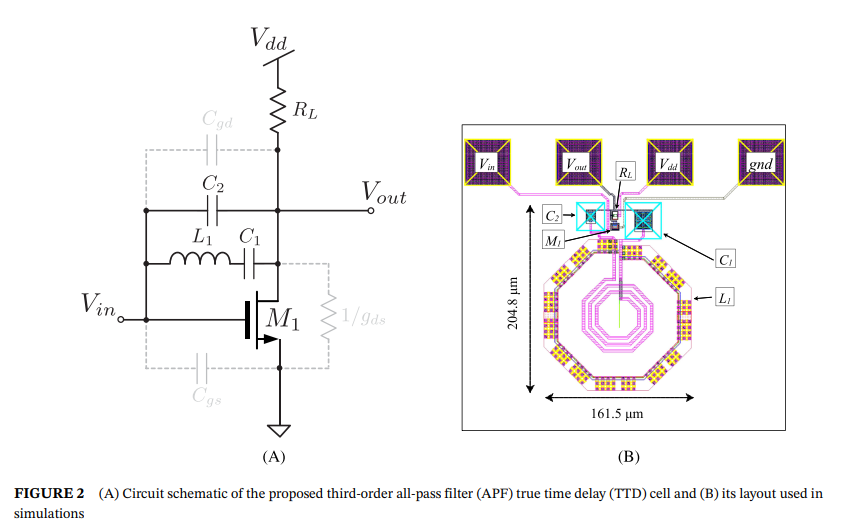
Wideband third-order single-transistor all-pass filter
In this letter, a third-order wideband voltage-mode all-pass filter (APF) is proposed for application as a true time delay (TTD) cell. The advantages of designing a single-stage higher order filter over cascading several lower order stages are illustrated. The proposed APF circuit is based on a single metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) transistor and is canonical because it requires one resistor, one inductor, and two capacitors. To the best of the authors' knowledge, this is the first single-transistor third-order APF circuit to be reported in the literature. The operation of the proposed APF is
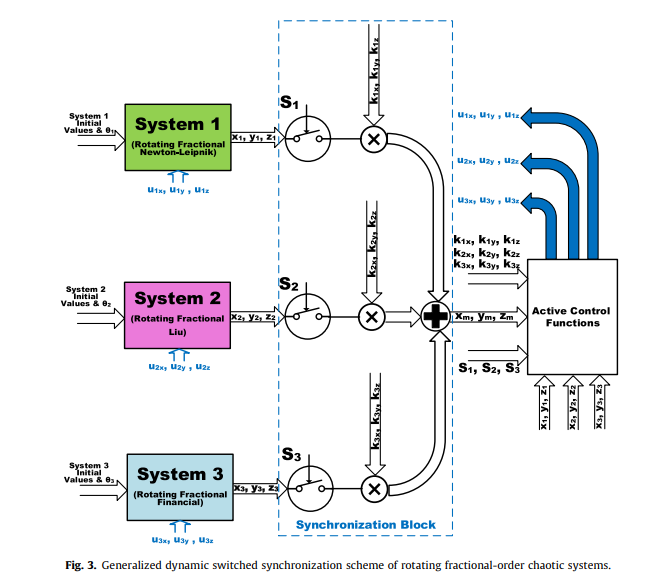
Generalized switched synchronization and dependent image encryption using dynamically rotating fractional-order chaotic systems
This paper presents a generalization, attractor control and multi-scroll generation method for fractional-order chaotic systems through rotation transformation. A novel synchronization-dependent colored image encryption and secure communication scheme is also proposed. The systems with dynamic rotation angle fit successfully in a generalized dynamic switched synchronization scheme. Dynamic control switches specify whether the system acts as a master or slave. Dynamic scaling factors determine whether the master is a single system or a combination of two or more systems. Simulation results
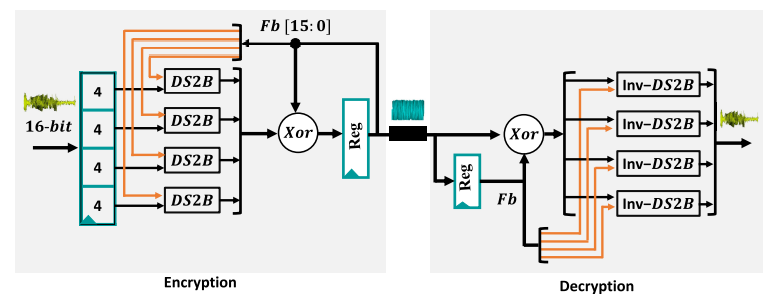
DS2B: Dynamic and Secure Substitution Box for Efficient Speech Encryption Engine
This paper proposes an efficient encryption technique based on Dynamic and Secure Substitution Box (DS2B) design suitable for IoT and resource-constrained platforms. The DS2B has the advantages of simple structure and good encryption performance. A different number of strong S-boxes could be generated with minor variations in the DS2B parameters. Performance analyses of the DS2B, including differential/linear cryptanalysis, bijective, nonlinearity, strict avalanche criterion (SAC), and bit independence criterion (BIC) have been presented where high nonlinearity , and low differential
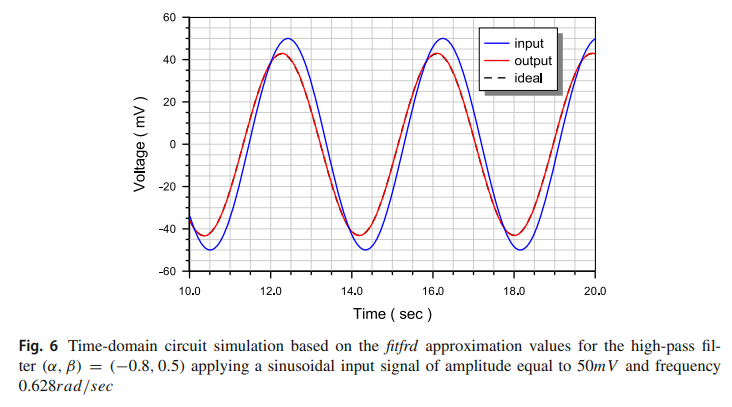
Double Exponent Fractional-Order Filters: Approximation Methods and Realization
