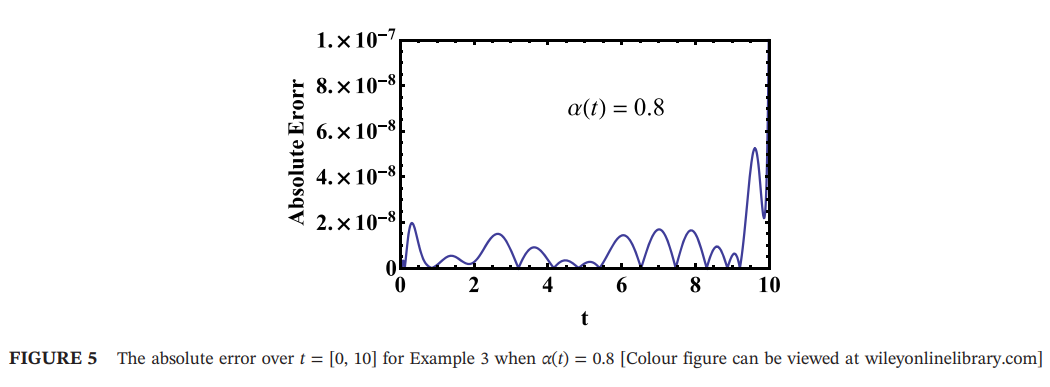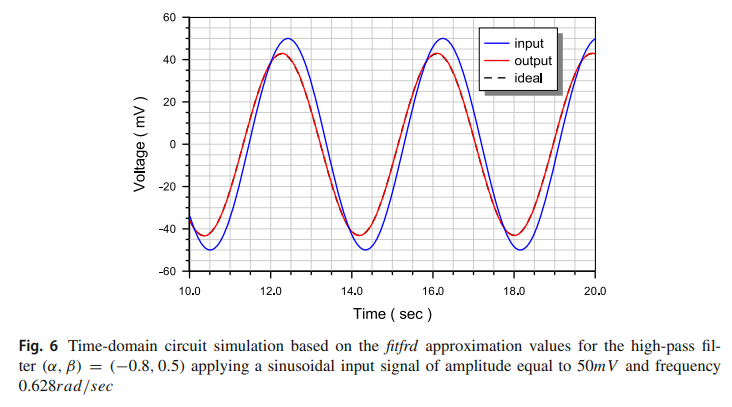
Double Exponent Fractional-Order Filters: Approximation Methods and Realization
The main goal of this work is to exploit different tools in order to approximate a general double exponent fractional-order transfer function. Through the appropriate selection of the two fractional orders of this function, different types of filters can be derived. The investigated approximation tools are either curve fitting based tools or the Padé approximation tool, and the derived approximated transfer functions in all cases have the form of rational integer-order polynomials, which can be easily realized electronically. © 2020, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer
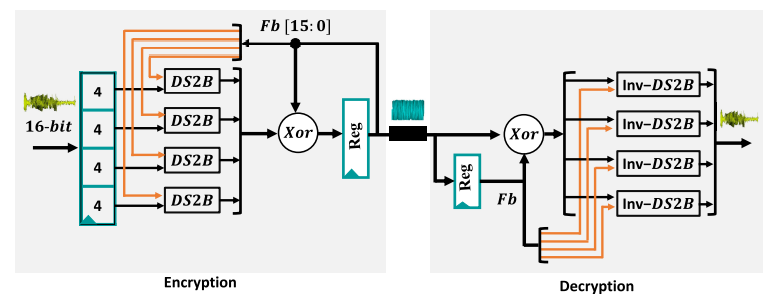
DS2B: Dynamic and Secure Substitution Box for Efficient Speech Encryption Engine
This paper proposes an efficient encryption technique based on Dynamic and Secure Substitution Box (DS2B) design suitable for IoT and resource-constrained platforms. The DS2B has the advantages of simple structure and good encryption performance. A different number of strong S-boxes could be generated with minor variations in the DS2B parameters. Performance analyses of the DS2B, including differential/linear cryptanalysis, bijective, nonlinearity, strict avalanche criterion (SAC), and bit independence criterion (BIC) have been presented where high nonlinearity , and low differential
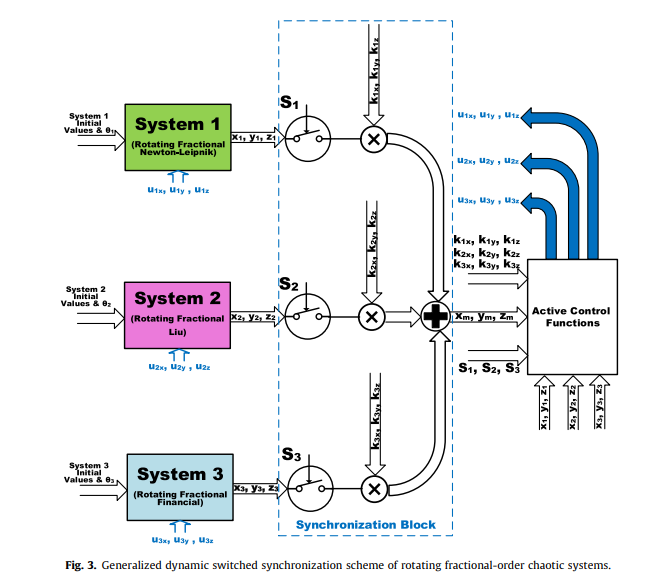
Generalized switched synchronization and dependent image encryption using dynamically rotating fractional-order chaotic systems
This paper presents a generalization, attractor control and multi-scroll generation method for fractional-order chaotic systems through rotation transformation. A novel synchronization-dependent colored image encryption and secure communication scheme is also proposed. The systems with dynamic rotation angle fit successfully in a generalized dynamic switched synchronization scheme. Dynamic control switches specify whether the system acts as a master or slave. Dynamic scaling factors determine whether the master is a single system or a combination of two or more systems. Simulation results
