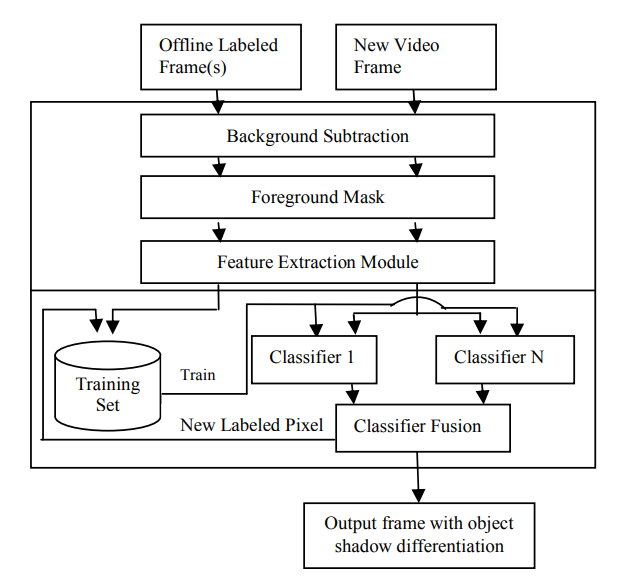
A semi supervised learning-based method for adaptive shadow detection
In vision-based systems, cast shadow detection is one of the key problems that must be alleviated in order to achieve robust segmentation of moving objects. Most methods for shadow detection require significant human input and they work in static settings. This paper proposes a novel approach for adaptive shadow detection by using semi-supervised learning which is a technique that has been widely utilized in various pattern recognition applications and exploits the use of labeled and unlabeled data to improve classification. The approach can be summarized as follows: First, we extract color
Motion history of skeletal volumes for human action recognition
Human action recognition is an important area of research in computer vision. Its applications include surveillance systems, patient monitoring, human-computer interaction, just to name a few. Numerous techniques have been developed to solve this problem in 2D and 3D spaces. However most of the existing techniques are view-dependent. In this paper we propose a novel view-independent action recognition algorithm based on the motion history of skeletons in 3D. First, we compute a skeleton for each volume and a motion history for each action. Then, alignment is performed using cylindrical
Complementary feature splits for co-training
In many data mining and machine learning applications, data may be easy to collect. However, labeling the data is often expensive, time consuming or difficult. Such applications give rise to semi-supervised learning techniques that combine the use of labelled and unlabelled data. Co-training is a popular semi-supervised learning algorithm that depends on splitting the features of a data set into two redundant and independent views. In many cases however such sets of features are not naturally present in the data or are unknown. In this paper we test feature splitting methods based on
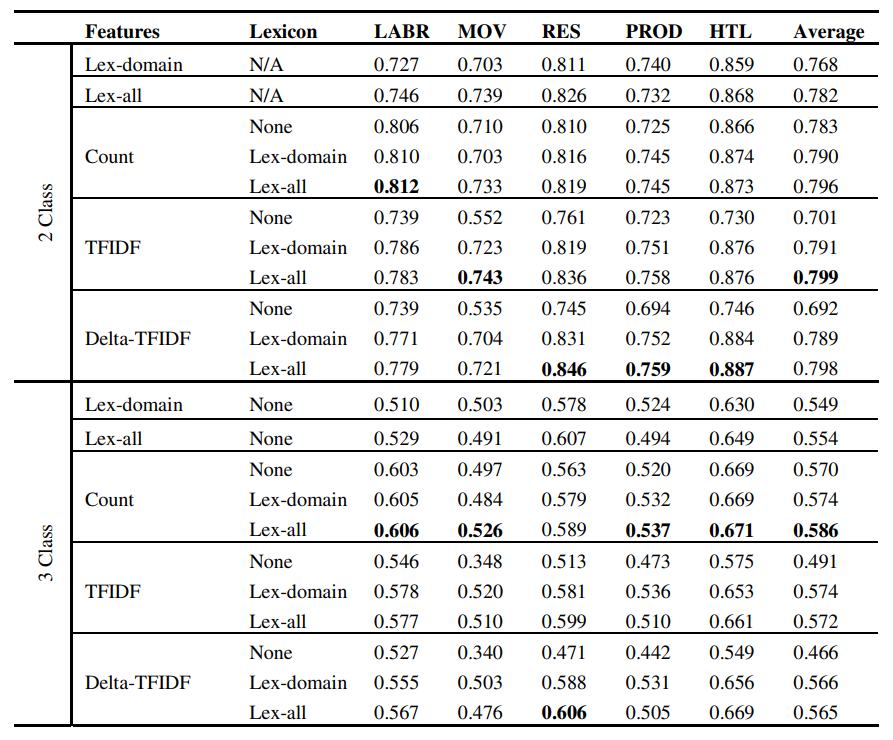
Building large arabic multi-domain resources for sentiment analysis