The main goal of this work is to exploit different tools in order to approximate a general double exponent fractional-order transfer function. Through the appropriate selection of the two fractional orders of this function, different types of filters can be derived. The investigated approximation tools are either curve fitting based tools or the Padé approximation tool, and the derived approximated transfer functions in all cases have the form of rational integer-order polynomials, which can be easily realized electronically. © 2020, Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer
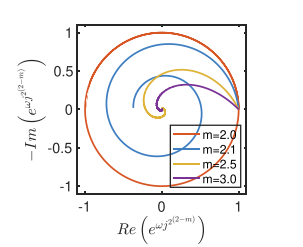
Decoupling the magnitude and phase in a constant phase element
The success of fractional-order fractance (FOF) as a modeling tool in (photo)bio(electro)chemical systems can be readily gauged by the large body of research work that has been conducted over the past few years in terms of materials fabrication, building integer-order emulators of their behavior, as well as applications in filter design, controller design, modeling of energy storage devices and biomaterials. The impedance of FOF has the general form Zα(s)=kαsα where kα and α are real constant and s=jω is the complex Laplace number. In this work, we investigate the possibility of decoupling the
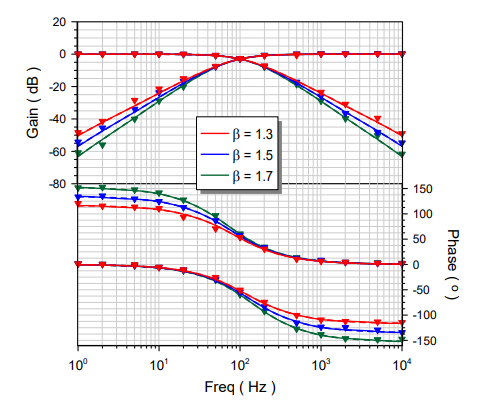
Versatile Field-Programmable Analog Array Realizations of Power-Law Filters
A structure suitable for implementing power-law low-pass and high-pass filter transfer functions is presented in this work. Through the utilization of a field-programmable analog array device, full programmability of the characteristics of the intermediate stages, as is required for realizing the rational integer-order transfer function that approximates the corresponding power-law function, was achieved, making the structure versatile. In addition, a comparison between power-law and fractional-order filters regarding the effect of the non-integer order was performed. The presented design
Parametric Analysis of Optical Microring Resonator
This article presents the parametric analysis of the optical microring resonator. It includes the numerically simulated analysis. The mathematical formulation represents the several relations that could influence the performance of optical microring resonator. The simulations give the graphical representations of ring resonator performances by the alteration of various parameters. In this paper, we have analyzed the variations in quality factor, extinction ratio and the resonance peak of an optical microring resonator with changes in effective refractive index, length of the ring and the group
