Experimental Path tracking optimization and control of a nonlinear skid steering tracked mobile robot
The skid steering tracked robot is consider one of the famous robots that used in the autonomous agricultural field. The robot model is considered as a coupled nonlinear model. So, a real kinematic model is required to develop the robot motion which will improve the high quality and quantity of the cultivated crops. So, in this research a mathematical model for the skid steering mobile robot (SSMR) and a mathamtical model has been presented to simulate the robot. The model has been validated based on experimental data for the Skid Steering model. The robot motion as position and velocity has
Experimental Lane Keeping Assist for an Autonomous Vehicle Based on Optimal PID Controller
Detection of the lane boundary is the primary task in order to control the trajectory of an autonomous car. In this paper, three methodologies for lane detection are discussed with experimental illustration: Blob analysis, Hough transformation and Birds eye view. The next task after receiving the boundary points is to apply a control law in order to trigger the steering and velocity control to the motors efficiently. In the following, a comparative analysis is made between different tuning criteria to tune PID controller for Lane Keeping Assist (LKA). In order to receive the information of the
Conceptual cost estimation of pump stations projects using fuzzy clustering
Conceptual cost estimates, are prepared at the very early stages of a project, and generally before the construction drawings and specifications are available. At this stage, cost estimates are needed by the owner, contractor, designer, or funding agencies for determination of the feasibility of a project, financial evaluation of a number of alternative projects, or establishment of an initial budget. Traditional approaches rely heavily on experienced engineers. This paper presents a method using fuzzy clustering technique for pump station projects cost estimation. The proposed conceptual cost
Modelling of Continuum Robotic Arm Using Artificial Neural Network (ANN)
Continuum robotic arm becomes the new area of scientific research nowadays. Its technology has grown and touched several vital applications included industry and agriculture thanks to many advantages made it a better choice than the conventional serial robotic manipulator. This paper represents a new designed model of continuum arm robot, which relates the motor shaft angle as the input parameter and transfers the motor torque to combined system of compression springs and results in six outputs: x,y and z 3D coordinates for the center point of the end effector and \theta,~\psi and \gamma to
Experimental Modeling of Hexapod Robot Using Artificial Intelligence
Hexapod Robots gave us the opportunity to study walking robots without facing problems such as stability and expensive custom made hardware. It has a great deal of flexibility in moving over different terrains even if some legs become malfunctioned or facing some difficulties in movement. In this study the kinematic analysis of CH3-R 18DOF Hexapod Robot is discussed where each leg contains three revolute joints in order to mimic the structure of a spider. To develop the overall kinematic model of CH3-R robot, direct and inverse kinematic analyses for each leg have been considered where the
Control design approaches for parallel robot manipulators: A review
In this article, different control design approaches for parallel robot manipulators are presented with two distinguished classes of control strategies in the literature. These are the model-free control and the dynamic control strategy, which is mainly a model-based scheme, and is mostly the alternative when the control requirements are more stringent. The authors strongly believe that this paper will be helpful for researchers and engineers in the field of robotic systems. Copyright 2017 Inderscience Enterprises Ltd.
