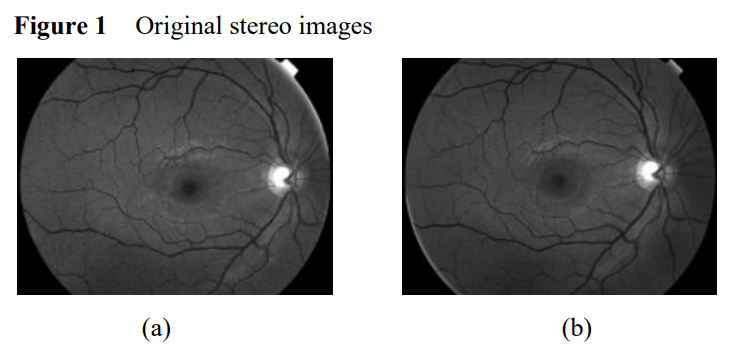
3D surface reconstruction of retinal vascular structures
We propose in this paper, a three-dimensional surface reconstruction of a retinal vascular network from a pair of 2D retinal images. Our approach attempts to address the above challenges by incorporating an epipolar geometry estimation and adaptive surface modelling in a 3D reconstruction, using three steps: segmentation, 3D skeleton reconstruction and 3D surface modelling of vascular structures. The intrinsic calibration matrices are found via the solution of simplified Kruppa equations. A simple essential matrix based on a self-calibration method has been used for the 'fundus camera-eye'
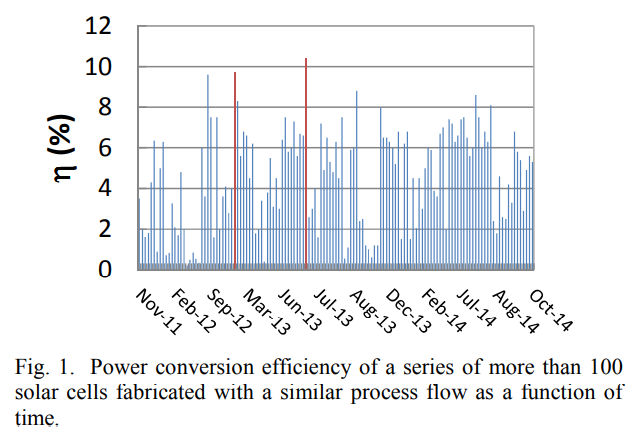
Process variability in Cu2ZnSnSe4 solar cell devices: Electrical and structural investigations
We have fabricated 9.7% efficient Cu2ZnSnSe4/CdS/ZnO solar cells by H2Se selenization of sequentially sputtered metal layers. Despite the good efficiency obtained, process control appears to be difficult. In the present contribution we compare the electrical and physical properties of two devices with nominal same fabrication procedure, but 1% and 9.7% power conversion efficiency respectively. We identify the problem of the lower performing device to be the segregation of ZnSe phases at the backside of the sample. This ZnSe seems to be the reason for the strong bias dependent photocurrent
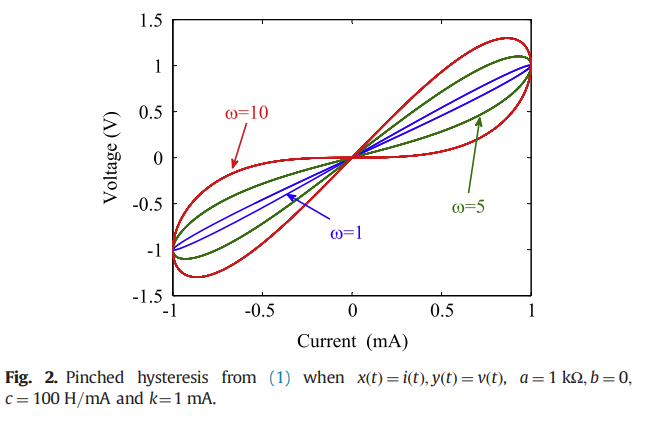
Pinched hysteresis with inverse-memristor frequency characteristics in some nonlinear circuit elements
Abstract Pinched hysteresis is considered to be a signature of the existence of memristance. However, here we report on a model that exhibits pinched hysteresis yet it may represent a nonlinear inductor or a nonlinear capacitor (both with quadratic nonlinearity) or a derivative-controlled nonlinear resistor/transconductor. Further, the lobe area of the pinched hysteresis loop in these devices has inverse-memristor characteristics; i.e. it is observed to widen rather than decline with increased operating frequency. Experimental results are provided to validate the model. © 2015 Elsevier Ltd.