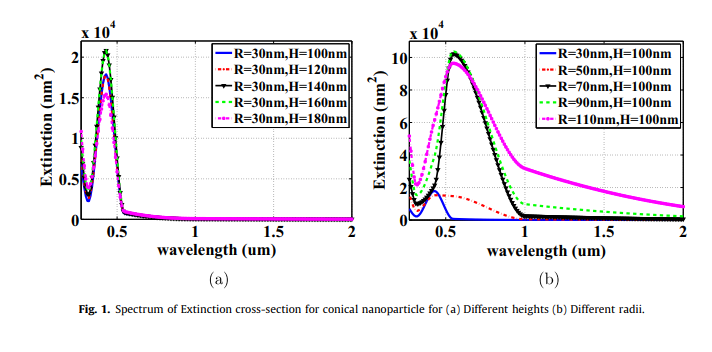
J-V characteristics of plasmonic photovoltaics with embedded conical and cylindrical metallic nanoparticles
Plasmonic photovoltaics (PVs) are promising structures that improve thin-film photovoltaics performance, where optical absorption is improved via embedding metallic nanoparticles in the PV's active layer to trap the incident optical wave into the photovoltaic cell. The presented work investigates the design of PV with both structures of conical and cylindrical metallic nanoparticles through studying their extinction cross-sections and electric field distributions. Also, the impact of these nanoparticles in silicon PVs on the optical absorption enhancement is investigated. The figure of merit
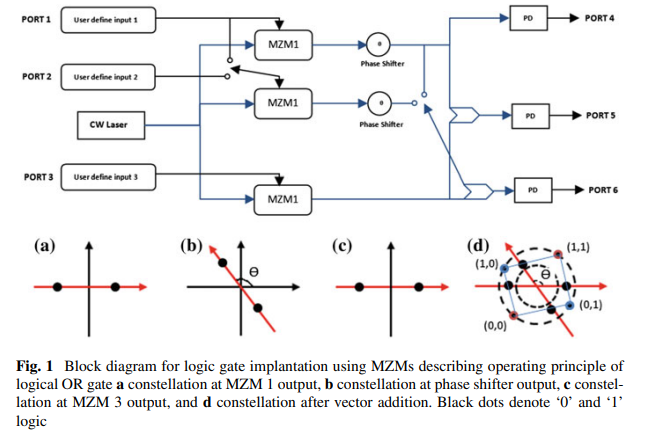
Polarization Encoded Multi-logic Functions with Direct Detection
In this paper, a new scheme for the realization of an optical logic circuit using Mach–Zehnder modulators (MZM) with direct detection has been proposed. Amplitude and phase information of the optical signals have been used for the differentiation of optical signals into four different states that can be represented using two binary inputs, while direct detection has been used for the effective mapping of these states with their respective binary outputs. The realization of seven logic gates, two reversible optical logic gates (Feynman and double Feynman gates) and half adder and half
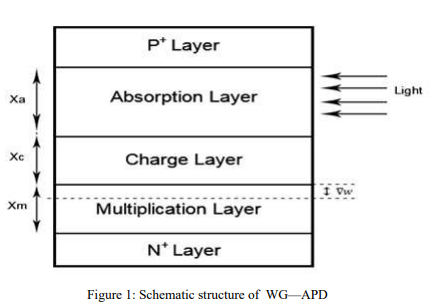
A Stochastic Modeling of the Gain in Waveguide Avalanche Photodetectors (WG-APDs)
Waveguide photodetectors are considered as a promising candidate for high speed photodetection where the tradeoff between the transit time bandwidth and the quantum efficiency is overcome as the incident optical signal and the photogenerated carriers move in perpendicular directions. In WG-Avalanche Photodetectors (WG-APDs), the avalanche multiplication gain enhances the photocurrent of the photodiodes. In these photodiodes, the inaccuracies in the ionizations coefficients of the photogenerated electrons and holes and in the dimensions of the multiplication layer affect the multiplication gain
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 25
- Next page ››