While there has been a recent progress in the area of Arabic SentimentAnalysis, most of the resources in this area are either of limited size, domainspecific or not publicly available. In this paper, we address this problemby generating large multi-domain datasets for Sentiment Analysis in Arabic.The datasets were scrapped from different reviewing websites and consist of atotal of 33K annotated reviews for movies, hotels, restaurants and products.Moreover we build multi-domain lexicons from the generated datasets. Differentexperiments have been carried out to validate the usefulness of the
Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Urban Signatures with Application to Drone Localization
Most commercial Small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (SUAVs) rely solely on Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSSs) - such as GPS and GLONASS - to perform localization tasks during the execution of autonomous navigation activities. Despite being fast and accurate, satellite-based navigation systems have typical vulnerabilities and pitfalls in urban settings that may prevent successful drone localization. This paper presents the novel concept of 'Deep Urban Signatures' where a deep convolutional neural network is used to compute a unique characterization for each urban area or district based on
Combining lexical features and a supervised learning approach for arabic sentiment analysis
The importance of building sentiment analysis tools for Arabic social media has been recognized during the past couple of years, especially with the rapid increase in the number of Arabic social media users. One of the main difficulties in tackling this problem is that text within social media is mostly colloquial, with many dialects being used within social media platforms. In this paper, we present a set of features that were integrated with a machine learning based sentiment analysis model and applied on Egyptian, Saudi, Levantine, and MSA Arabic social media datasets. Many of the proposed
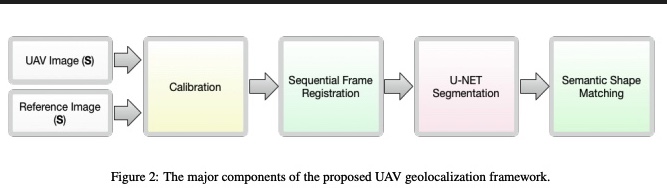
A deep CNN-based framework for enhanced aerial imagery registration with applications to UAV geolocalization
In this paper we present a novel framework for geolocalizing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) using only their onboard camera. The framework exploits the abundance of satellite imagery, along with established computer vision and deep learning methods, to locate the UAV in a satellite imagery map. It utilizes the contextual information extracted from the scene to attain increased geolocalization accuracy and enable navigation without the use of a Global Positioning System (GPS), which is advantageous in GPS-denied environments and provides additional enhancement to existing GPS-based systems