Experimental Kinematic Modeling of 6-DOF Serial Manipulator Using Hybrid Deep Learning
According to its significance, robotics is always an area of interest for research and further development. While robots have varying types, design and sizes, the six degrees of freedom (DOF) serial manipulator is a famous robotic arm that has a vast areas of applications, not only in industrial application, but also in other fields such as medical and exploration applications. Accordingly, control and optimization of such robotic arm is crucial and needed. In this paper, different analyses are done on the chosen design of robotic arm. Forward kinematics are calculated and validated, then
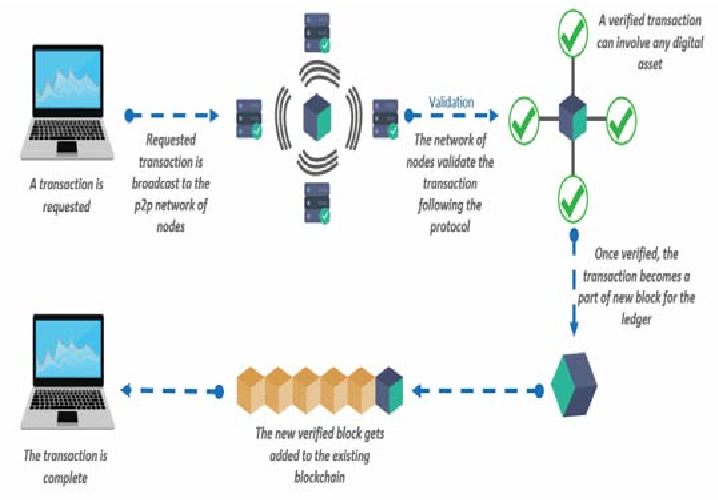
IoT Systems Internal Mapping using RTT with the integration of Blockchain technology
The degree to which innovators adopt Blockchain as a tool to create relevant and useful business solutions will determine how fast and far the platform moves into our daily lives. There are limitless opportunities for technology to define and shape future innovation. In a world dominated by digital technology, IoT plays a prominent role in our lives. It has created an ecosystem that links many systems to give smart performances in every task. The proliferation of the IoT has created a new evolution of cell phones, home and other embedded applications that are all connected to the internet
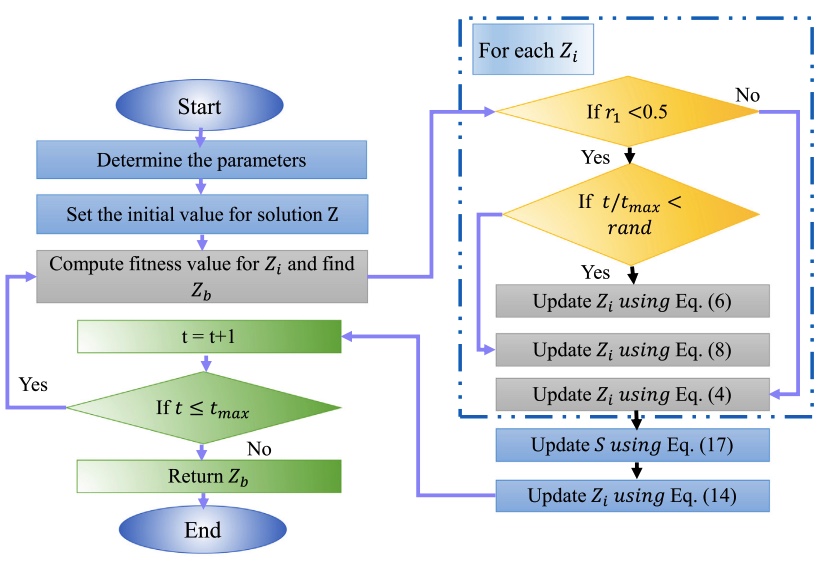
A Grunwald–Letnikov based Manta ray foraging optimizer for global optimization and image segmentation
This paper presents a modified version of Manta ray foraging optimizer (MRFO) algorithm to deal with global optimization and multilevel image segmentation problems. MRFO is a meta-heuristic technique that simulates the behaviors of manta rays to find the food. MRFO established its ability to find a suitable solution for a variant of optimization problems. However, by analyzing its behaviors during the optimization process, it is observed that its exploitation ability is less than exploration ability, which makes MRFO more sensitive to attractive to a local point. Therefore, we enhanced MRFO by
Modified fuzzy c-means clustering approach to solve the capacitated vehicle routing problem
Fuzzy C-Means clustering is among the most successful clustering techniques available in the literature. The capacitated vehicle routing problem (CVRP) is one of the most studied NP-hard problems. CVRP has attracted the attention of many researchers due to its importance within the supply chain management field. This study aims to develop a fuzzy c-means clustering heuristic to efficiently solve the CVRP with large numbers of customers by using cluster-first route-second method (CFRS). CFRS is a two-phase technique, where in the first phase customers are grouped into, and in the second phase
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 13
- Next page ››