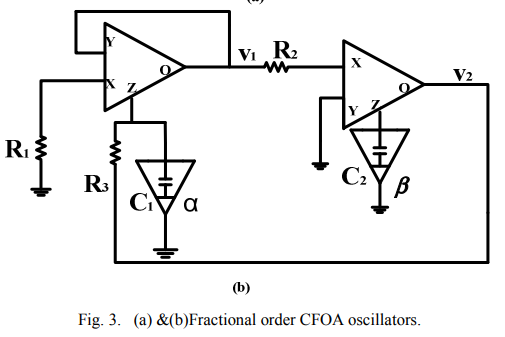
Current feedback operational amplifier (CFOA) based fractional order oscillators
This paper presents a study of fractional order oscillators based on current feedback operational amplifiers (CFOA). Two general cases have been discussed for the oscillation frequency and condition with the use of two fractional order elements of different orders. Design procedure for the two general cases is illustrated with numerical discussions. Circuit simulations for some special cases are presented to validate the theoretical findings. The simulations have been done using Ad844 commercial CFOA model © 2014 IEEE.
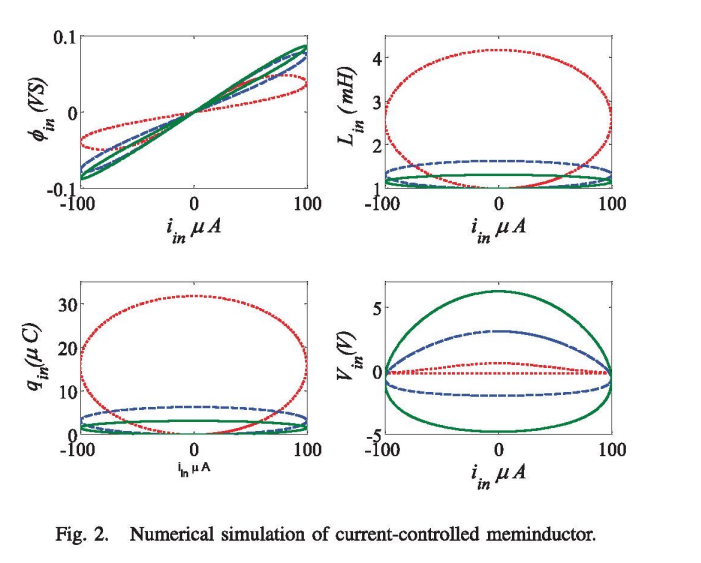
Memristor-less current- and voltage-controlled meminductor emulators
This paper introduces two mathematical models of meminductor based on a simple symmetrical double-loop equation with their generic formulas and analysis. Moreover, new circuits based on CCII are developed for emulating the behavior of the current-controlled and voltage-controlled models. The proposed circuits are realized without using a memristor unlike the previous emulators. Finally, the proposed emulators are verified using PSPICE simulations. © 2014 IEEE.
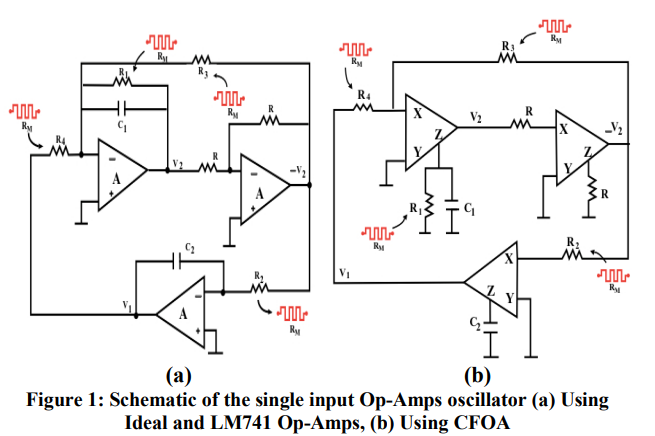
The modified single input Op-Amps memristor based oscillator
This paper introduces the modified single input Op-Amps memristor based oscillator. The oscillator is realized with ideal, LM741 and current feedback (AD844) Op-Amps where memristors replace resistors. The effect of memristor on the oscillation frequency and the oscillation condition that are totally independent is studied. This helped in studying the whole operation regime of the memristor. The effect of initial conditions on the circuit behavior is discussed. The dynamic poles of the oscillator after resistors replacement are illustrated. Sustained oscillation is obtained and simulated
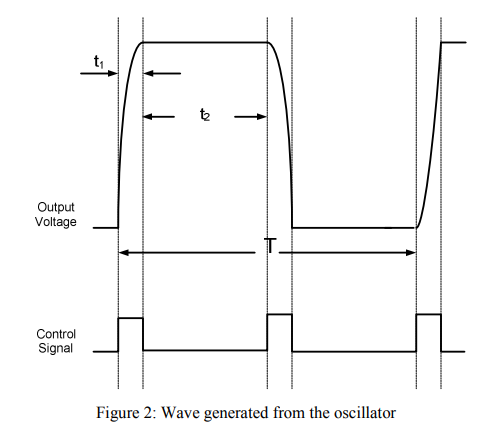
Design methodology for square wave resonant clock generators
Resonant clocking is a promising low power alternative for conventional clocking method. In this work, a design methodology is presented for square wave resonant clocking technique to assure minimum power consumption. These equations were verified by designing a differential clock generator which showed 55% power savings compared to conventional clocking. © 2012 IEEE.