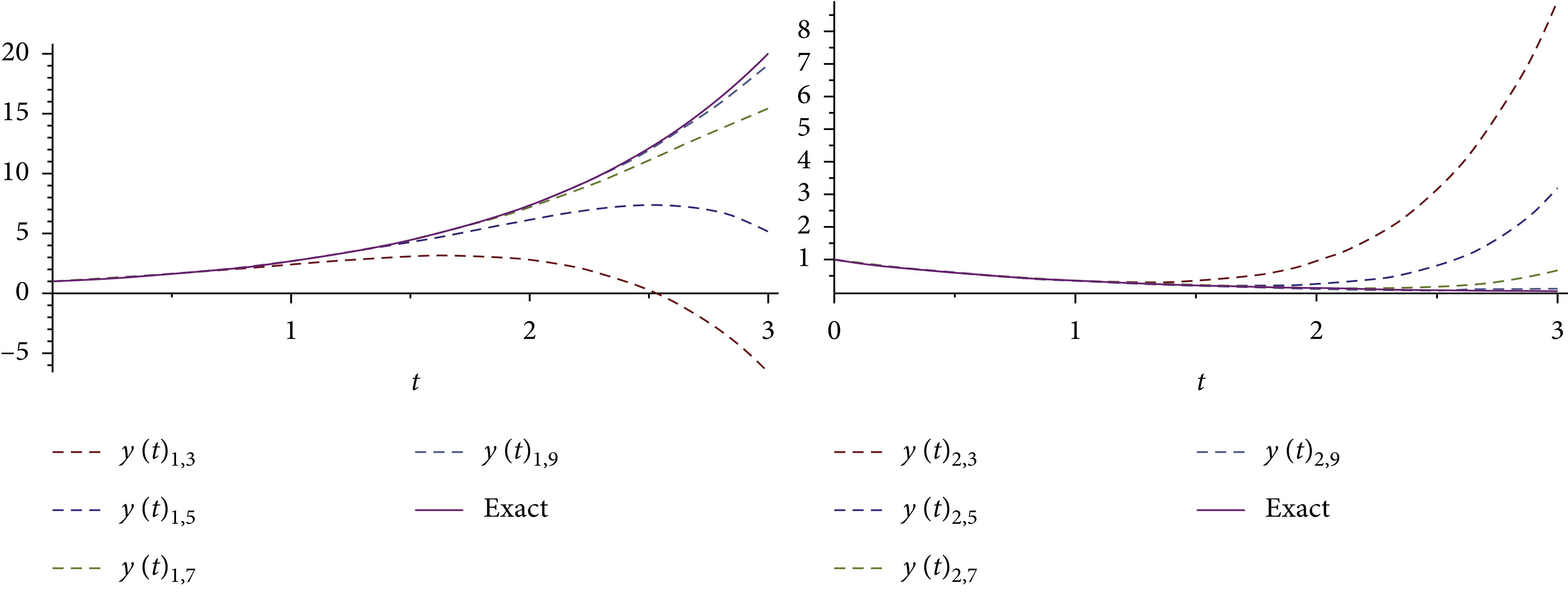
An Analytical Computational Algorithm for Solving a System of Multipantograph DDEs Using Laplace Variational Iteration Algorithm
In this research, an approximation symbolic algorithm is suggested to obtain an approximate solution of multipantograph system of type delay differential equations (DDEs) using a combination of Laplace transform and variational iteration algorithm (VIA). The corresponding convergence results are acquired, and an efficient algorithm for choosing a feasible Lagrange multiplier is designed in the solving process. The application of the Laplace variational iteration algorithm (LVIA) for the problems is clarified. With graphics and tables, LVIA approximates to a high degree of accuracy with a few
Multi projection fusion for real-time semantic segmentation of 3D LiDAR point clouds
Semantic segmentation of 3D point cloud data is essential for enhanced high-level perception in autonomous platforms. Furthermore, given the increasing deployment of LiDAR sensors onboard of cars and drones, a special emphasis is also placed on non-computationally intensive algorithms that operate on mobile GPUs. Previous efficient state-of-the-art methods relied on 2D spherical projection of point clouds as input for 2D fully convolutional neural networks to balance the accuracy-speed trade-off. This paper introduces a novel approach for 3D point cloud semantic segmentation that exploits
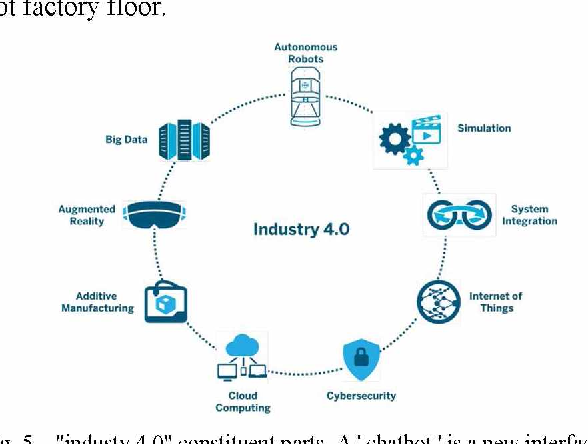
IoT Based AI and its Implementations in Industries
The Internet of Things (IoT) is an Internet revolution that is increasingly used in business, industry, medicine, the economy and other modern information society. IoT, particularly transport, industrial robots and automation systems are supported by artificial intelligence in a wide range of daily implementations with dominant industrial applications. IoT is an interconnected network of physical objects, which enables them to gather and share information, using software, sensor units and network connectivity. In industries; IoT brought about a new revolution in industries. In the field of IoT
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 12
- Next page ››