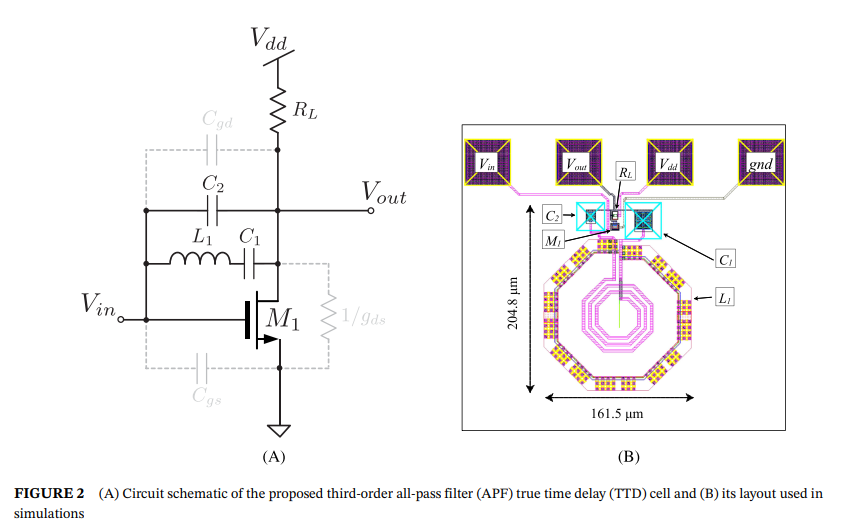
Wideband third-order single-transistor all-pass filter
In this letter, a third-order wideband voltage-mode all-pass filter (APF) is proposed for application as a true time delay (TTD) cell. The advantages of designing a single-stage higher order filter over cascading several lower order stages are illustrated. The proposed APF circuit is based on a single metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) transistor and is canonical because it requires one resistor, one inductor, and two capacitors. To the best of the authors' knowledge, this is the first single-transistor third-order APF circuit to be reported in the literature. The operation of the proposed APF is
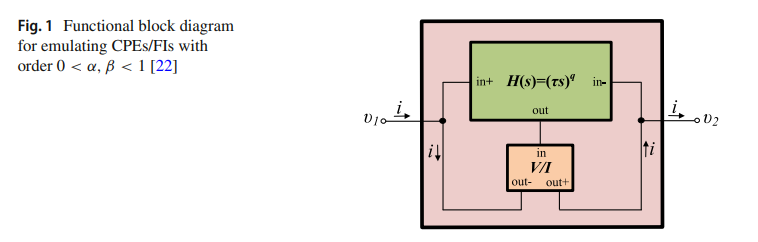
Generalized Fully Adjustable Structure for Emulating Fractional-Order Capacitors and Inductors of Orders less than Two
A novel scheme suitable for the emulation of fractional-order capacitors and inductors of any order less than 2 is presented in this work. Classically, fractional-order impedances are characterized in the frequency domain by a fractional-order Laplacian of the form s± α with an order 0 < α< 1. The ideal inductor and capacitor correspond, respectively, to setting α= ± 1. In the range 1 < α< 2 , fractional-order impedances can still be obtained before turning into a Frequency- Dependent Negative Resistor (FDNR) at α= ± 2. Here, we propose an electronically tunable fractional-order impedance

Quantification of memory in fractional-order capacitors
In this study we quantify and interpret the inherent memory in fractional-order capacitors when subjected to constant current charging/discharging waveforms. This is done via a finite difference approximation of the fractional order rate equation I(t) = Cαdαv(t)/dtα (0 le; α ≤ 1) relating current to voltage in these devices. It is found that as the fractional exponent α decreases, the weight of the voltage memory trace that results from the contribution of past voltage activity increases, and thus the measured response of the device at any time is increasingly correlated to its past. Ideal