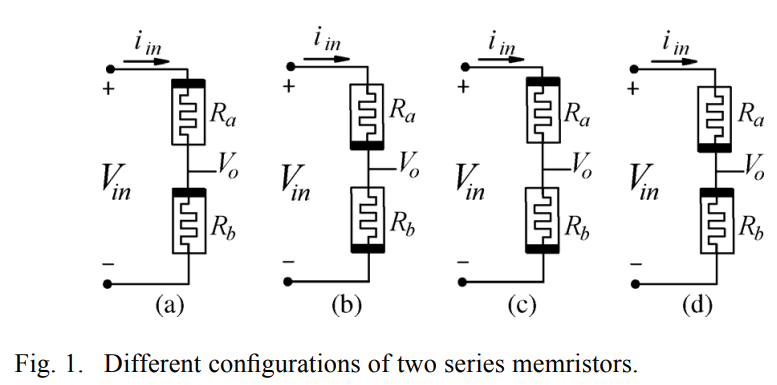
Generalized analysis of symmetric and asymmetric memristive two-gate relaxation oscillators
Memristive oscillators are a novel topic in nonlinear circuit theory, where the behavior of the reactive elements is emulated by the memristor. This paper presents symmetric and asymmetric memristive two-gate relaxation oscillators. First, the analysis of the two series memristors is introduced to study the effect of changing their polarities, as well as the mobility factor to be used in the two-gate relaxation oscillator instead of the RC circuit. The generalized analysis for the proposed memristive two-gate oscillator is introduced, where the generalized expressions for the oscillation
Current source based standard-cell model for accurate timing analysis of combinational logic cells
Timing verification is an essential process in nanometer design. Therefore, static timing analysis (STA) is currently the main aspect of performance verification. Traditional STA is based on lookup tables with input slew and output load capacitance. It is becoming insufficient to accurately characterize many significant aspects of the conventional cell delays models, such as: the process variations, nonlinear waveforms, nonlinear loads, and multiple inputs switching (MIS). Therefore, the current trend in modern designs is to use current source based models (CSM), which model MOSFETs as a
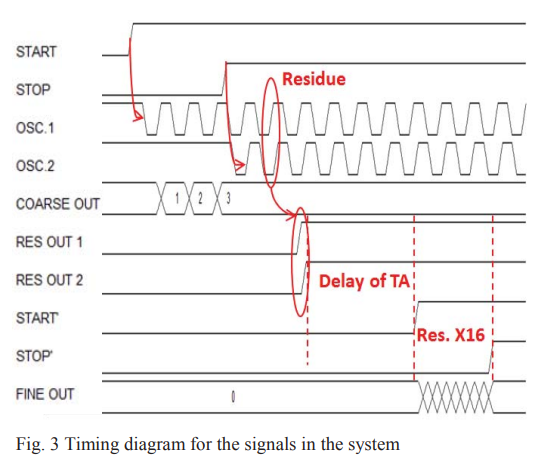
A novel high throughput high resolution two-stage oscillator-based TDC
This paper presents a new technique to reduce the conversion time, hence improve the throughput, of the two-stage Time to Digital Converter (TDC) architecture. An oscillator based TDC is used in the first and second stages. The time residue from the first stage is generated directly after the stop signal is asserted and saved in the form of phase-shift between two oscillating signals. A throughput of 400 MS/s, a DNL of 0.38, and an INL of 0.36 are achieved. © 2013 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 28
- Next page ››