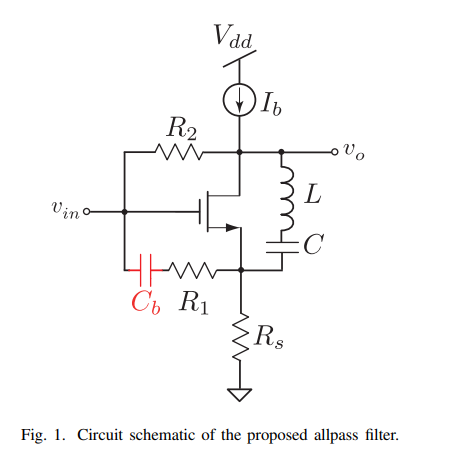
8-GHz low-power voltage-mode second-order allpass filter in 65-nm CMOS
In this paper, a CMOS wide-band low-power second-order voltage-mode allpass filter design is proposed as a true time delay element. The proposed allpass filter core design consists of a single transistor, three resistors, one capacitor and one inductor. As a time delay element, the proposed circuit exhibits a group delay of 34 ps within a bandwidth of 8 GHz while consuming only 926 μW from a 1-V supply voltage. The proposed filter was designed in 65-nm CMOS technology and verified through post-layout simulation results. © 2019 IEEE.
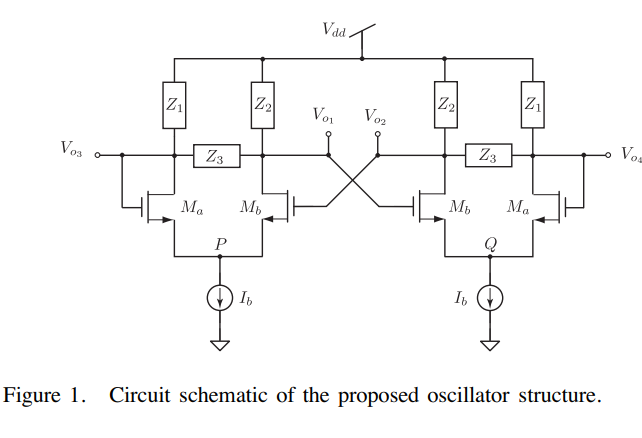
On a class of quadrature phase oscillators using differential pairs
A new class of quadrature phase oscillators based on cross-coupled differential pairs is introduced. This class contains eight possible circuits which produce four output voltages with phase differences of ±π or ±π/2, depending on the choice of output node, and does not require balanced differential-pair loads. Phase error analysis is provided along with experimental and simulation results using discrete MOS and BJT transistors as a proof of concept. © 2018 IEEE
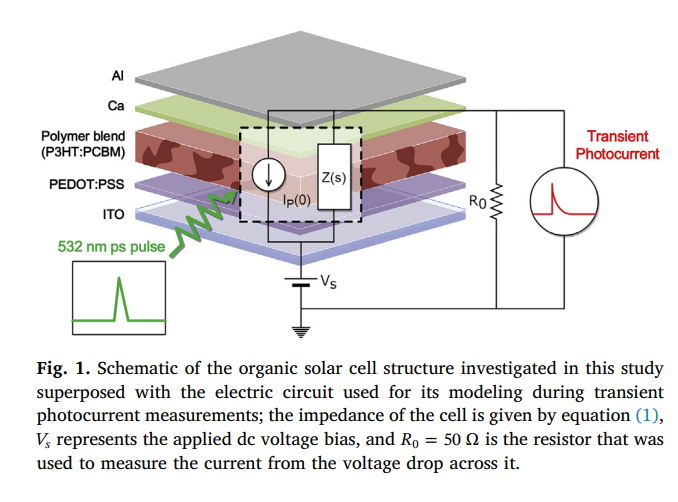
On the modeling of dispersive transient photocurrent response of organic solar cells
The current methods used for estimating the electrical parameters of organic solar cells (OSC) from time-domain measurements are based on integer-order impedance models. Meanwhile, in the frequency-domain, the adopted circuit models usually contain a constant phase element which is known to capture effectively the fractional-order dispersive behavior of these devices. Therefore, inconsistency arises between the two analyses. In this work, we derive the time-domain relaxation response of an OSC, found to follow a Mittag-Leffler function, using the same fractional-order impedance model. The
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 24
- Next page ››